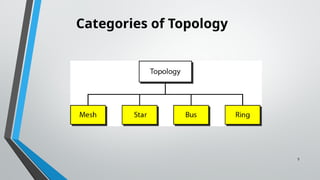
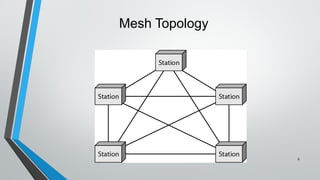
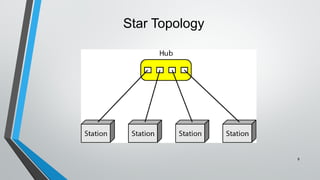
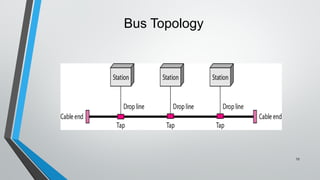
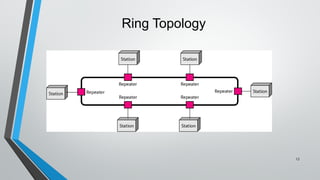
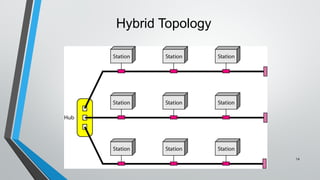
The document discusses various network topologies including mesh, star, bus, ring, and hybrid topologies, detailing their structures, advantages, and disadvantages. Mesh topology allows all devices to be interconnected for robust communication, while star topology offers ease of device management through a central hub. Bus and ring topologies serve smaller networks but come with limitations such as difficulty in troubleshooting and dependency on a single cable or node.