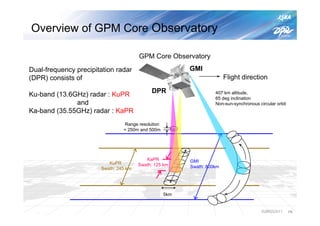
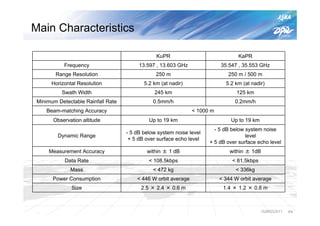
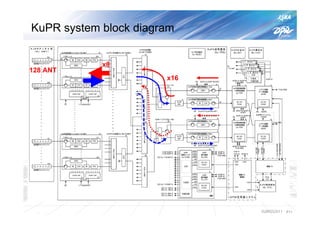
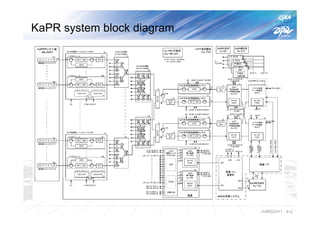
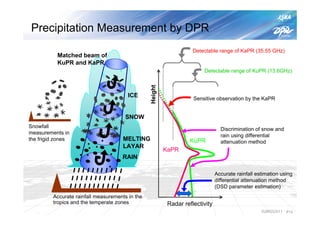
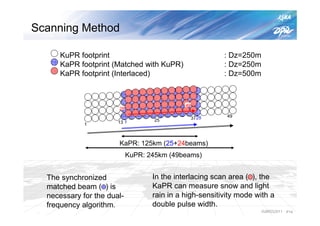
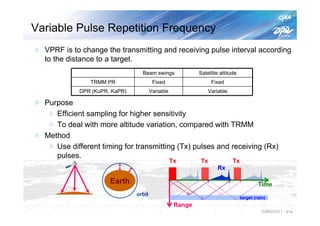
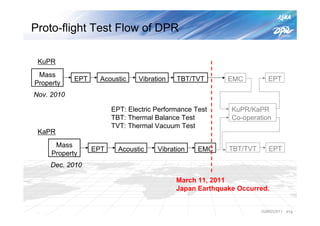
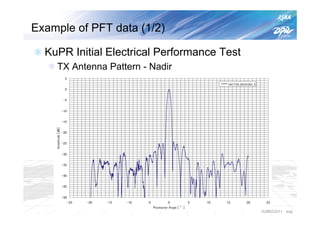
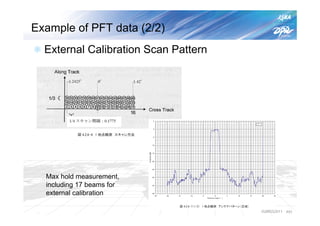
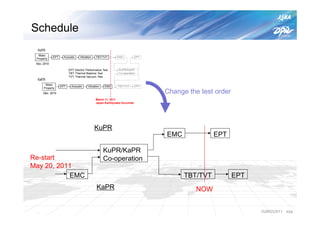
The document summarizes the proto-flight test of the Dual-frequency Precipitation Radar (DPR) for NASA's Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) mission. The DPR consists of Ku-band and Ka-band radars that will provide accurate 3D precipitation measurements from space. Electrical performance, vibration, and thermal tests have been conducted on each radar. While the proto-flight test was interrupted by an earthquake, it has resumed and will be completed to verify the radars can function as intended in space. The DPR will improve global precipitation observations when launched aboard the GPM core observatory.