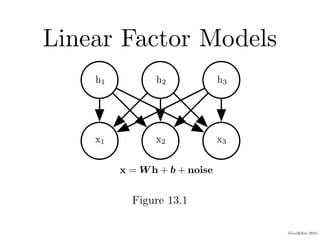
1) Linear factor models represent observed data vectors as a linear combination of latent factors plus noise. They include probabilistic principal component analysis (PCA) and factor analysis.
2) Independent component analysis learns components that are closer to statistically independent than the raw features, and can separate signals like voices or EEG signals.
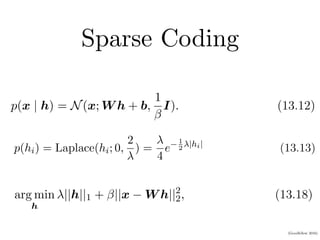
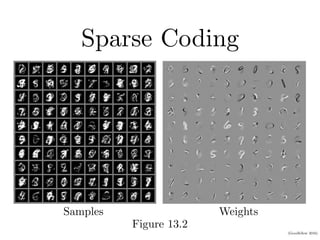
3) Sparse coding finds a sparse representation of data by solving an optimization problem that minimizes a factor's value and reconstruction error, producing sparse weights.