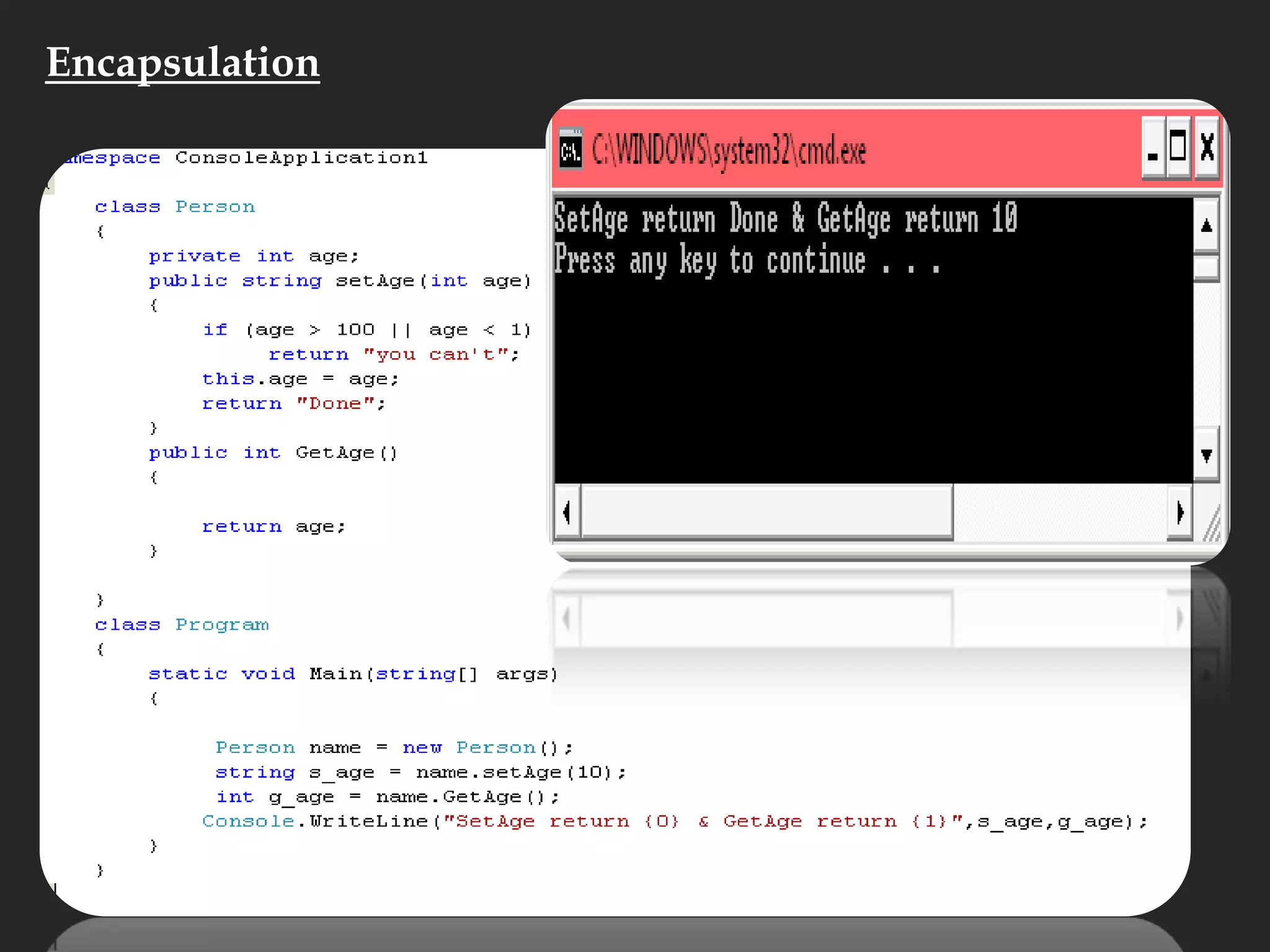
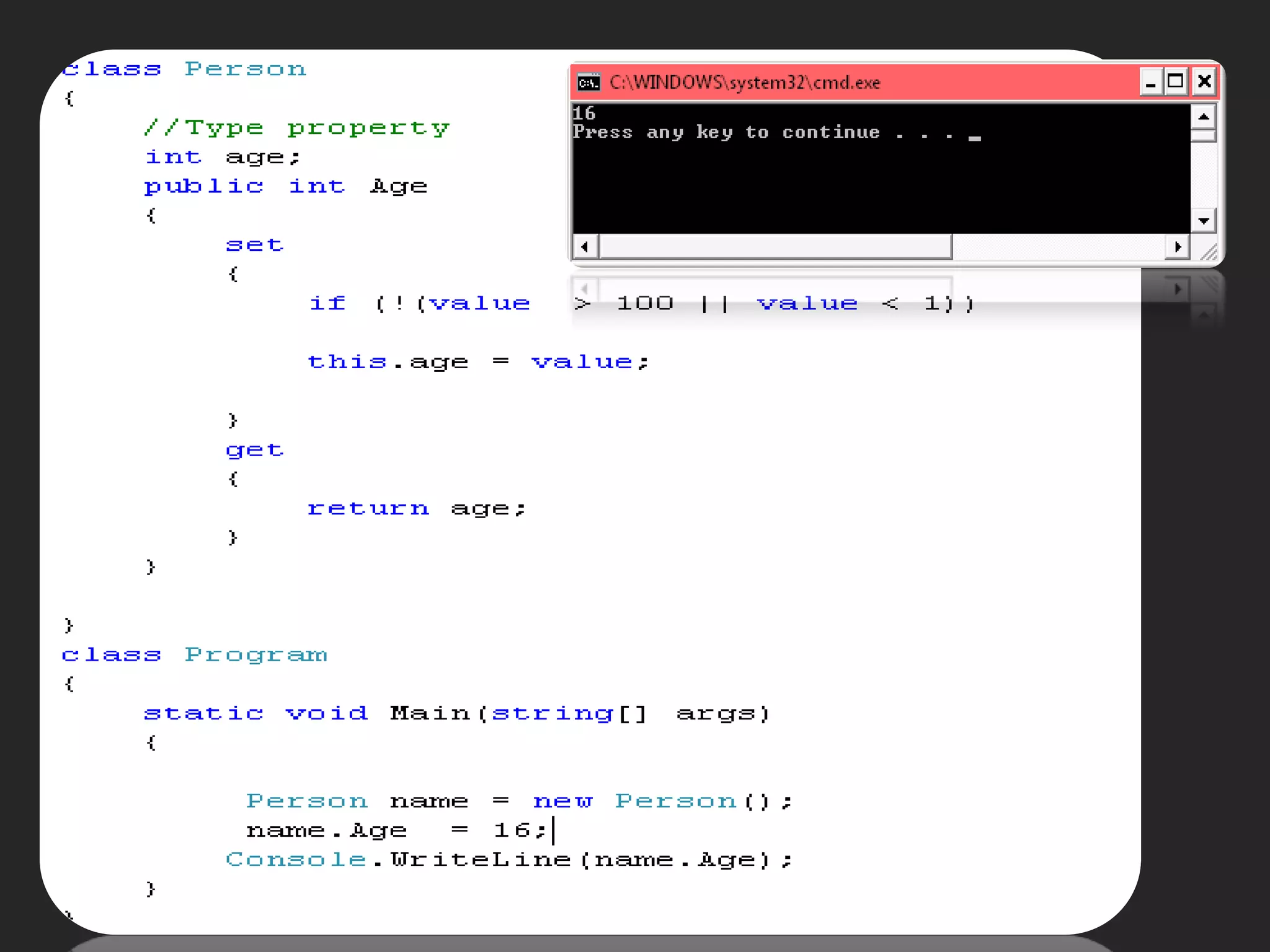
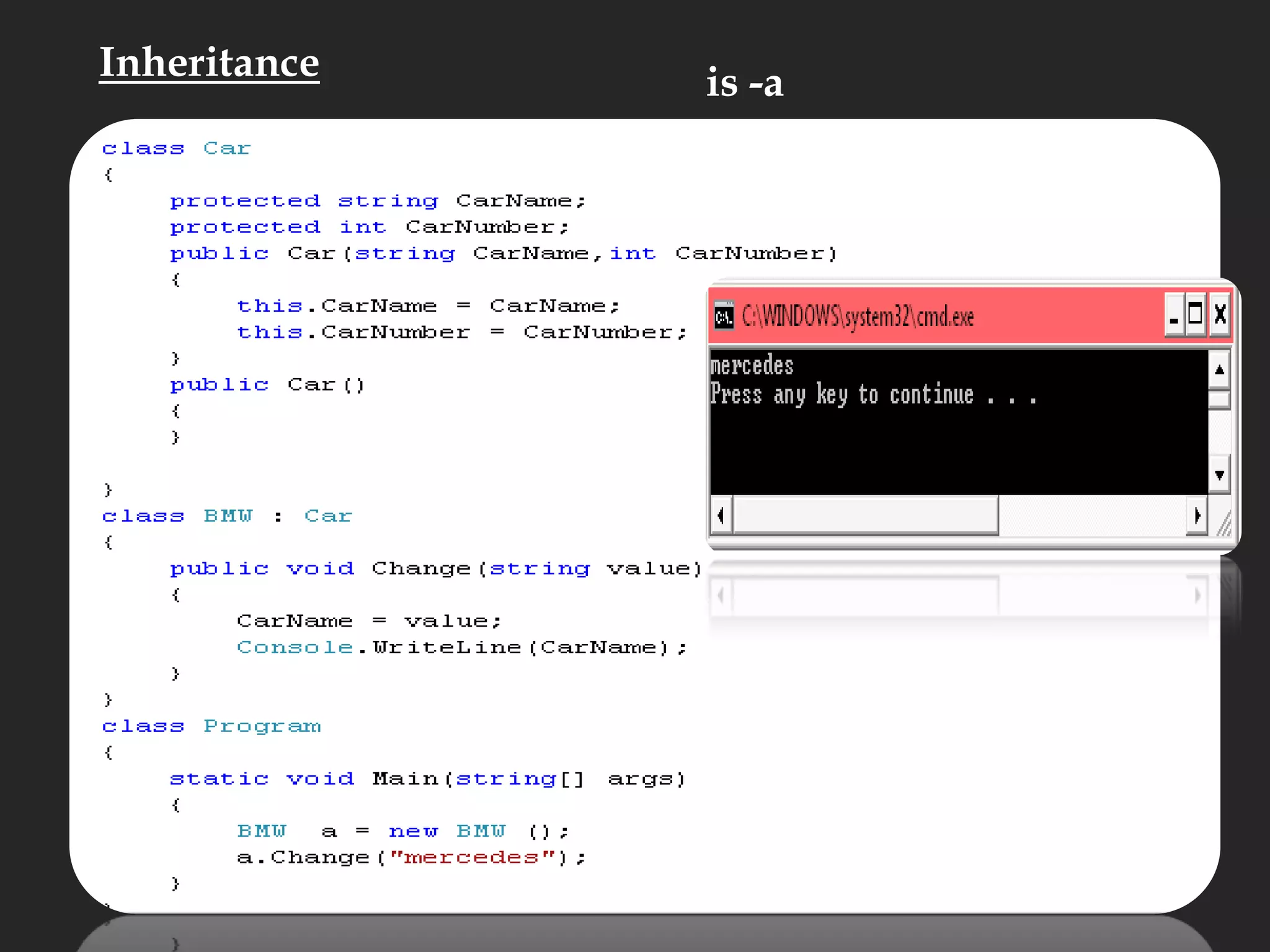
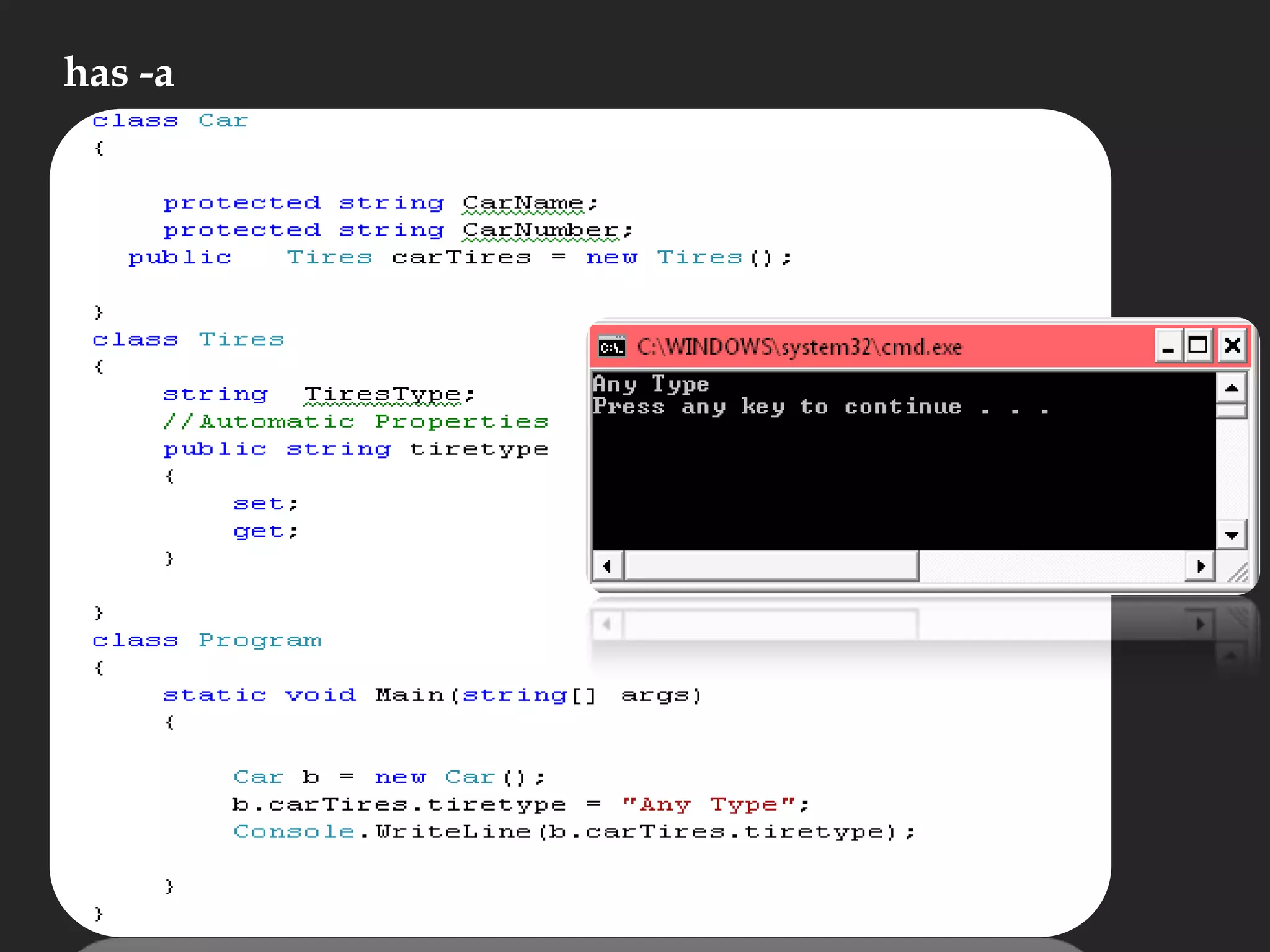
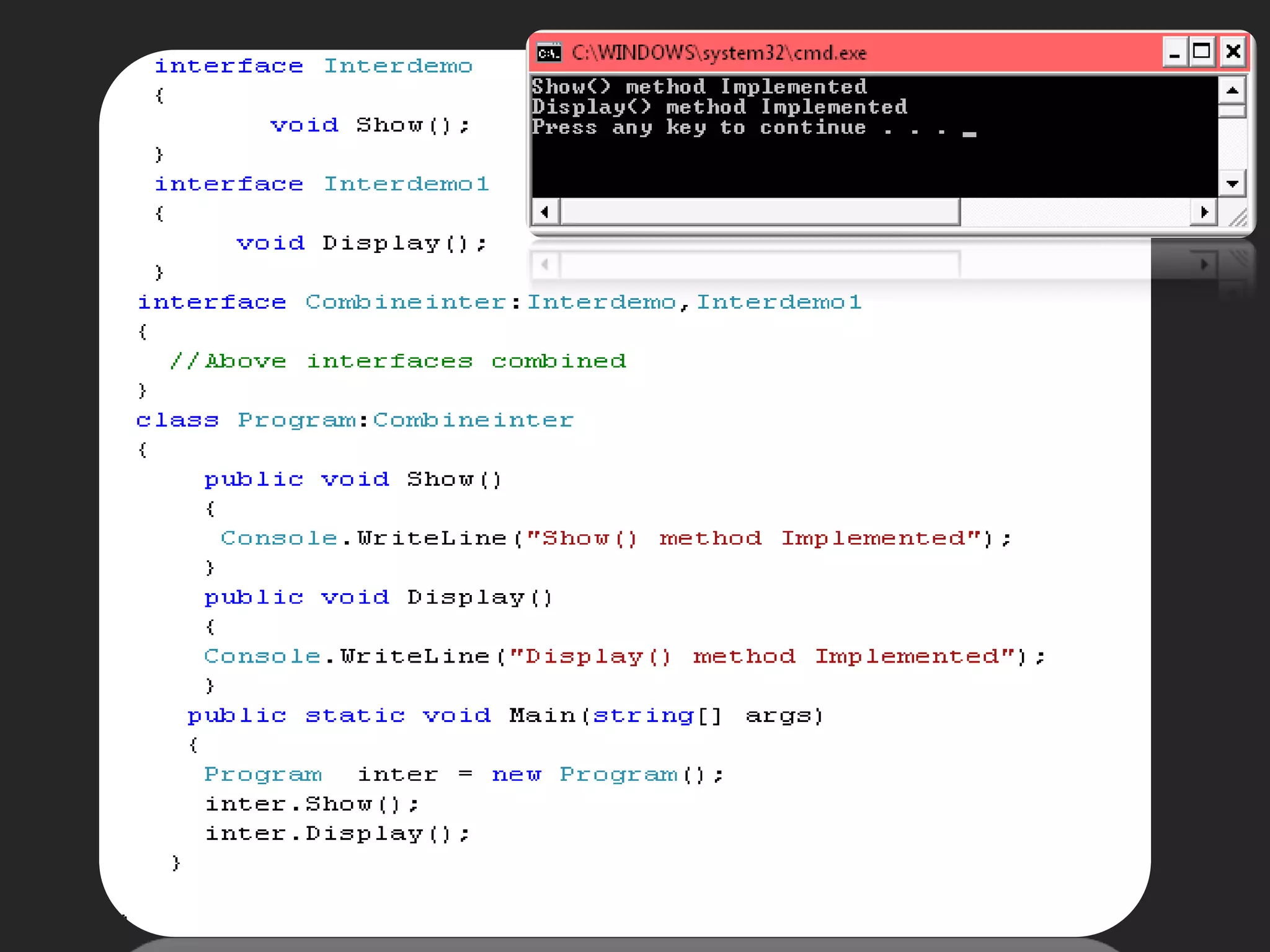
The document discusses various aspects of arrays in C# including:
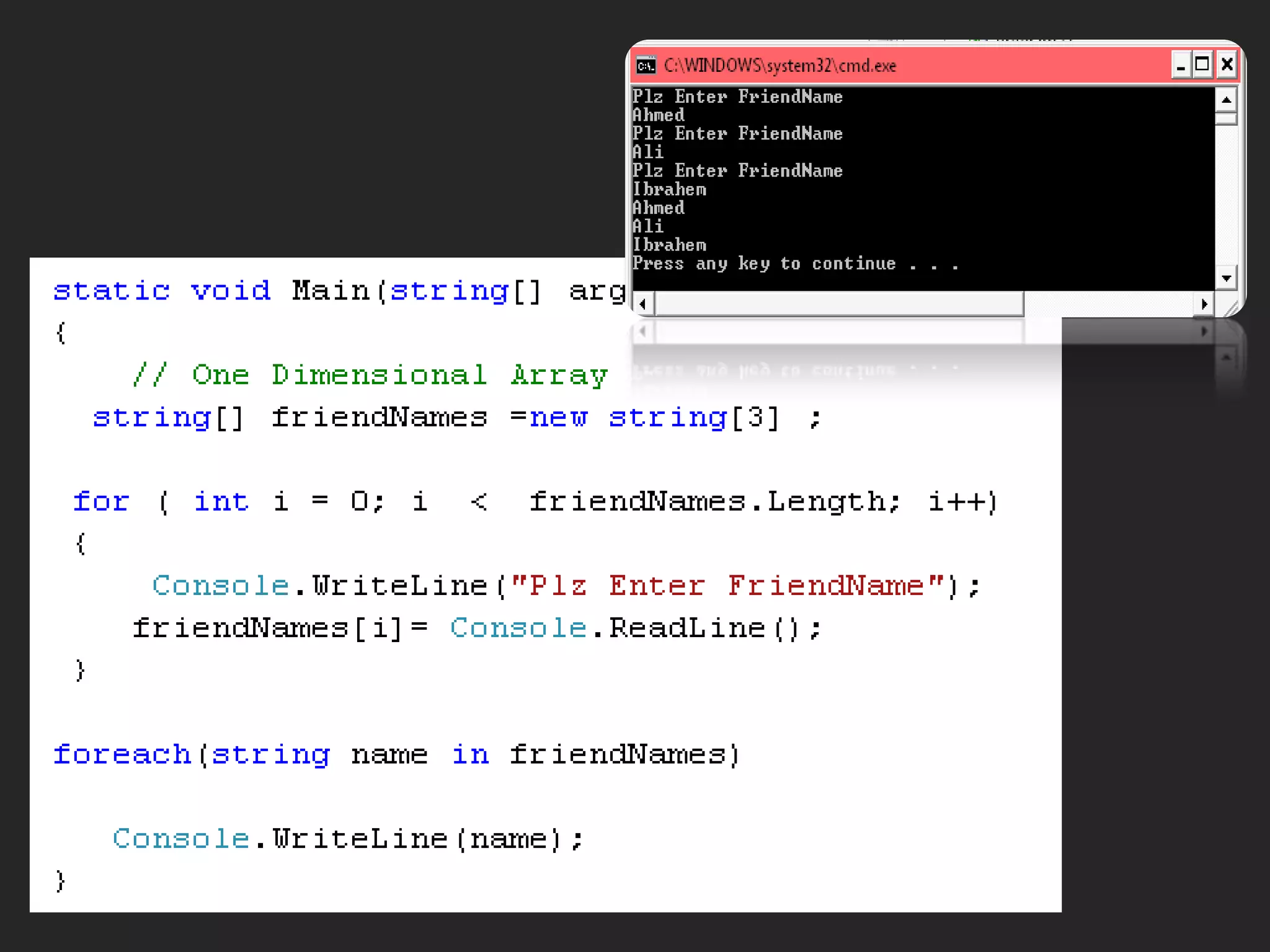
- One dimensional arrays which contain variables of the same type and can be declared using syntax like int[] arrayName = new int[size];.
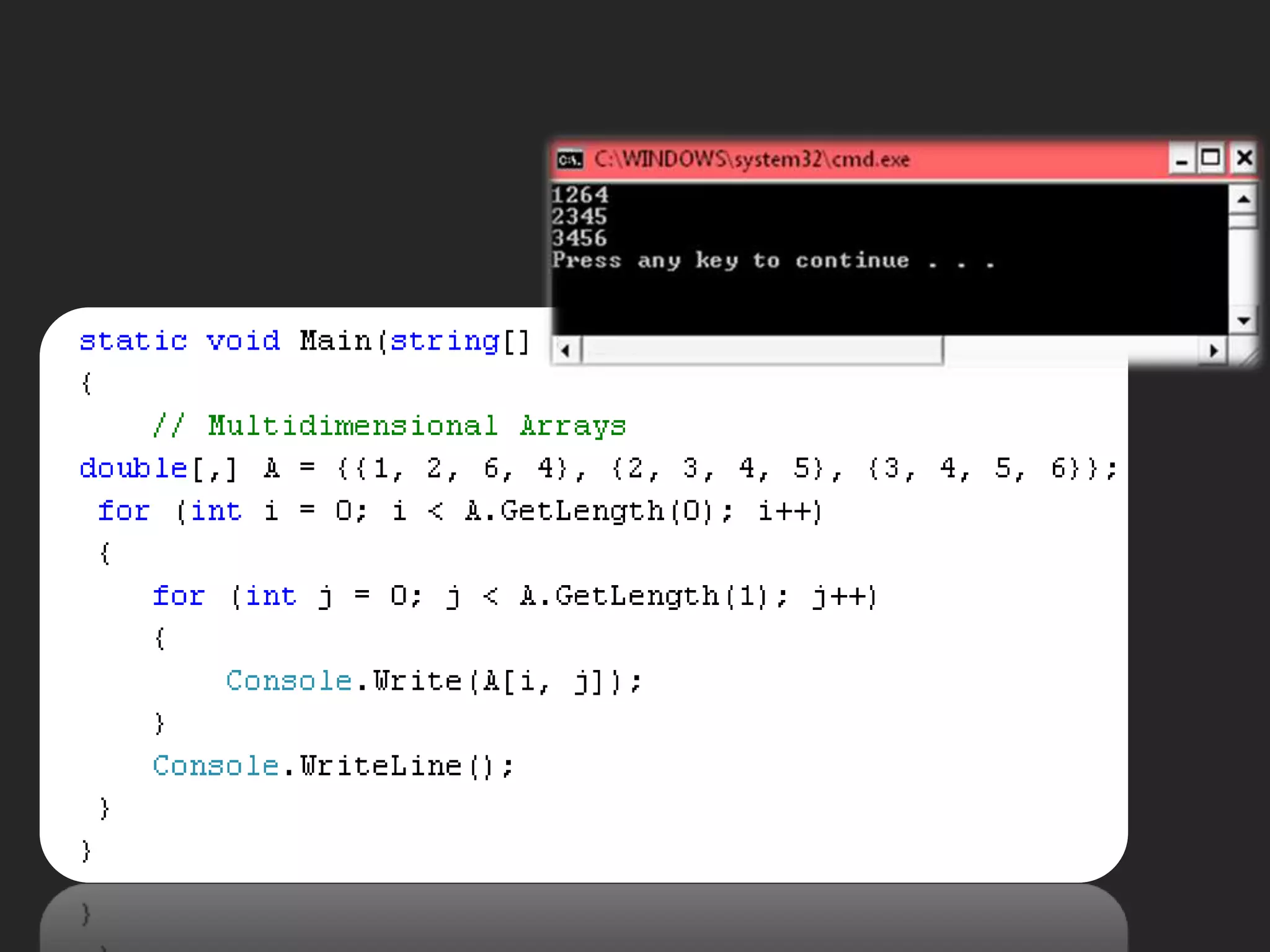
- Multidimensional arrays which are arrays of arrays and can be declared using syntax like double[,] arrayName = new double[rows,columns];
- Arrays of arrays which allow arrays to be nested inside other arrays.
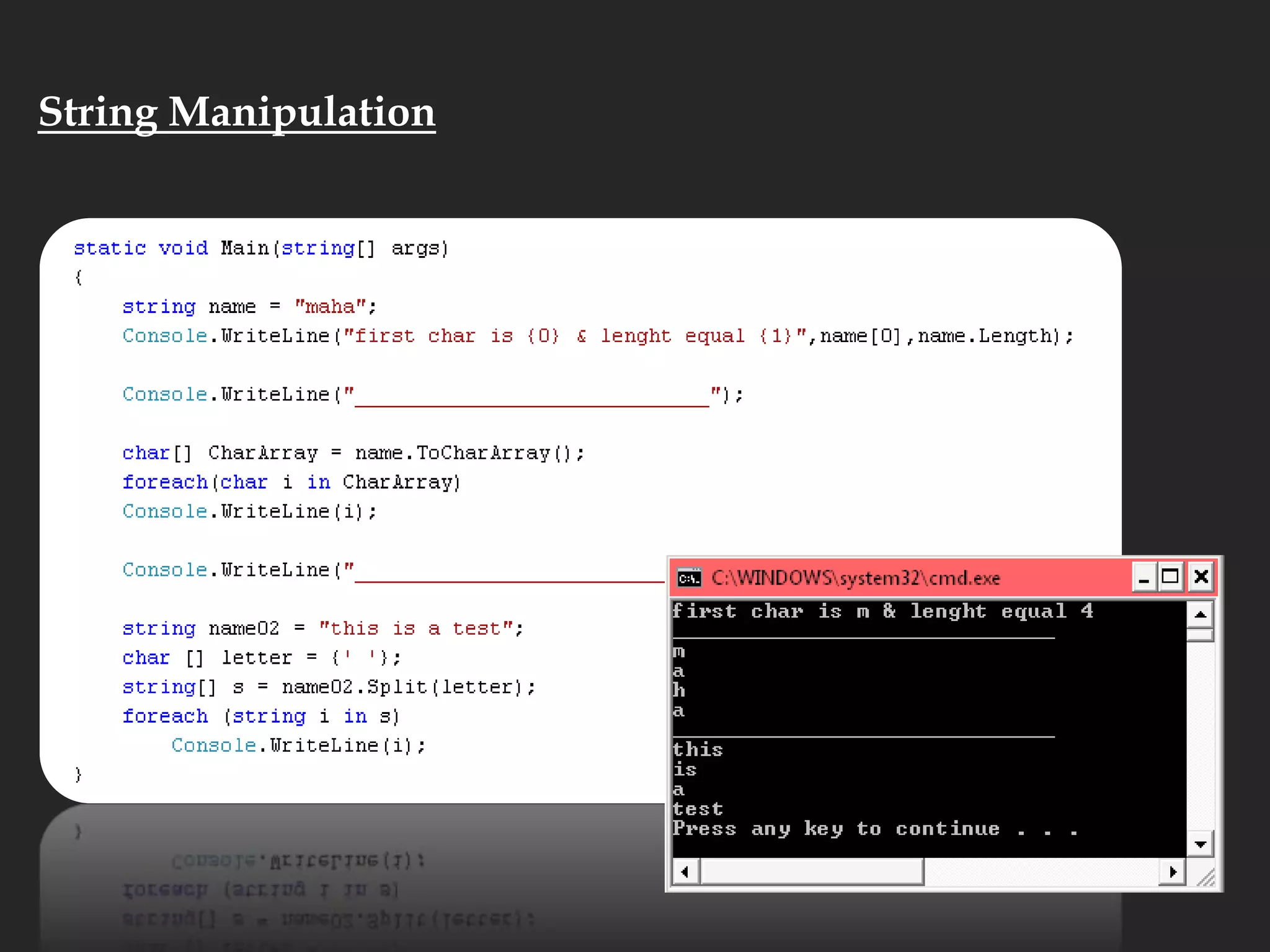
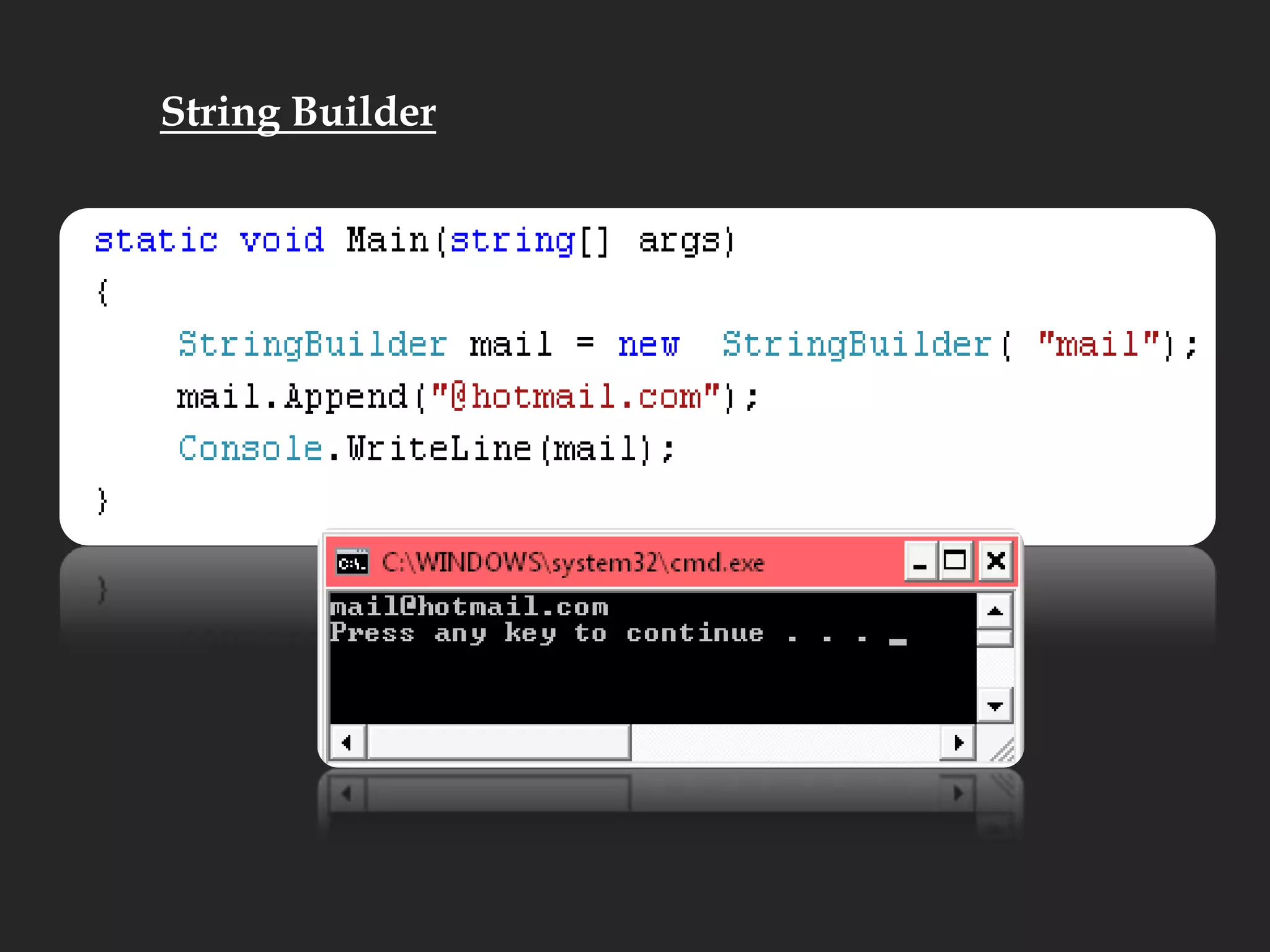
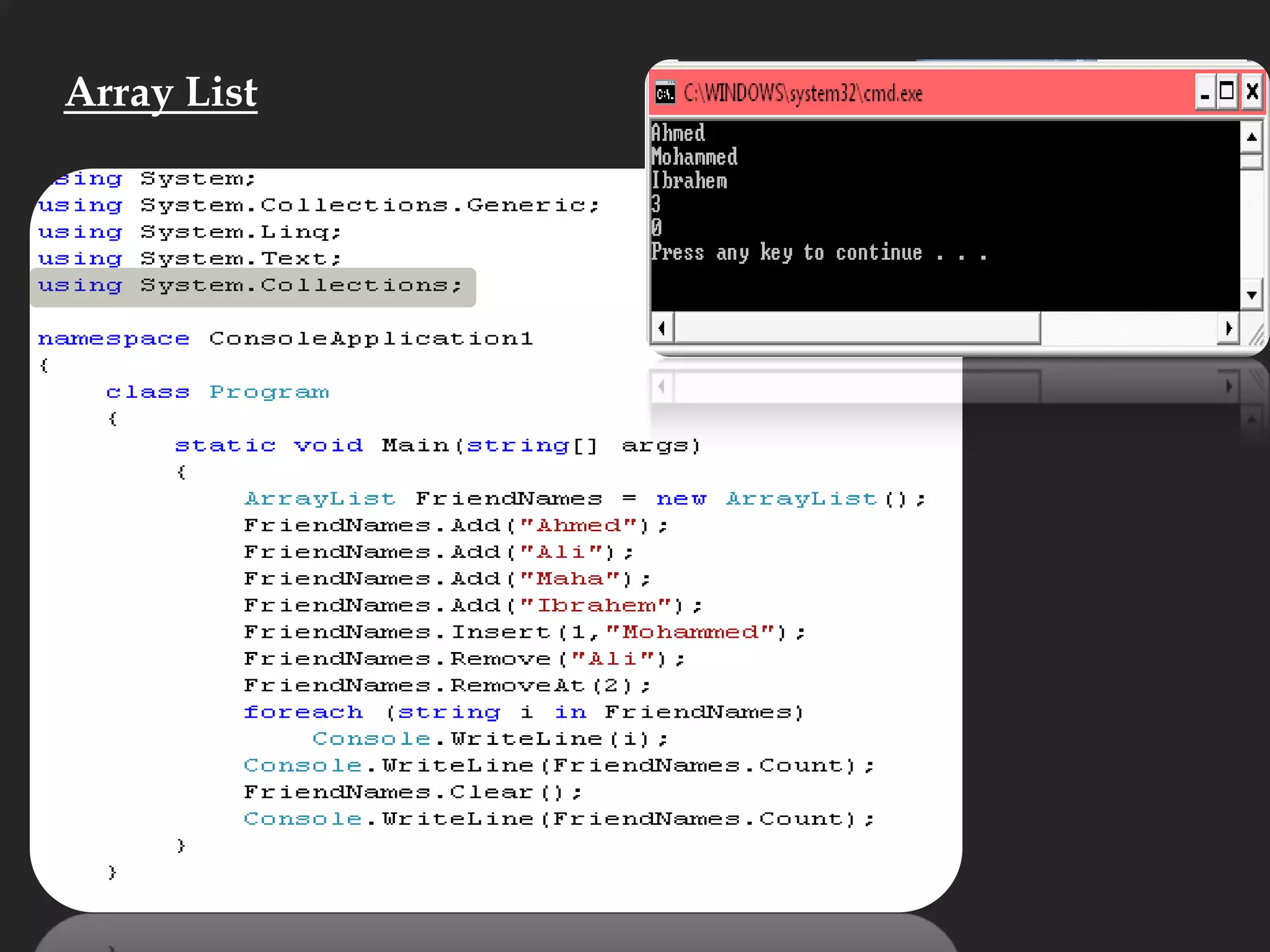
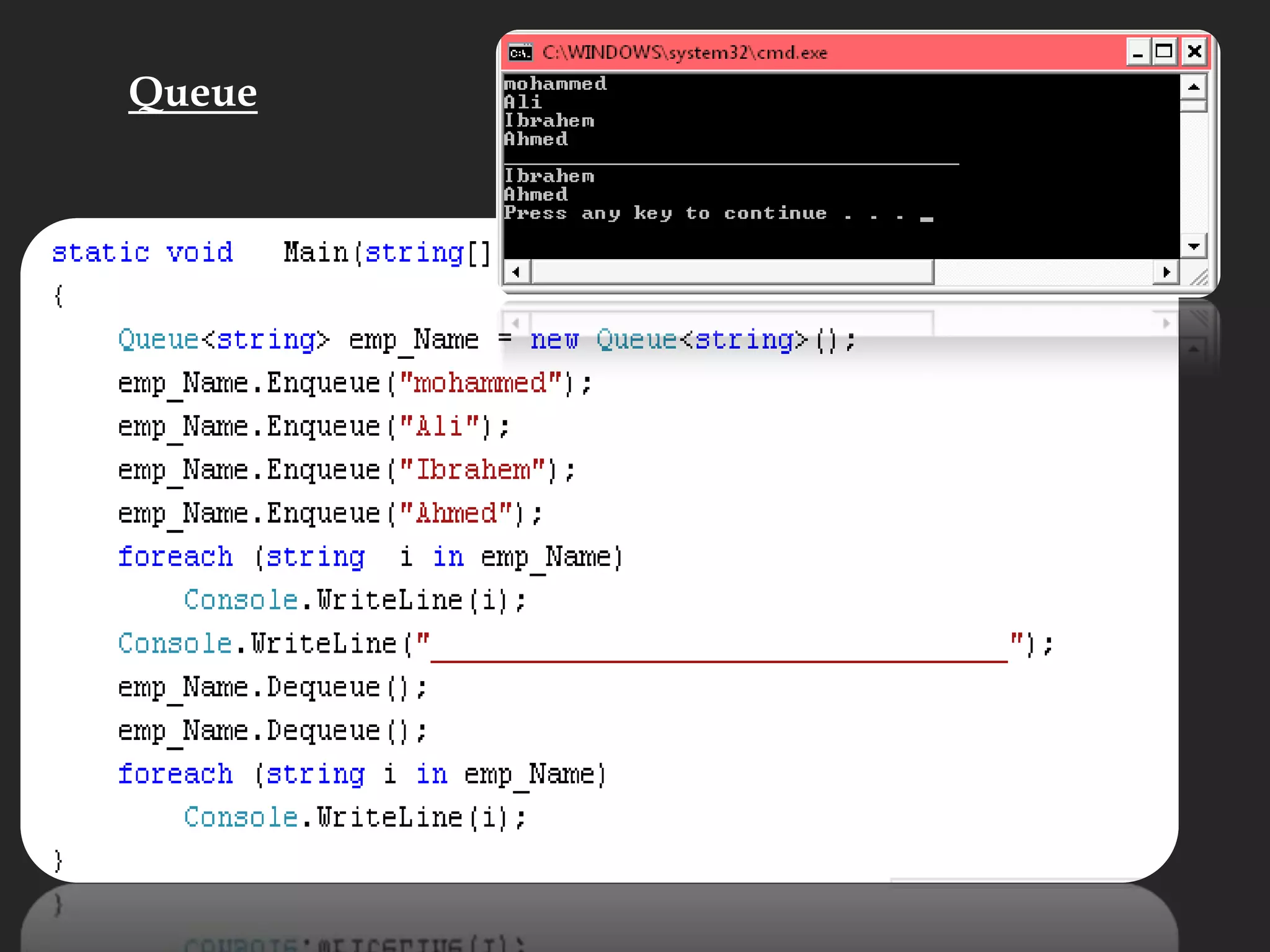
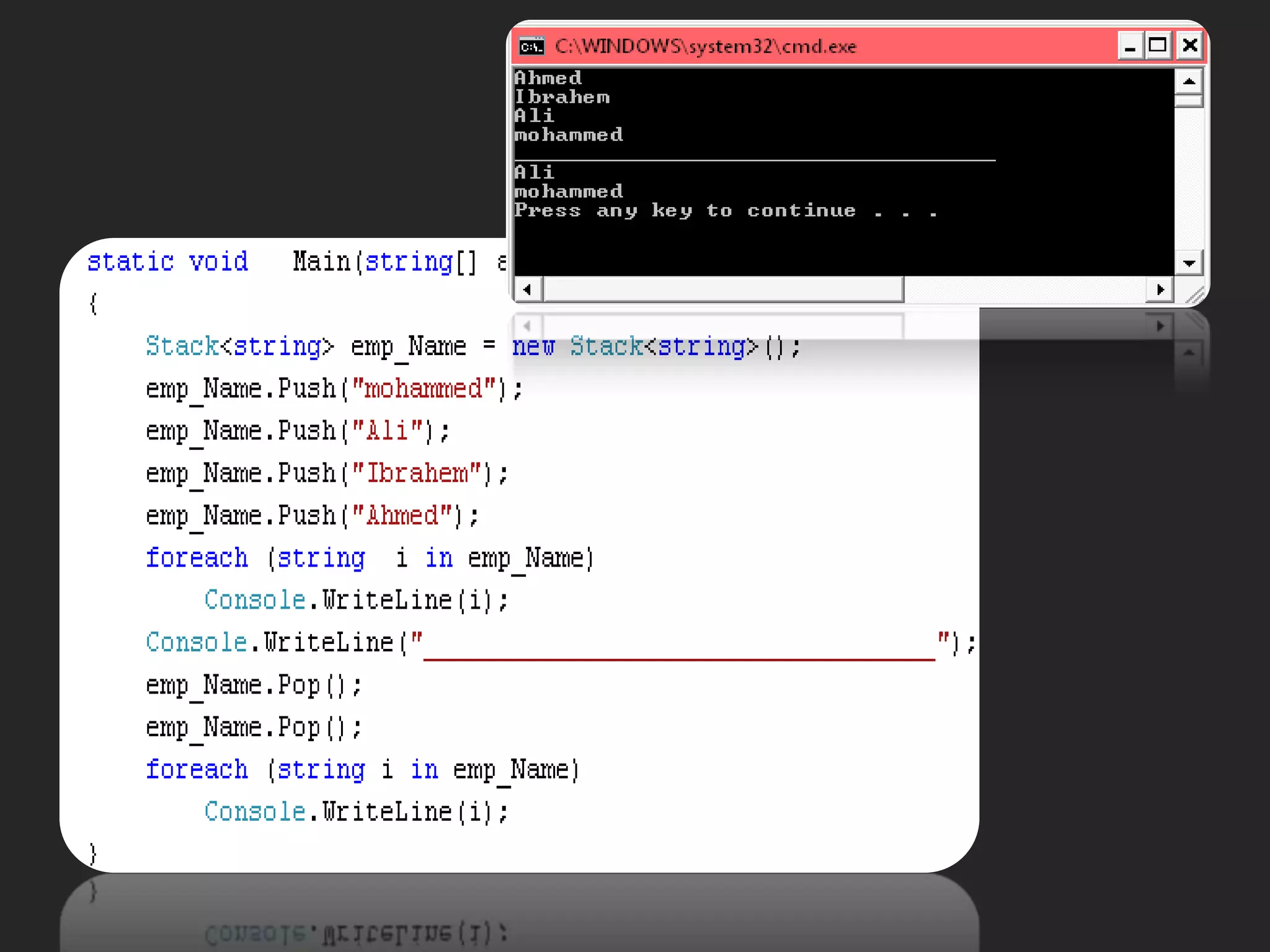
- Other array topics covered include string manipulation, array lists, queues, and functions that can operate on arrays.


![Arraya data structure that contains several variables of the same type. One Dimensional ArrayType [ ] Array_Name = new int [arraySize]; Examplesint[] myIntArray = {5, 9, 10, 2, 99}; int[] myIntArray = new int[5]; int[] myIntArray = new int[5] {5, 9, 10, 2, 99};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csharp2-110224144248-phpapp02/75/OOP-in-C-3-2048.jpg)
![Multidimensional Arrays -A two - dimensional array such as this is declared as follows: < baseType > [ , ] < name > Examplesdouble[ , ] hillHeight = new double[3,4]; int[ , ] hillHeight = {{1, 2, 3, 4}, {2, 3, 4, 5}, {3, 4, 5, 6}};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csharp2-110224144248-phpapp02/75/OOP-in-C-5-2048.jpg)
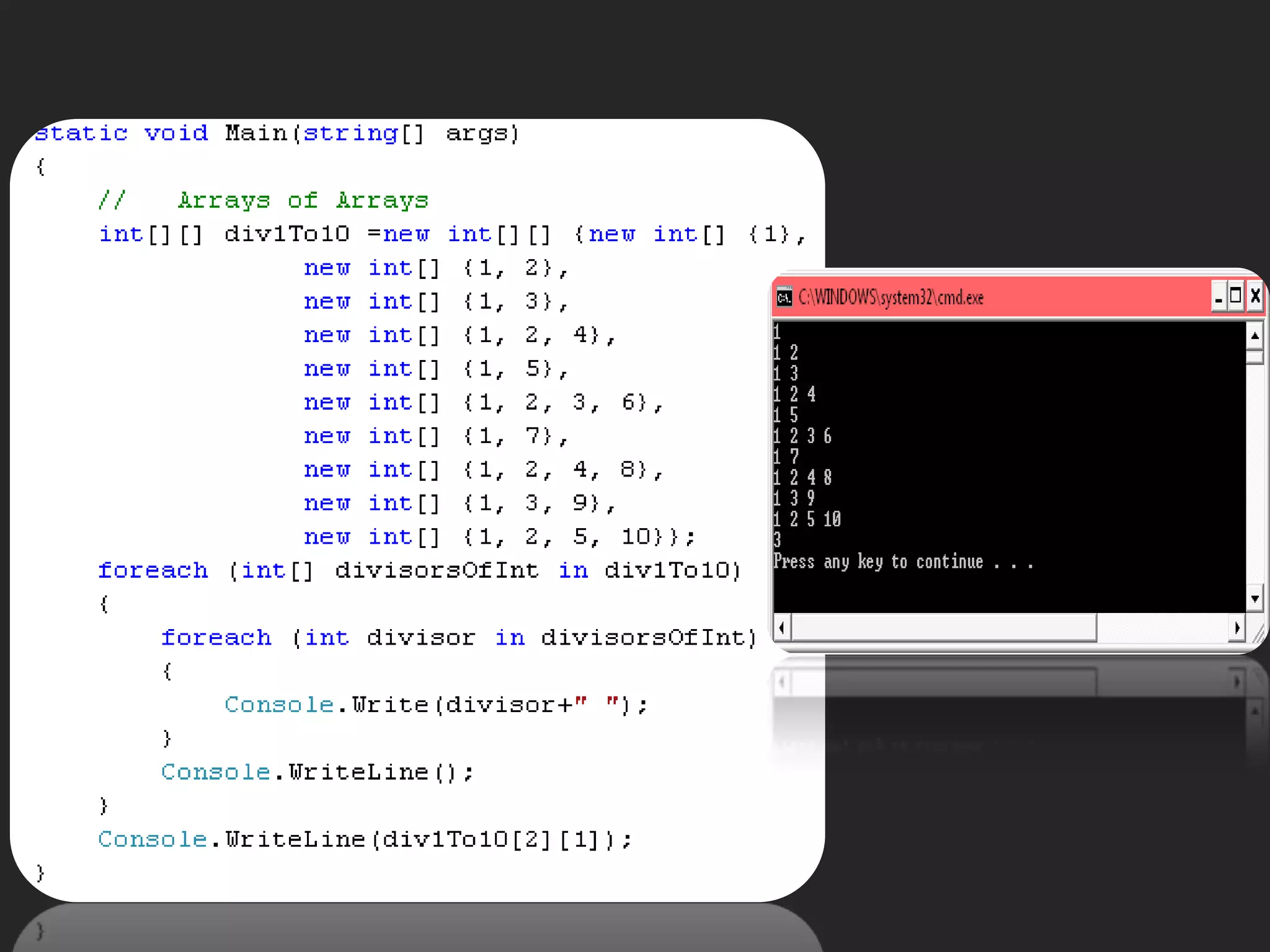
![Arrays of Arraysint[][] MyArray; MyArray = {{1, 2, 3}, {1}, {1, 2}}; int[][] MyArray = {new int[] {1, 2, 3}, new int[] {1}, new int[]{1,2}}; MyArray = new int[2][];MyArray[0] = new int[3];MyArray[1] = new int[4]; MyArray= new int[3][] {new int[] {1, 2, 3}, new int[] {1},new int[] {1, 2}};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csharp2-110224144248-phpapp02/75/OOP-in-C-7-2048.jpg)

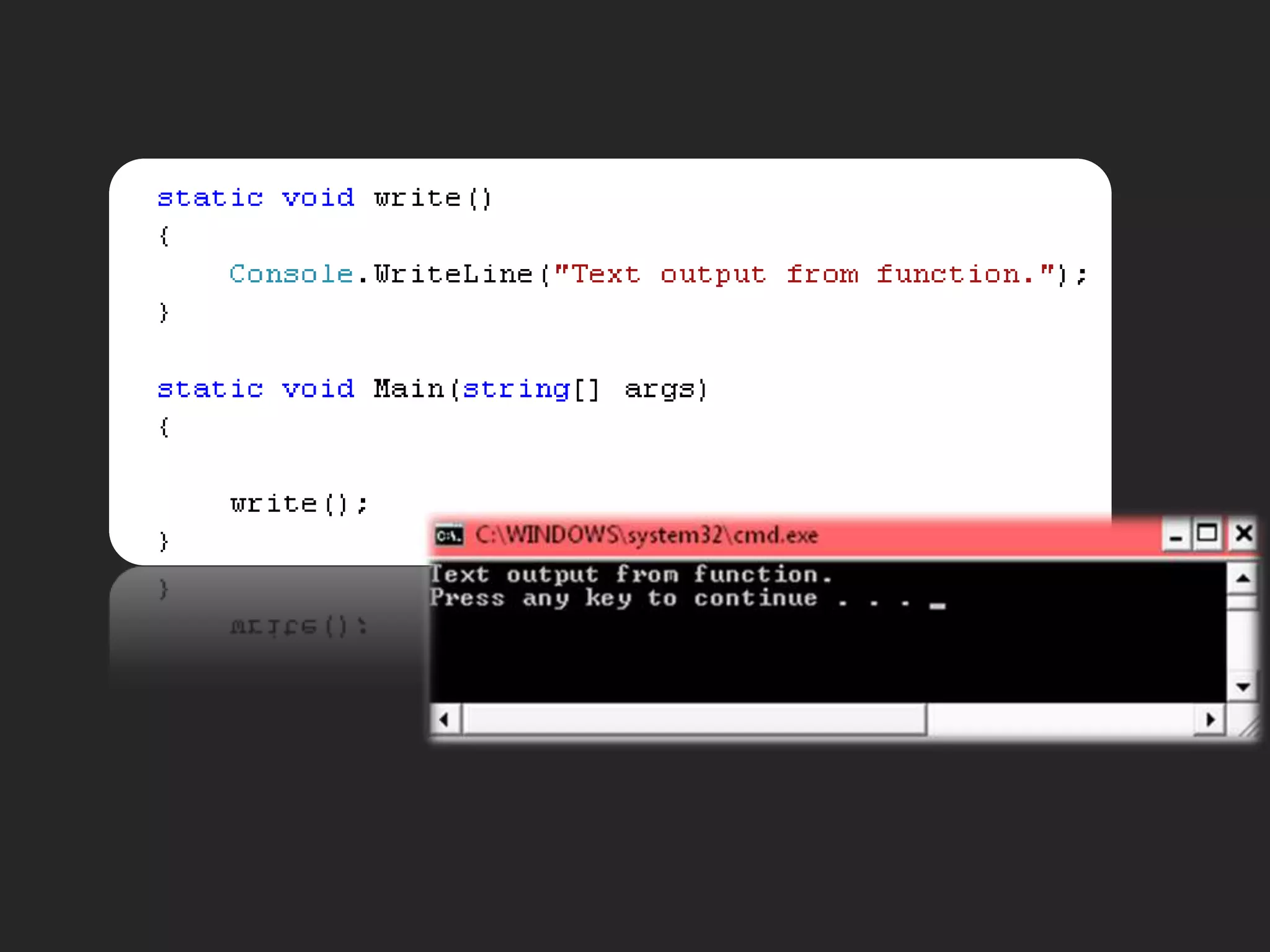
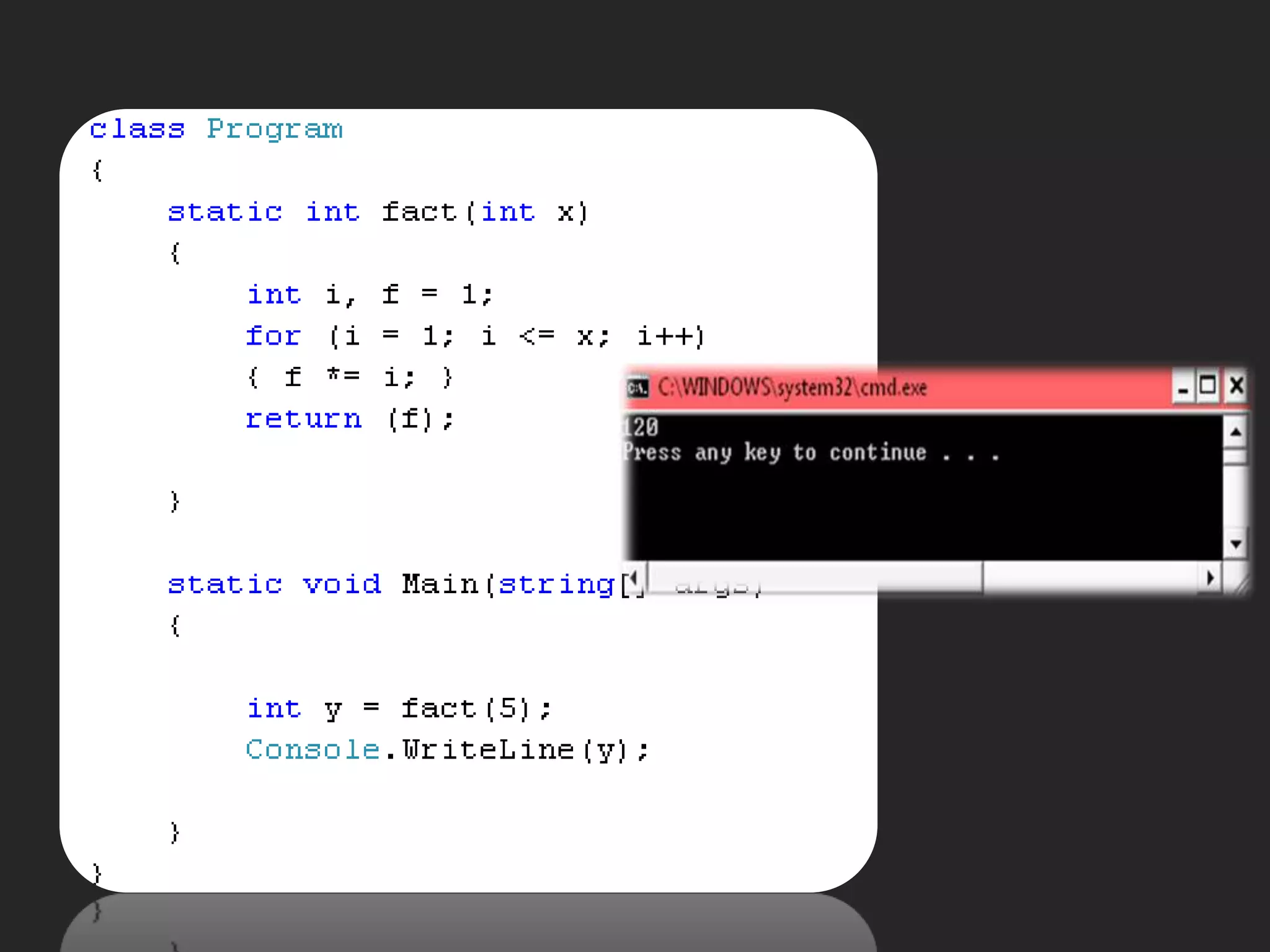
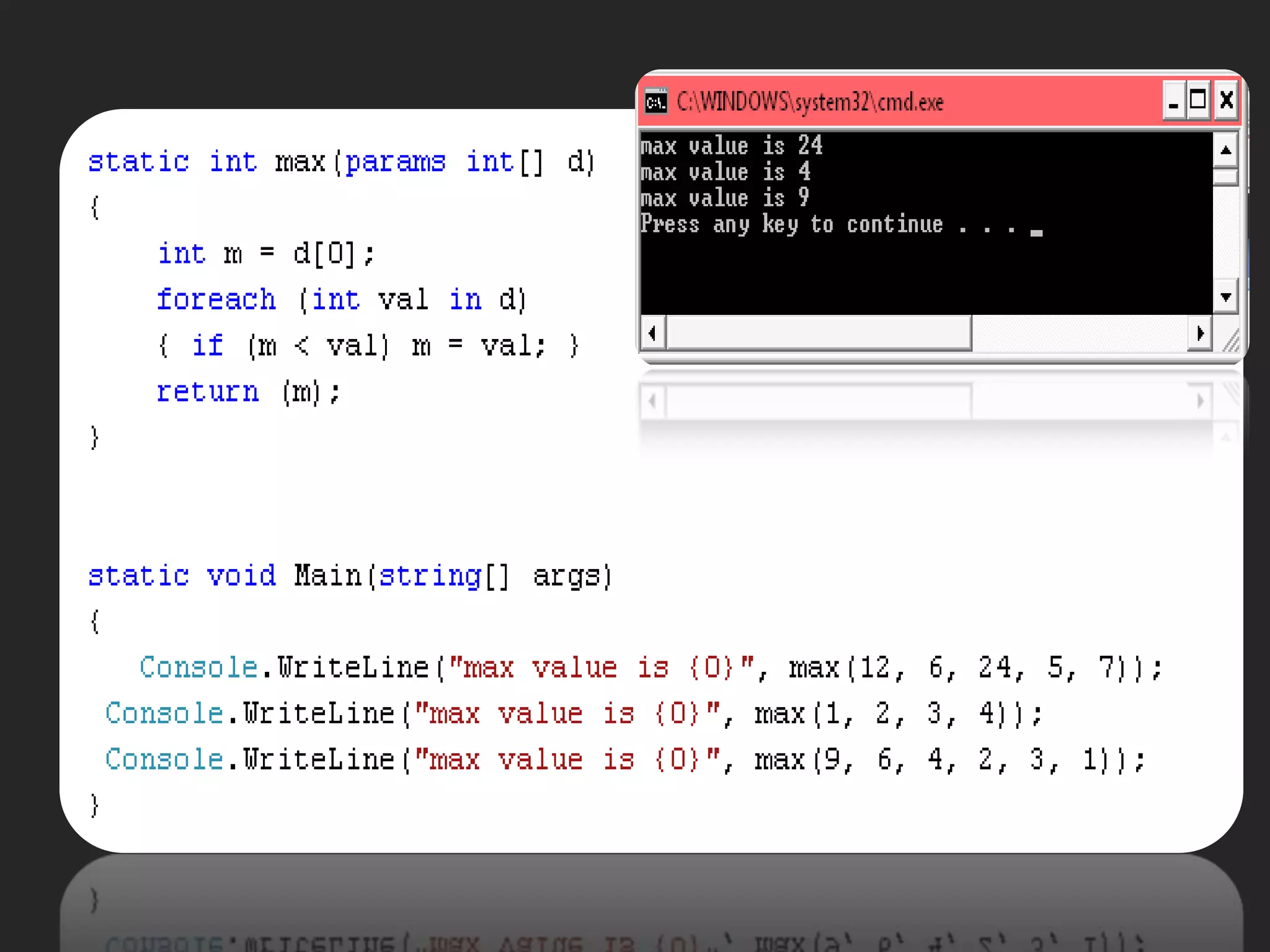
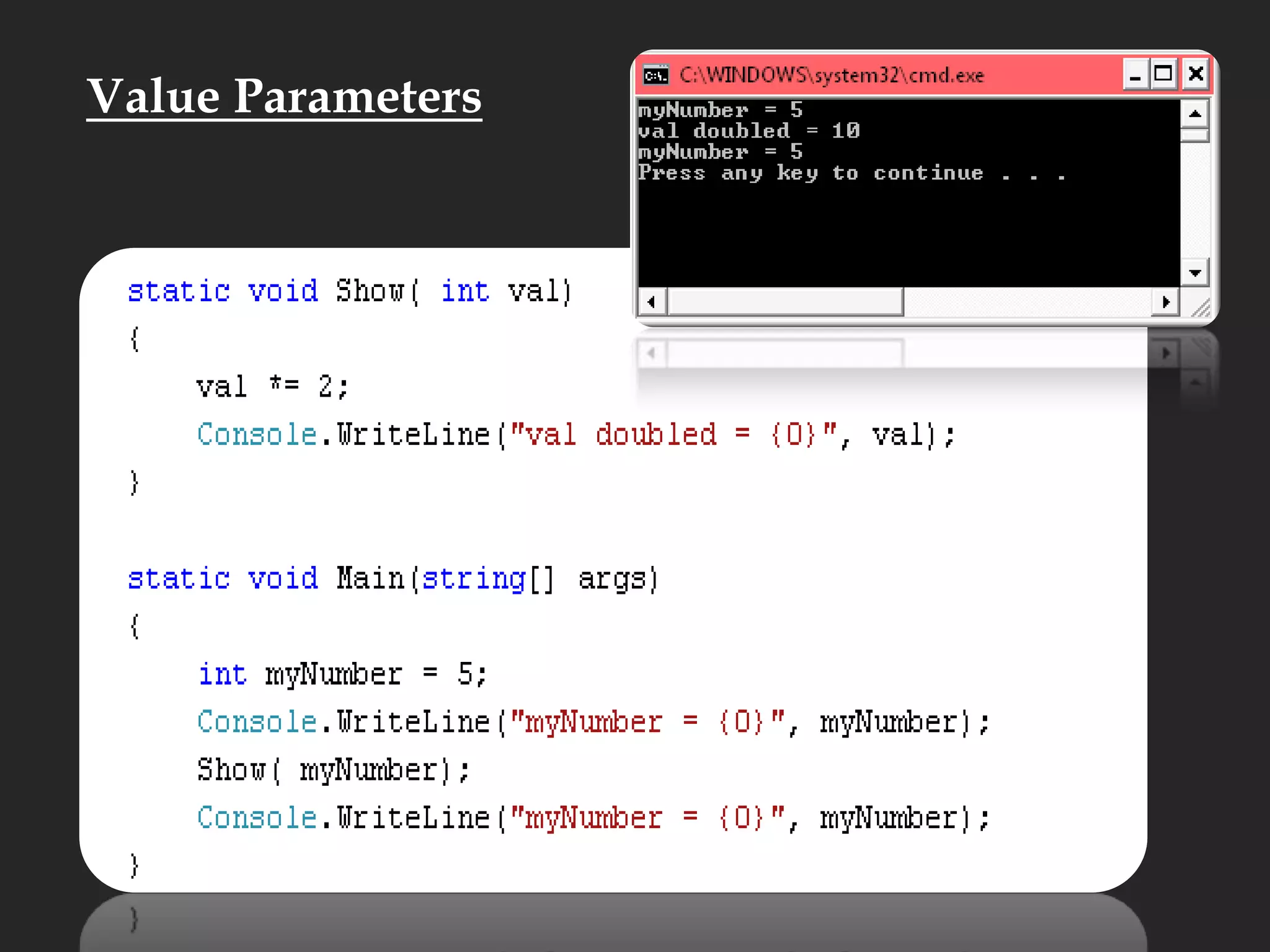
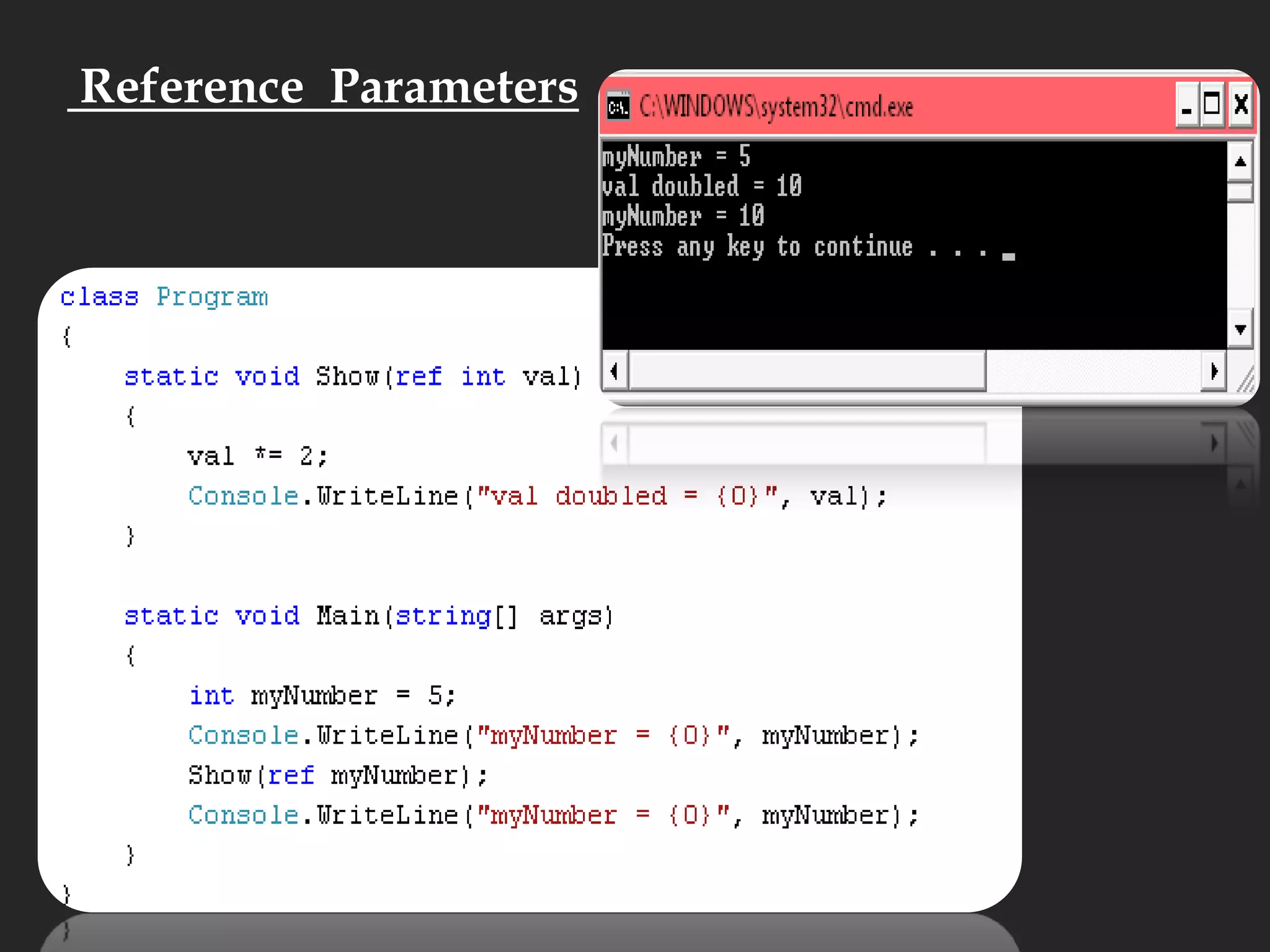
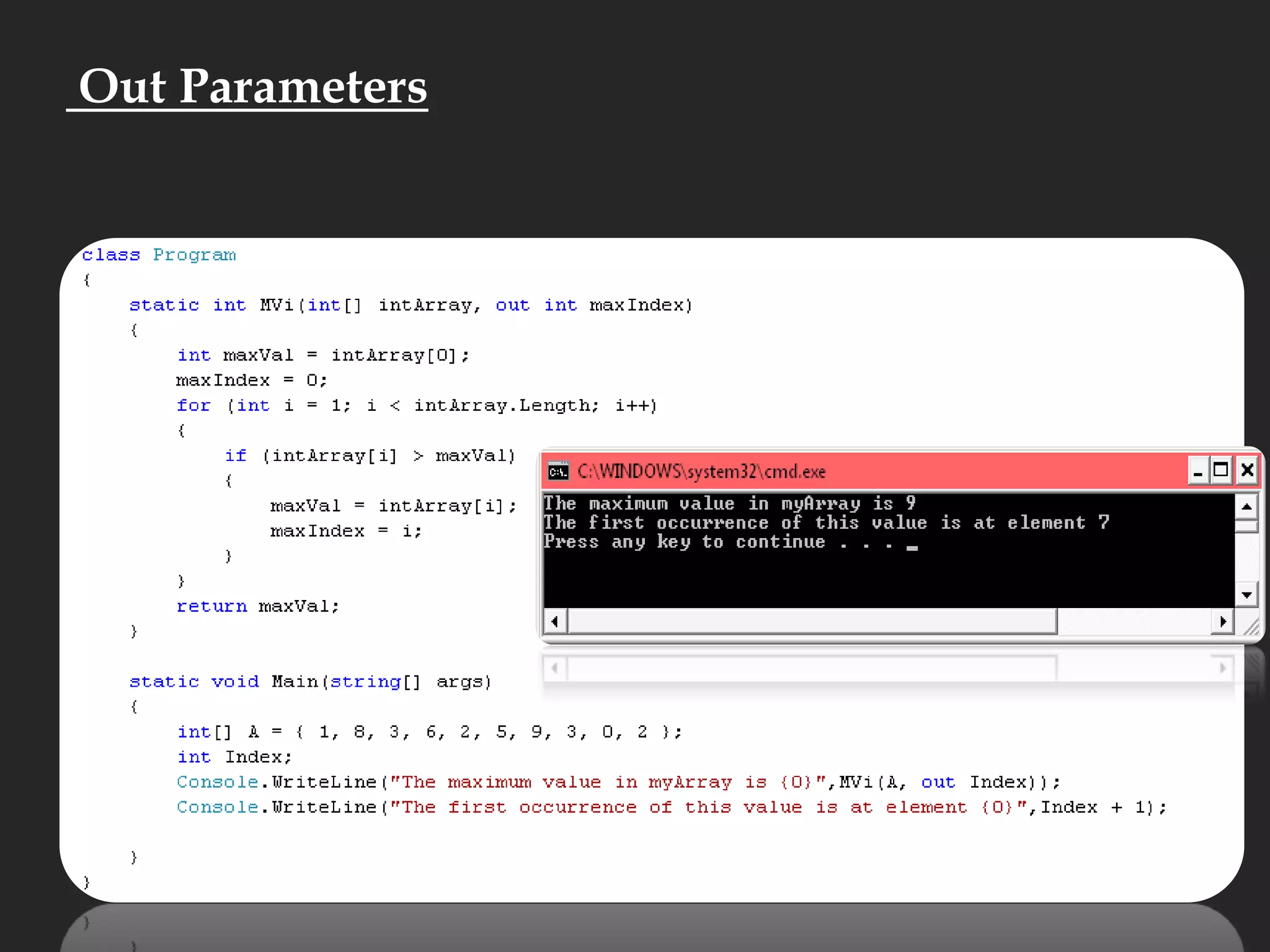
![Main Function static void Main( )static void Main(string[] args)static int Main()static StringMain(string[] args)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csharp2-110224144248-phpapp02/75/OOP-in-C-21-2048.jpg)