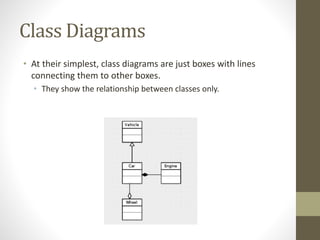
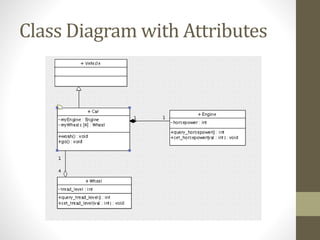
The document discusses encapsulation in object-oriented programming, emphasizing the importance of keeping data and functions together within classes to prevent issues associated with global scope. It highlights private and public visibility modifiers, the impact of changes in code, and the necessity of maintaining a clear interface to ensure usability and consistency. Lastly, it introduces class diagrams as tools to represent relationships and attributes within classes, enhancing the understanding of complex object-oriented architectures.