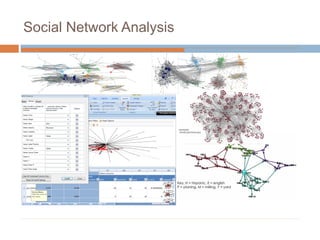
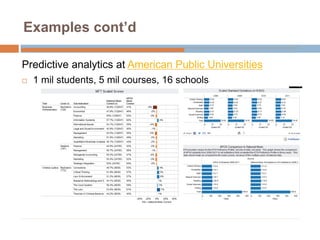
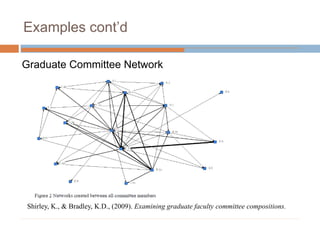
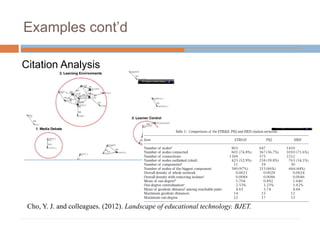
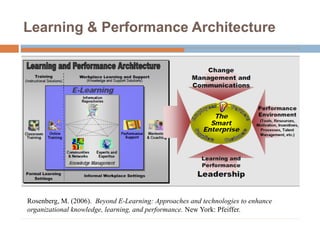
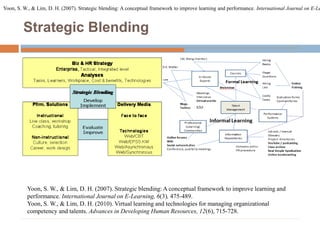
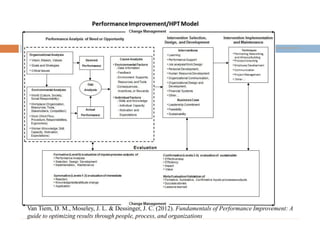
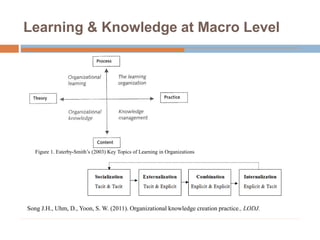
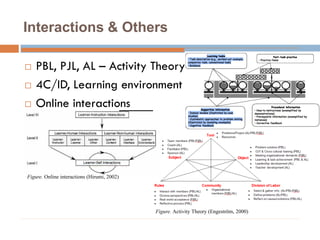
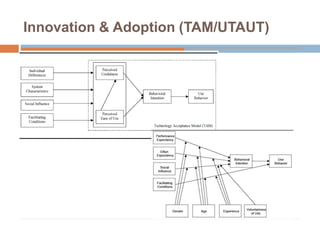
This document discusses data-centric education and learning. It begins by outlining past and present technologies used in education. It then discusses how data-centric learning is enabled by devices that connect to the cloud and collect real-time student data. This data can provide adaptive instruction, feedback, and insights into learning processes. Examples are given of social network analysis and predictive analytics projects using large educational datasets. Finally, frameworks for designing data-driven learning environments and strategies to improve performance are presented. The conclusion emphasizes using data and analytics responsibly and strategically to improve education.