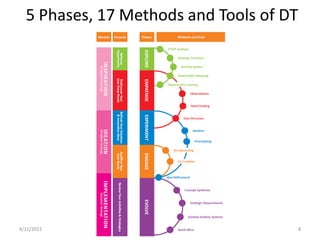
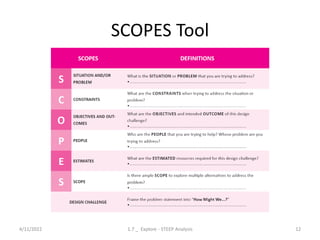
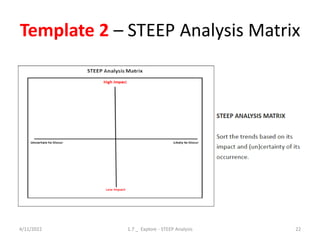
The document provides an overview of design thinking and STEEP analysis. It discusses the 5 phases and 17 tools of the design thinking process, with a focus on the explore phase. The explore phase involves reframing a design challenge by analyzing trends through STEEP analysis (social, technological, economic, environmental, political) to understand opportunities and implications. Templates are provided to conduct a STEEP analysis, including a trends analysis matrix to identify important trends and their impact, and prioritization to determine which trends are most significant.