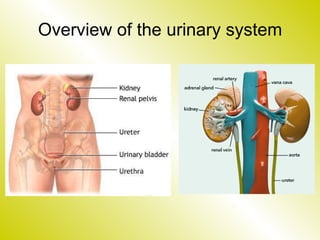
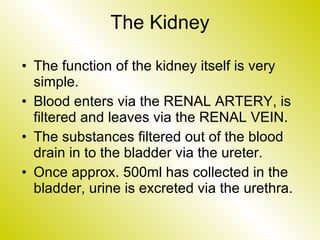
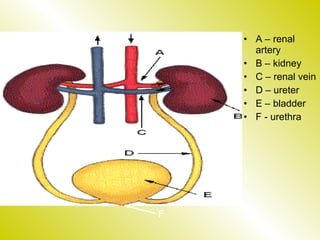
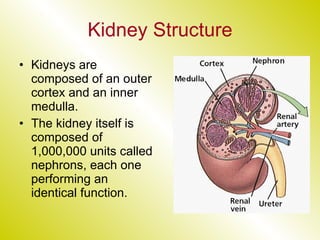
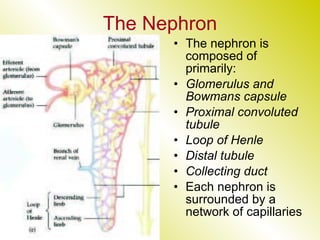
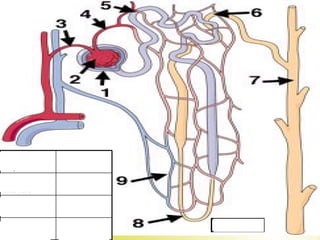
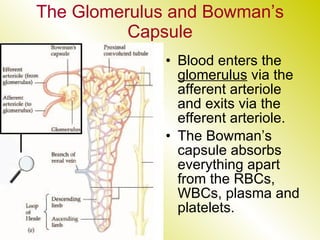
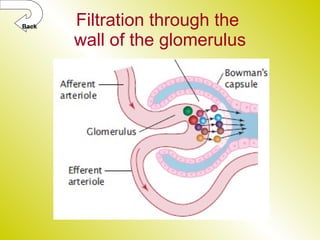
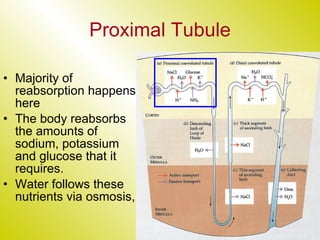
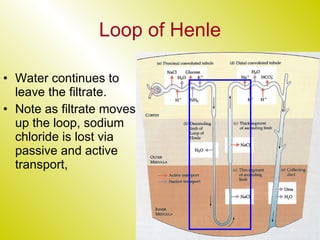
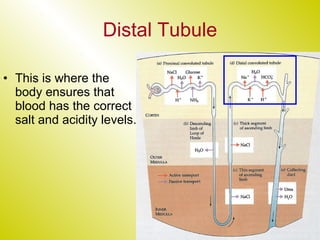
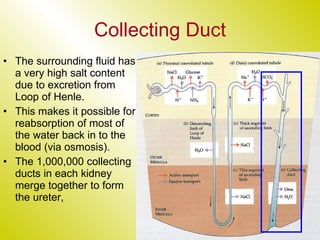
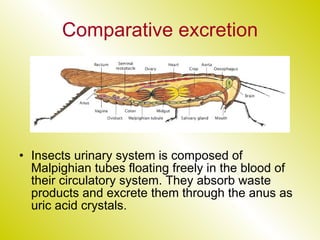
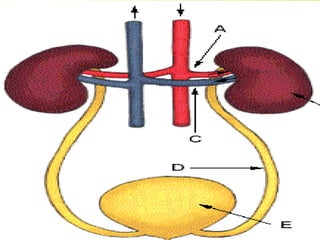
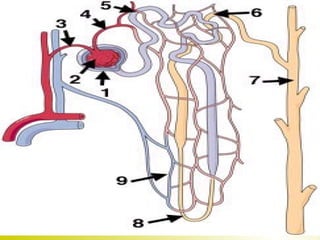
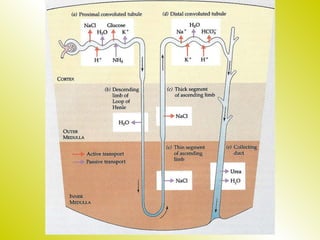
The document discusses the renal (urinary) system and how it transports nitrogenous waste out of animals. The kidney filters blood and removes waste, which drains into the bladder via the ureters. The nephron is the basic functional unit of the kidney, containing a glomerulus and tubules that allow filtration, reabsorption, and production of urine. Different species excrete different forms of nitrogenous waste at varying concentrations depending on whether they live in freshwater, saltwater, or on land.