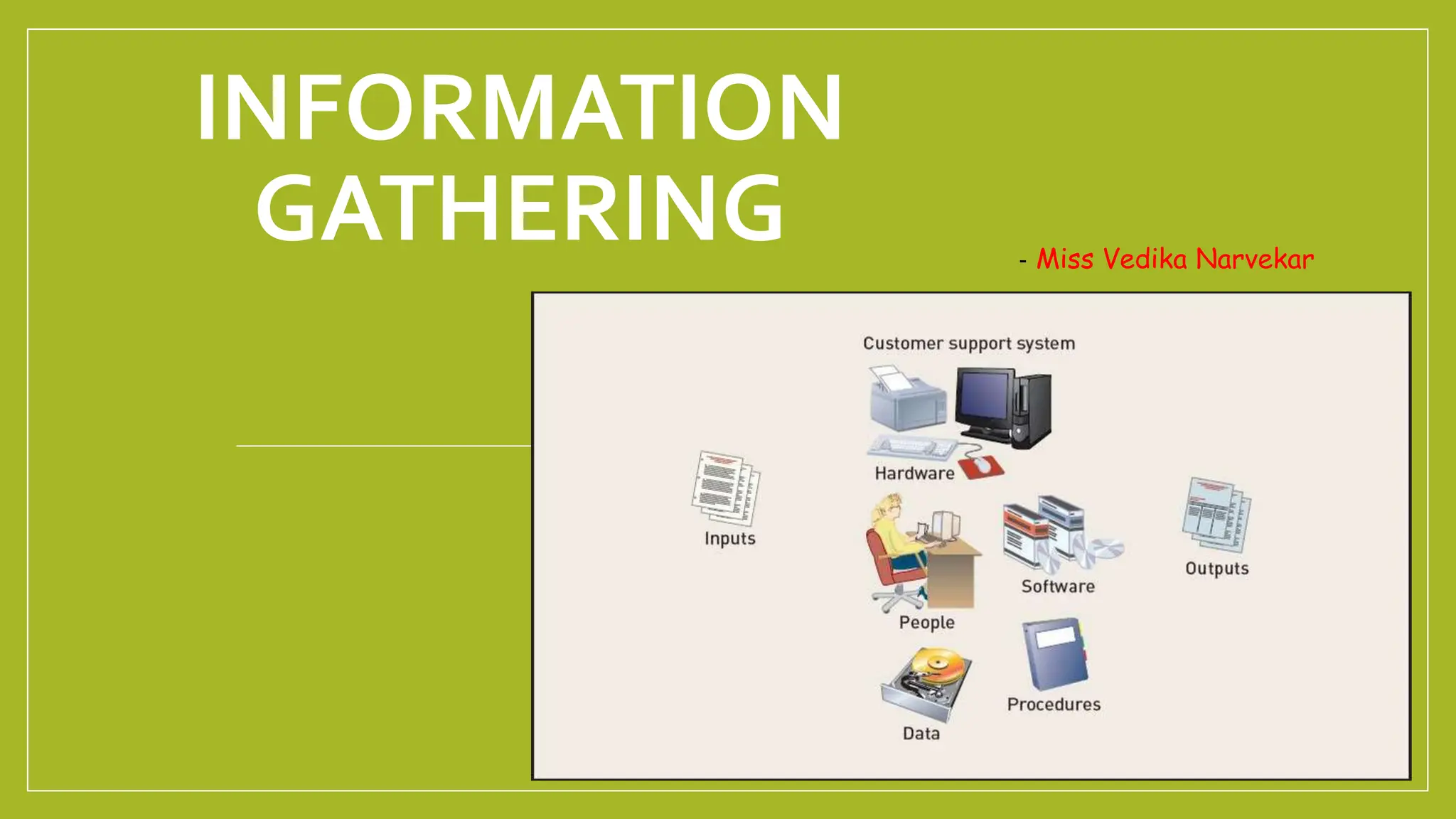
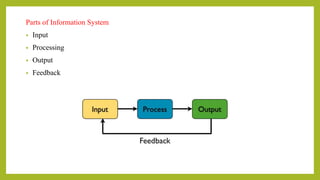
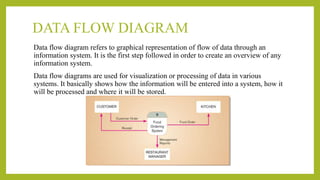
The document provides a comprehensive overview of information systems, detailing their components, types, and processes, including data collection, processing, storage, and output. It highlights the importance of requirement and feasibility analysis for successful project implementation, as well as methodologies for managing such projects. Additionally, it discusses design aspects for input and output processes, as well as the life cycle of project management in information systems.