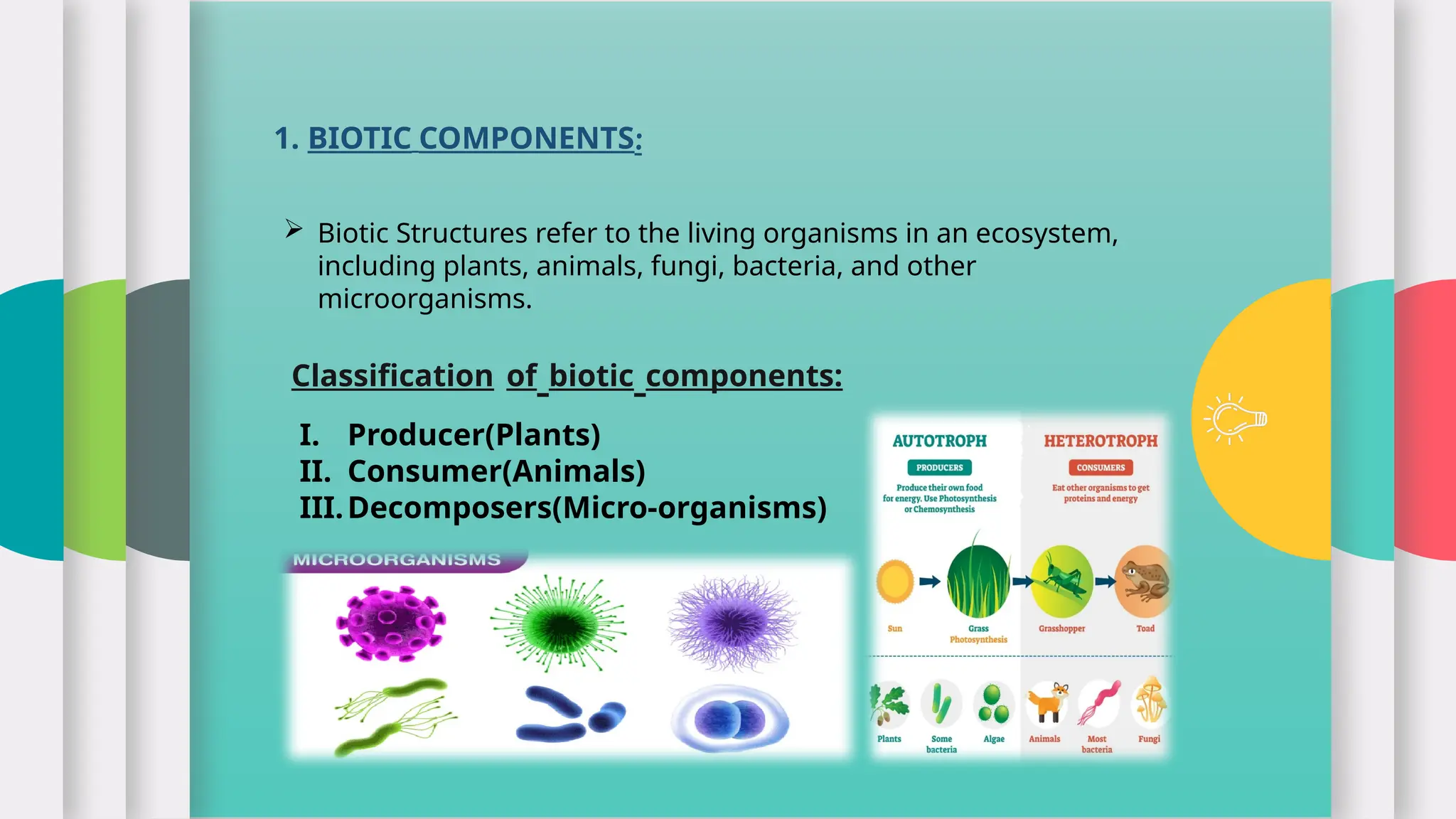
The document presents an overview of ecosystems, defining them as communities of living (biotic) and non-living (abiotic) components that interact within an environment. It categorizes biotic components into producers, consumers (herbivores, carnivores, omnivores), detritivores, and decomposers, while abiotic components include physical and chemical factors like climate and nutrients. The presentation credits A.G. Tansley for coining the term 'ecosystem' in 1935.
![WELCOME
STRUCTURE OF ECOSYSTEM
PRESENTED BY :
[RAHUL KUMAR (1322232)]
PRESENTATION ON](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structureofecosysteminevs-241016164017-368e617d/75/Structure-of-Ecosystem-1-2048.jpg)


![I. PRODUCERS(Autotrophs):
Producers are organisms that can make their own food
using sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide.
Examples: All green plants, trees, algae.
They are the base of the food chain in an ecosystem and
provide energy and nutrients to all other organisms.
Producers synthesize their food themselves through
photosynthesis.
[AUTOTROPHS- “Self-feeders”]
II. CONSUMERS(Heterotrophs):
Consumers are organisms that depend on other organisms for
food.
They cannot make own food.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structureofecosysteminevs-241016164017-368e617d/75/Structure-of-Ecosystem-5-2048.jpg)







