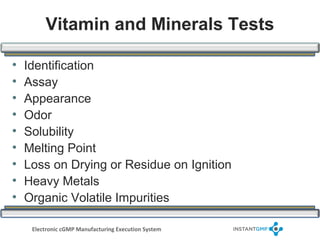
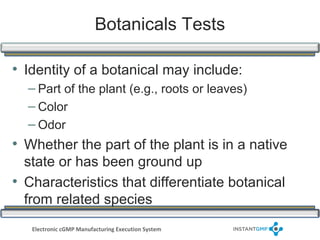
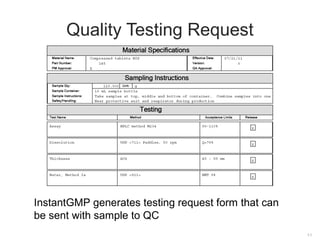
The document outlines compliance issues in cGMP testing for dietary supplements, highlighting a specific FDA warning to a lab for failing to test the identity of dietary ingredients as required by regulations. It discusses the importance of rigorous testing to ensure product quality, safety, and adherence to specifications for various dietary components. Additionally, it covers responsibilities for sponsors and quality control personnel in testing finished products and emphasizes the necessity of valid testing methods.