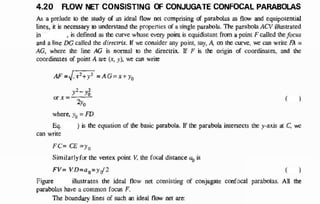
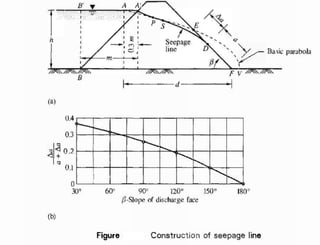
This document discusses seepage pressure and flow through earthen dams. It explains that seepage pressure is the force per unit volume exerted by flowing water on the soil, acting along the flow line. It describes how flow nets can be used to determine seepage pressure at any point. The document also discusses the phreatic line (seepage line) and how its position within a dam is important for stability. It provides details on analyzing seepage flow through homogeneous earthen dams using confocal parabolas with a common focus.




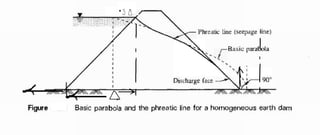
![ingbyV.Murthy x [] Untitled1
E
Discharge
fa
c
e
Directrix
- - - - E
V D
i
'
•
f.
i
s
{
8
-
,
; r e ,
G w , ' , t i s
x
h
B
Figure Ideal flownet consisting of conjugate confocal parabolas
2.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/18-211108174131/85/18-seepage-through-earth-dam-7-320.jpg)


![Seepage 335
Example
The cross section of an earth dam is shown in Figure 7.35. Calculate
the rate of seepage through the dam [q in m3/(min ∙ m)] by (a) Dupuit’s
method; (b) Schaffernak’s method; (c) L. Casagrande’s method; and
(d) Pavlovsky’s method.
25 m 2
2
Impermeable layer
b
c
30 m
k =3 ×10–4
m/min
a
a΄
0.3 ×50
=15 m
1 1
5 m
60 m
5 m
10 m
50 m
Figure 7.35
Seepage through an earth dam.
Ref: Adv. Soil Mechanics - B.M.Das
x
y
x
y
'
'
Yo
Directrix
Focus](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/18-211108174131/85/18-seepage-through-earth-dam-11-320.jpg)