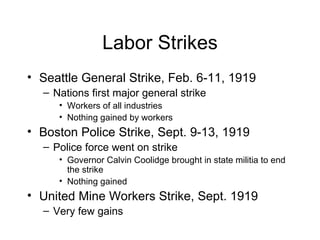
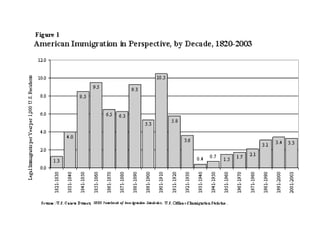
After World War I, Europe and the United States faced political, economic, and social upheaval. In Europe, monarchies were overthrown as new ideologies like communism rose. Economies were devastated and reparations further burdened Germany. The U.S. experienced an economic boom but also struggled with returning soldiers, labor issues, and intolerance as patriotism and "100% Americanism" grew. Americans feared the spread of communism and the Palmer Raids arrested thousands of suspected radicals intensifying the First Red Scare. Large strikes in 1919 damaged unions' reputation amid nativism and immigration restrictions passed in the 1920s.