This document provides a summary of three topics:
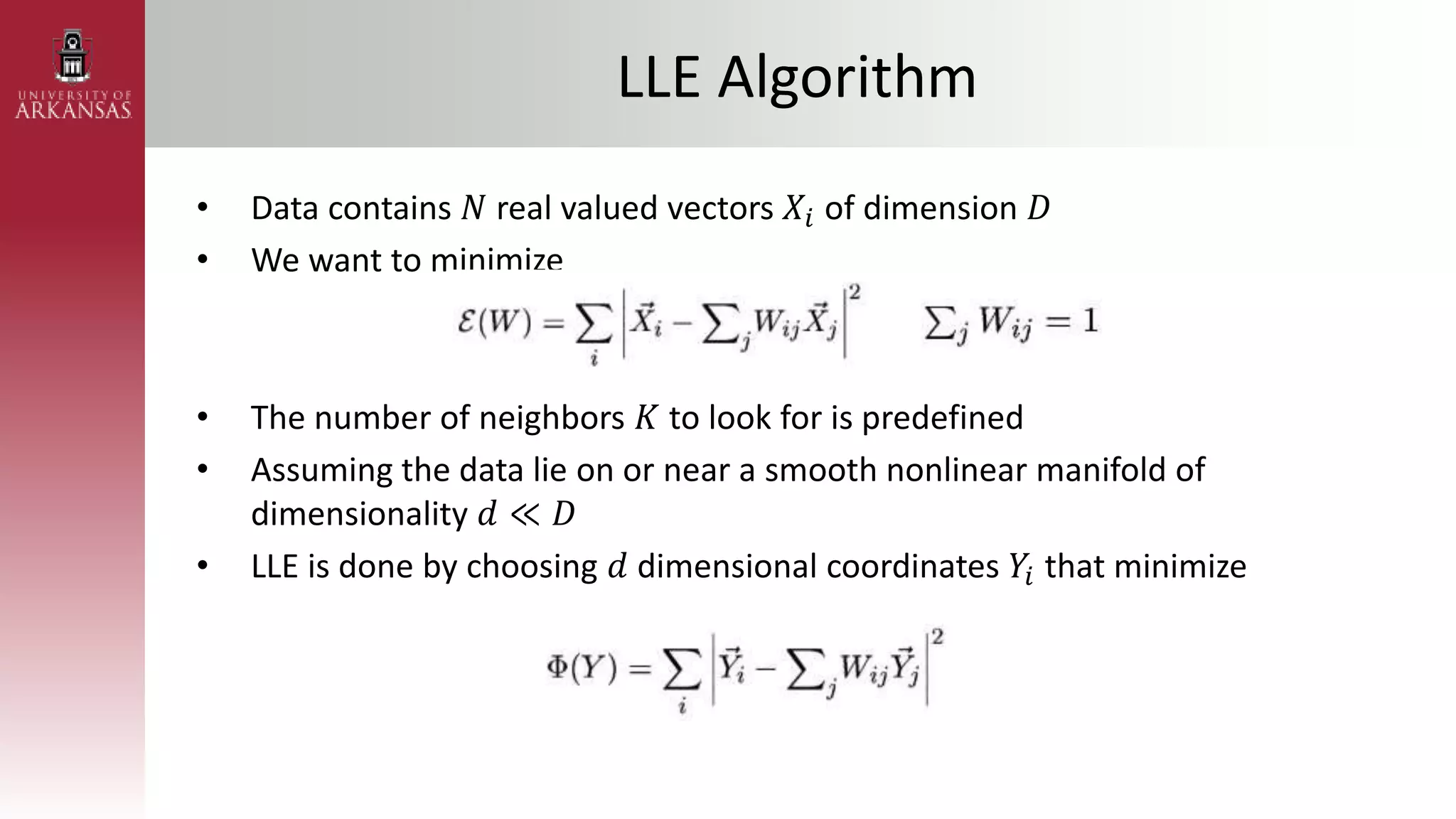
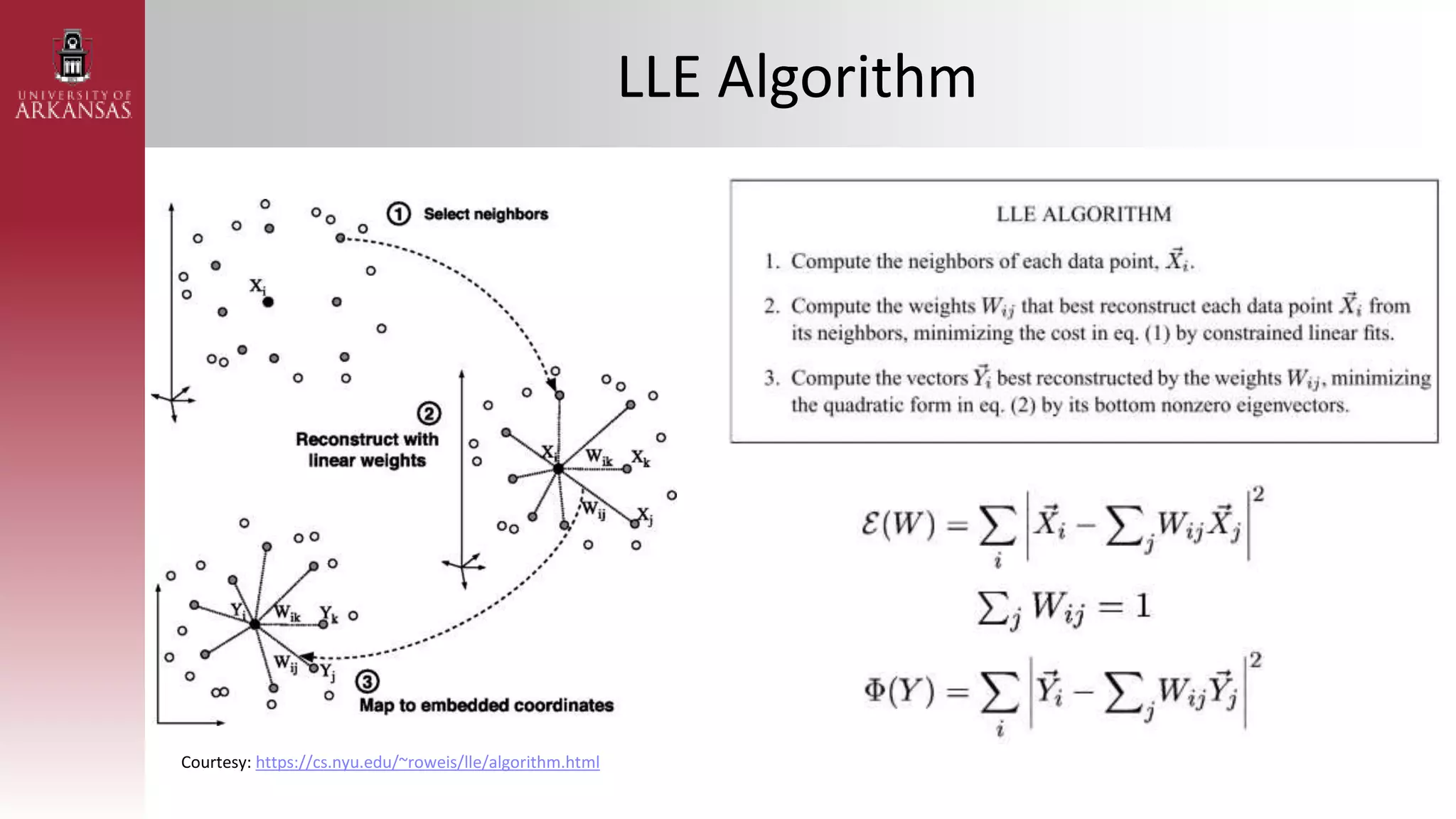
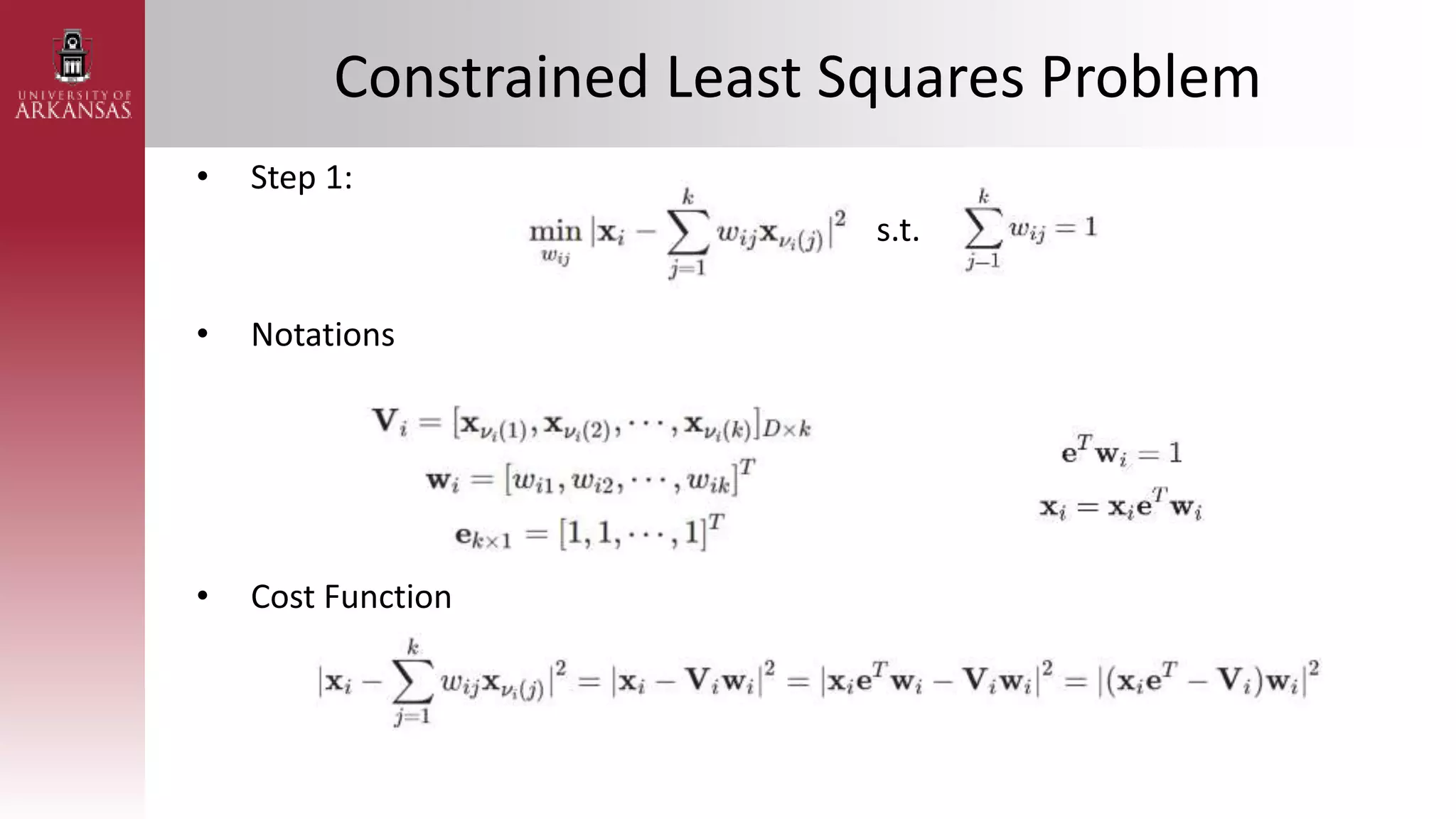
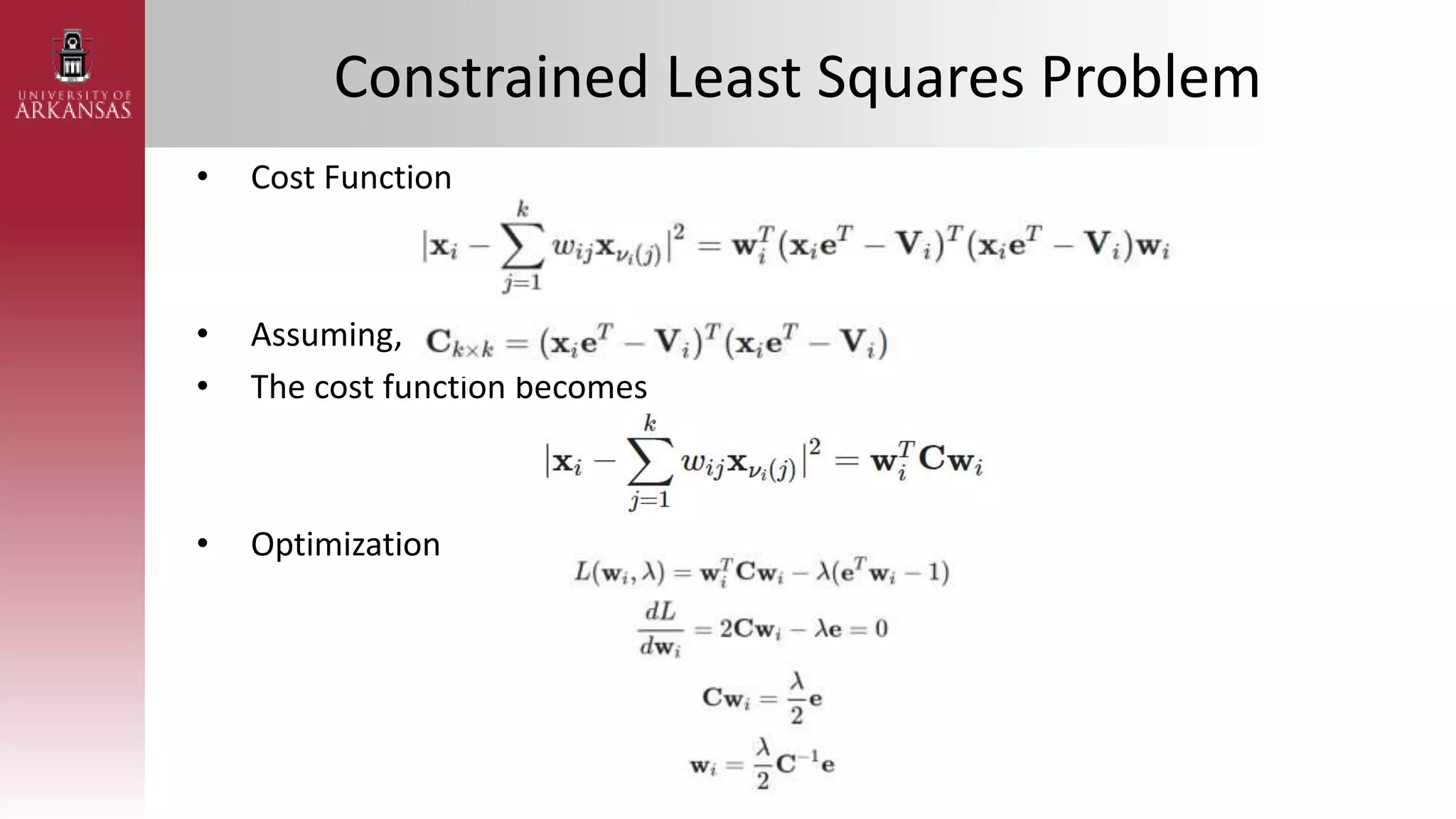
1) An introduction to Locally Linear Embedding (LLE), an unsupervised nonlinear dimensionality reduction technique. It describes the objective, idea, and algorithm of LLE.
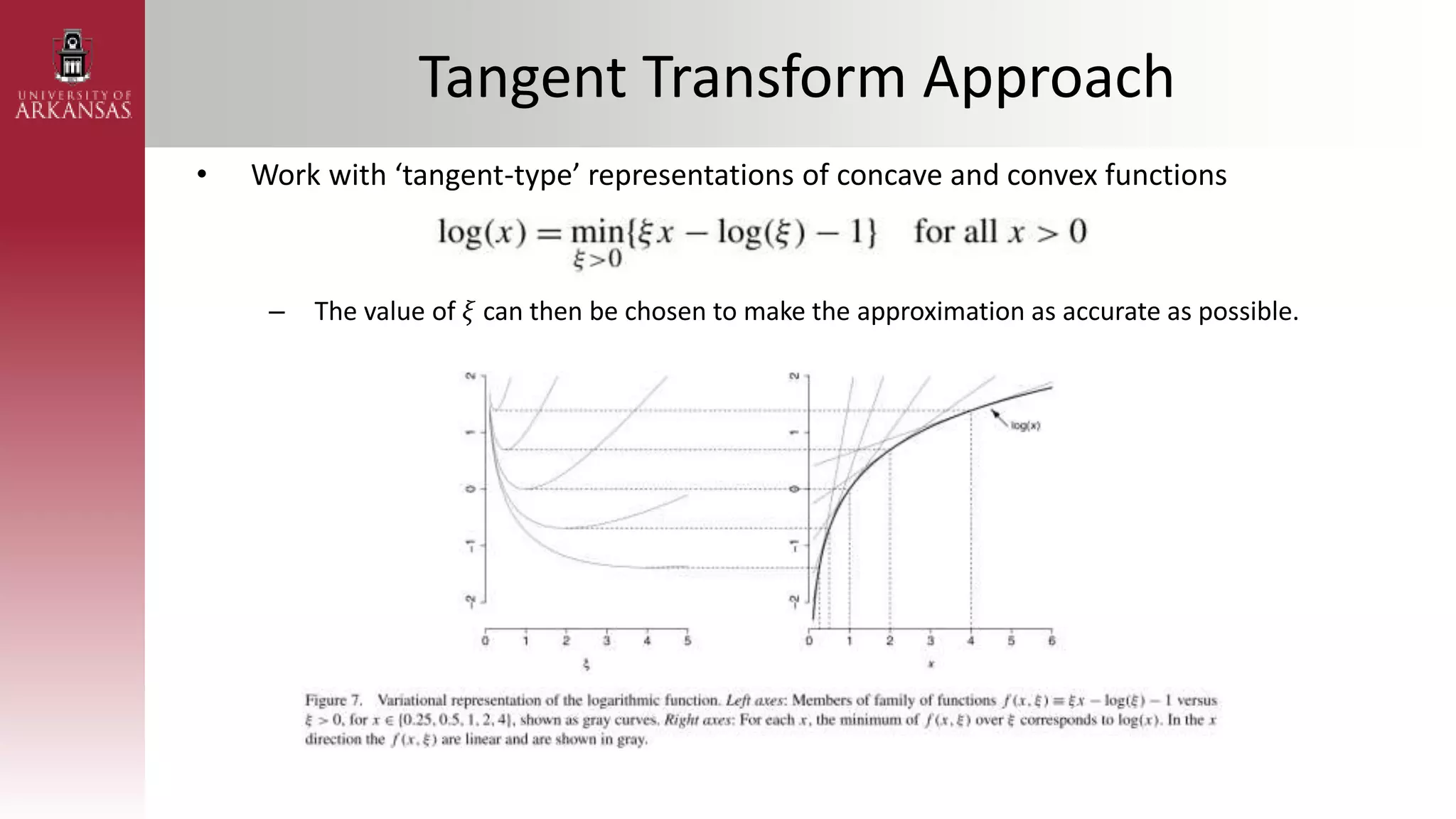
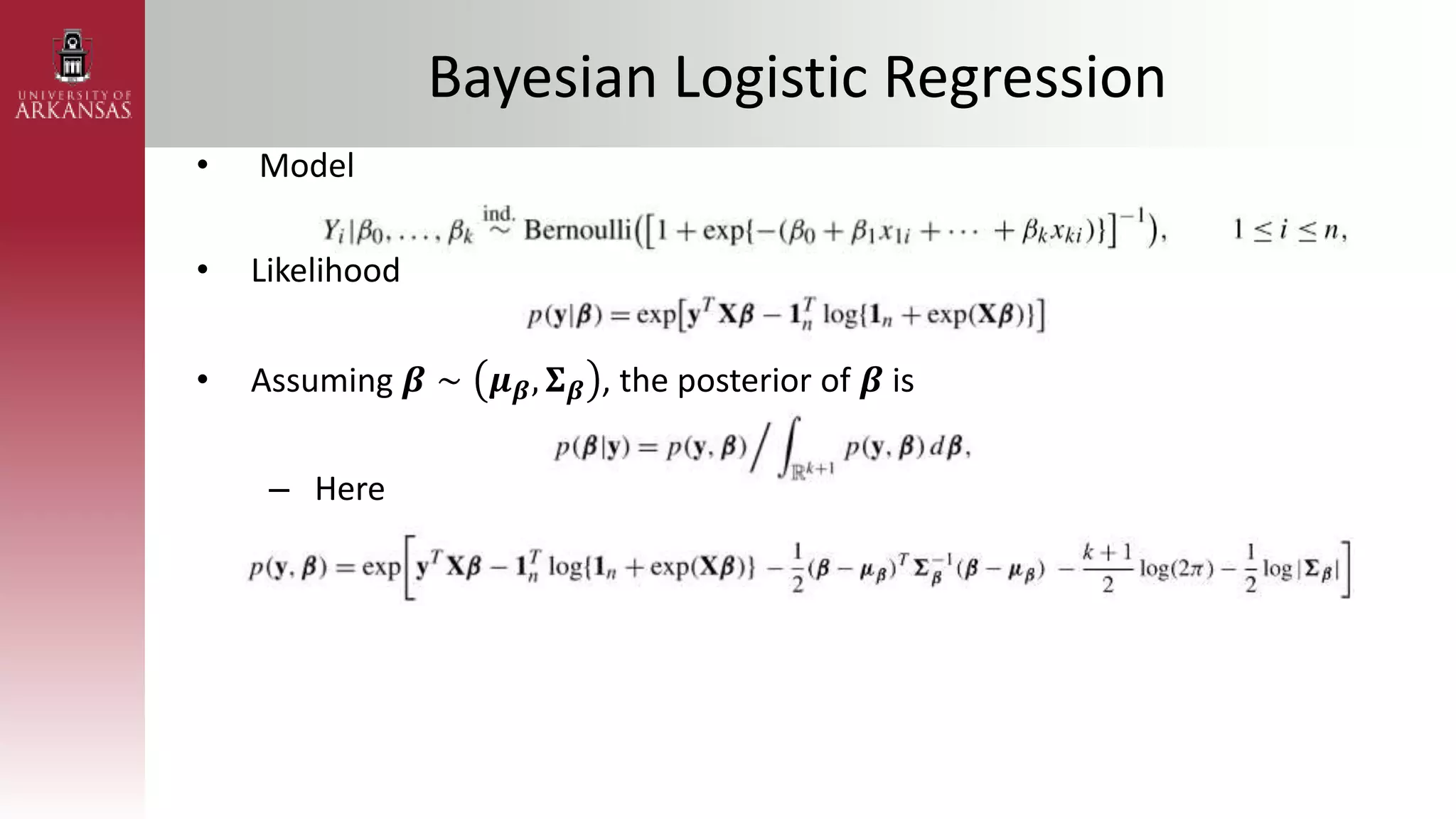
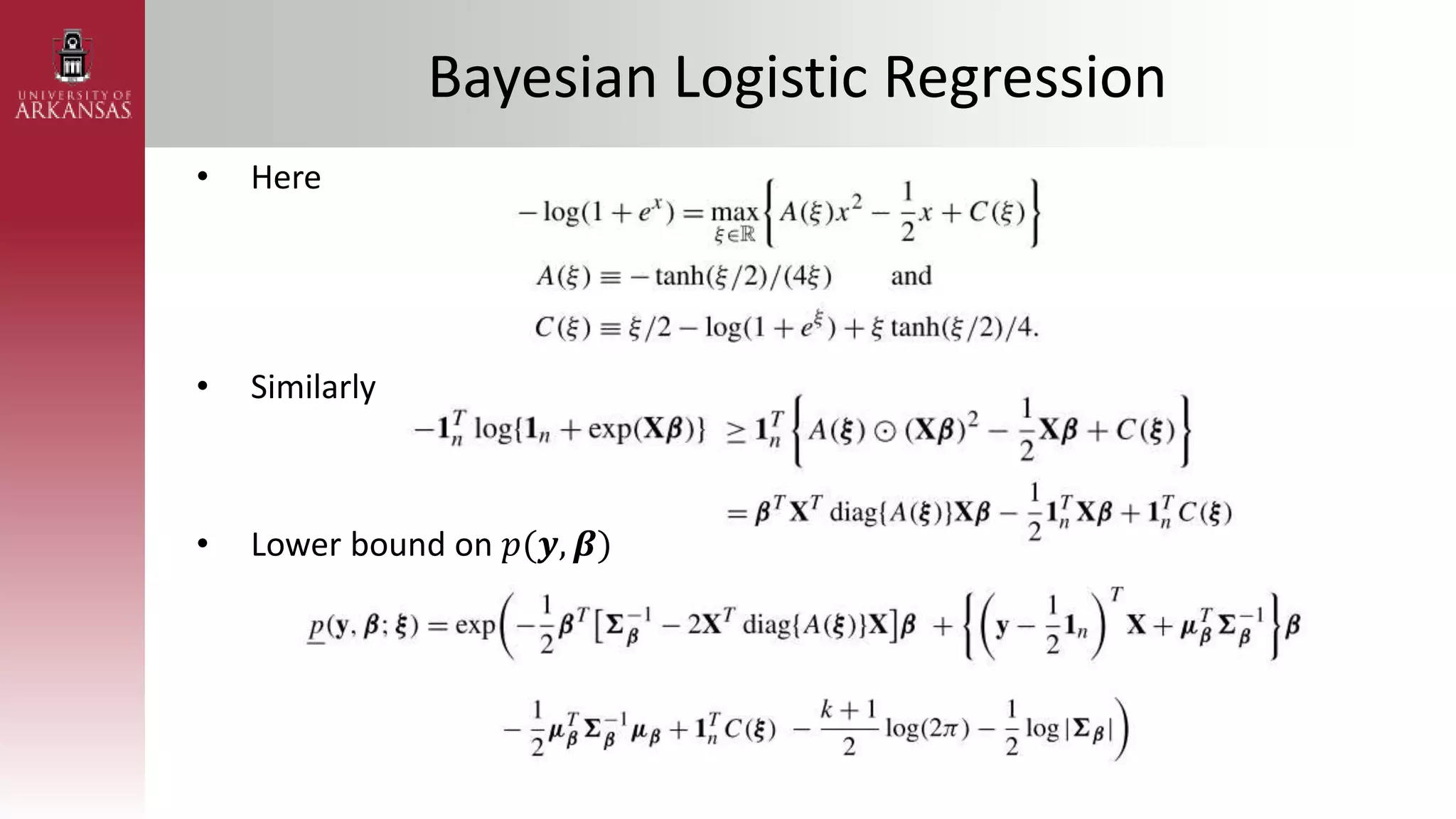
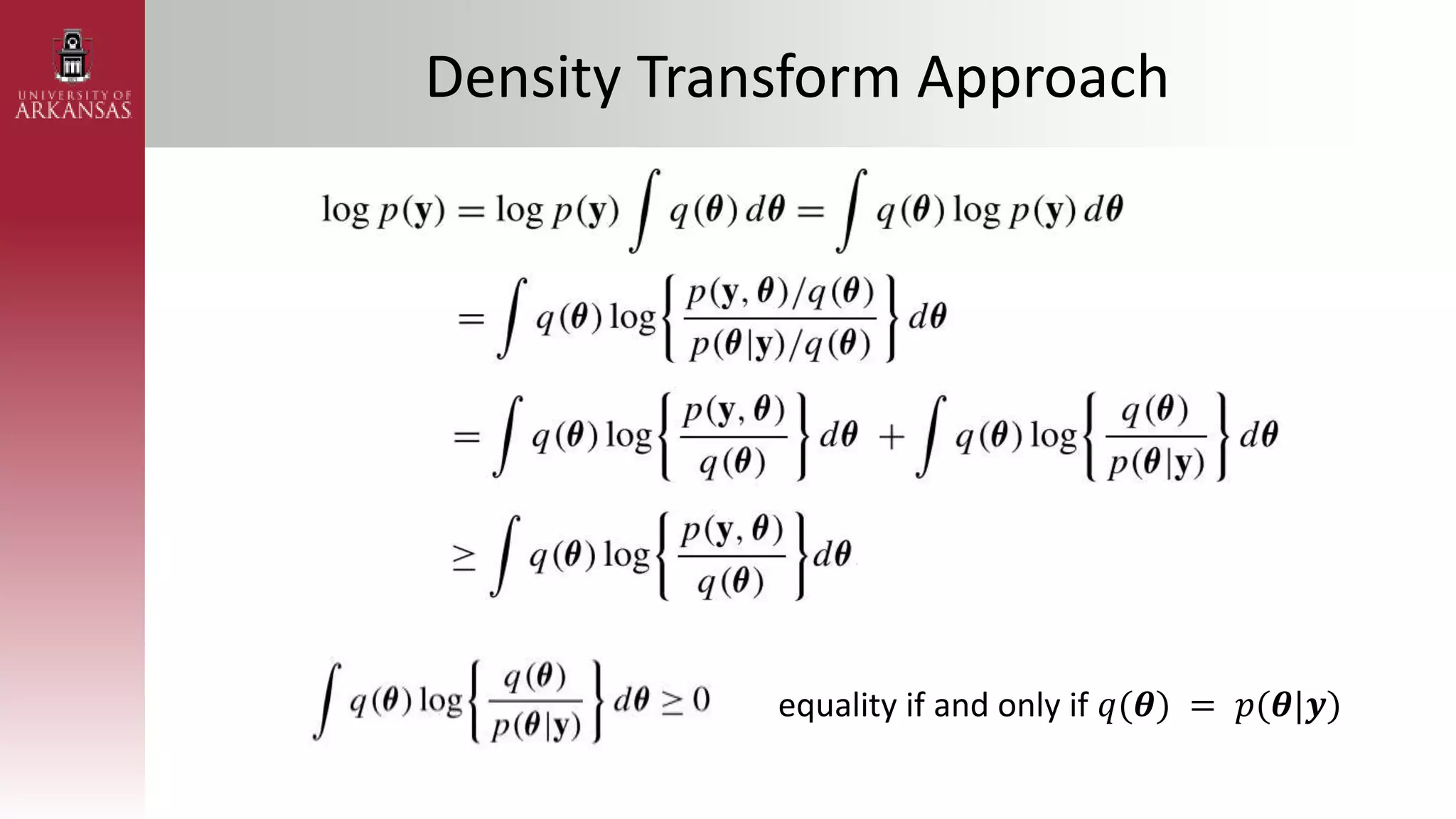
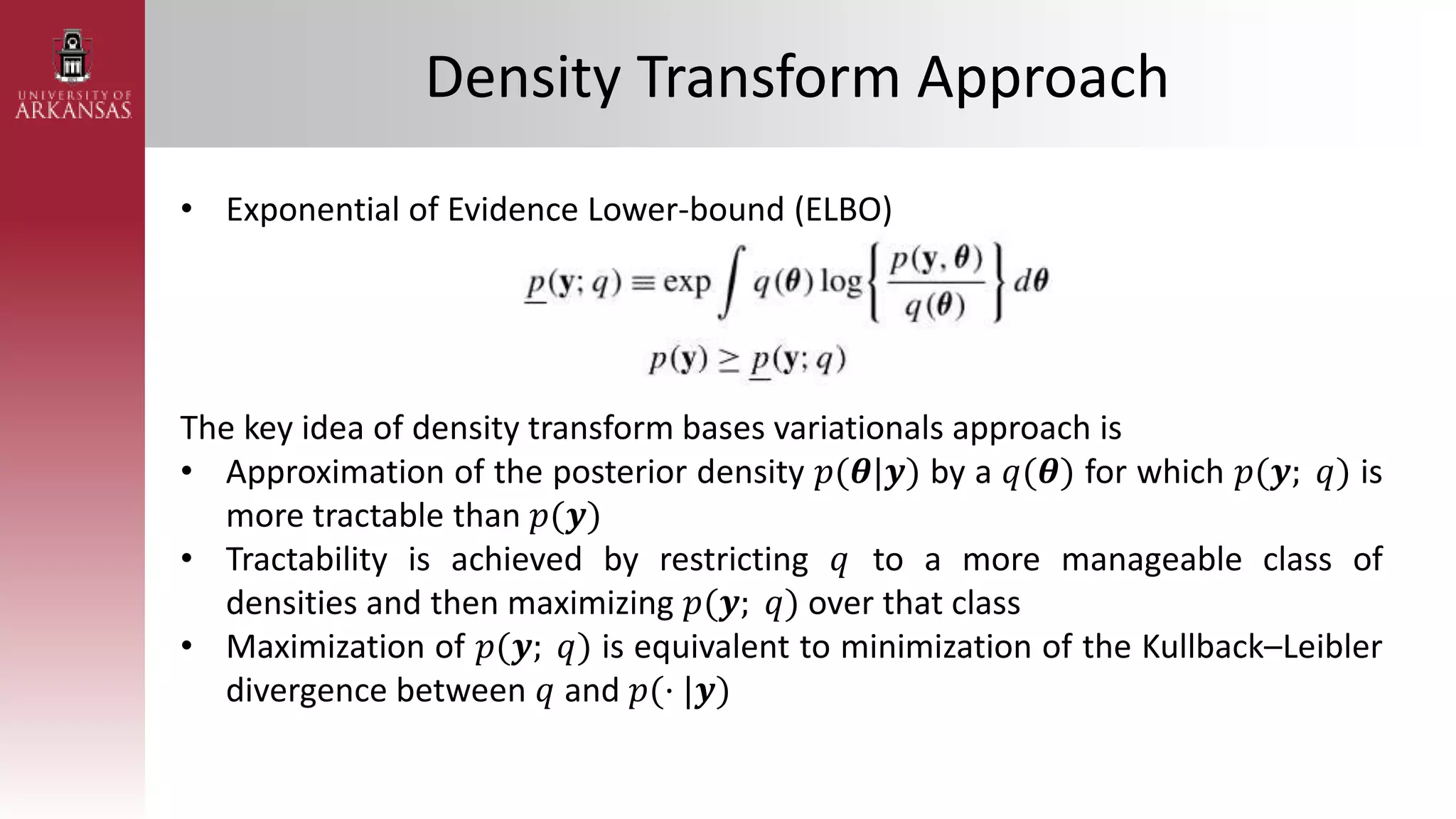
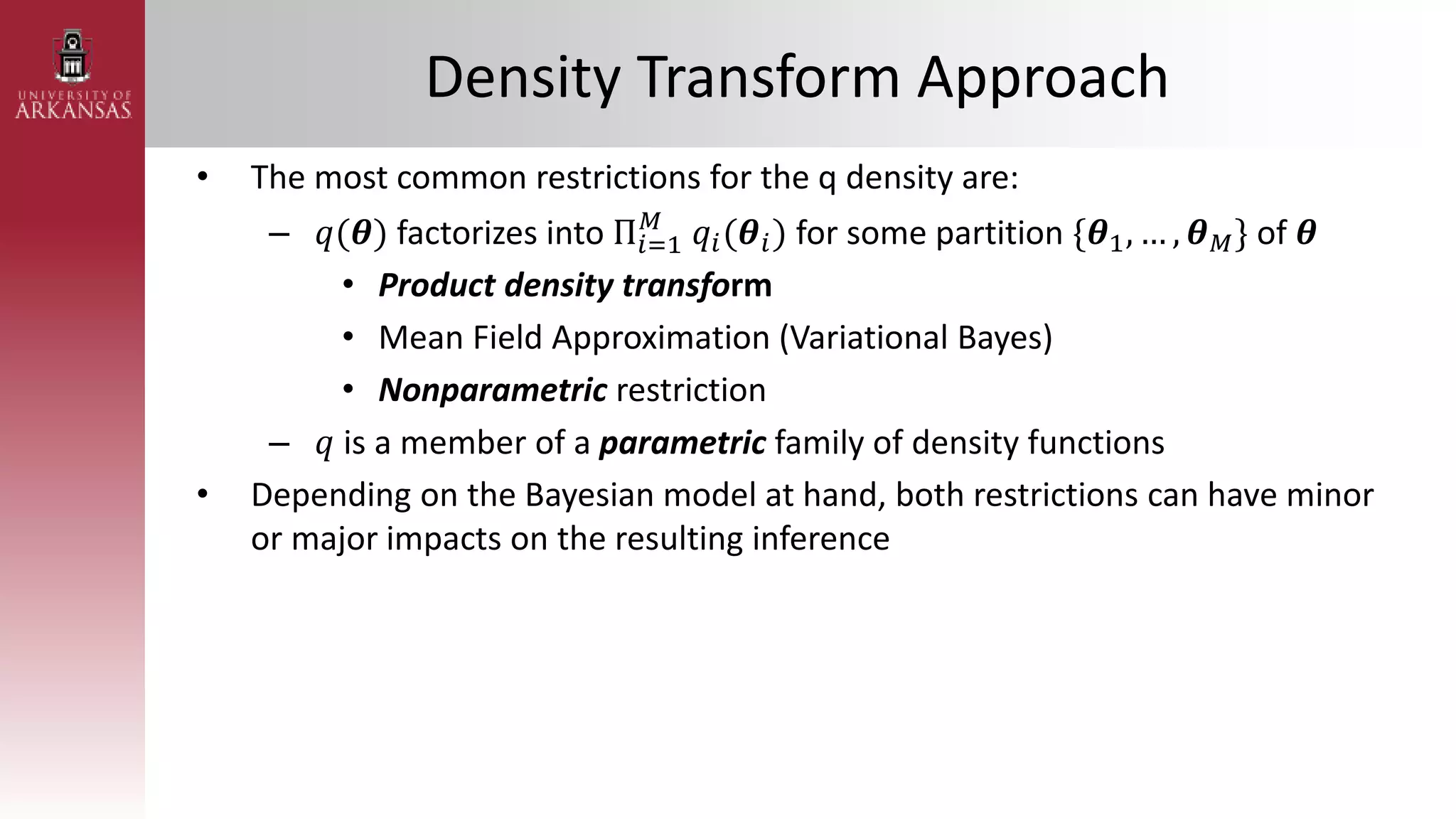
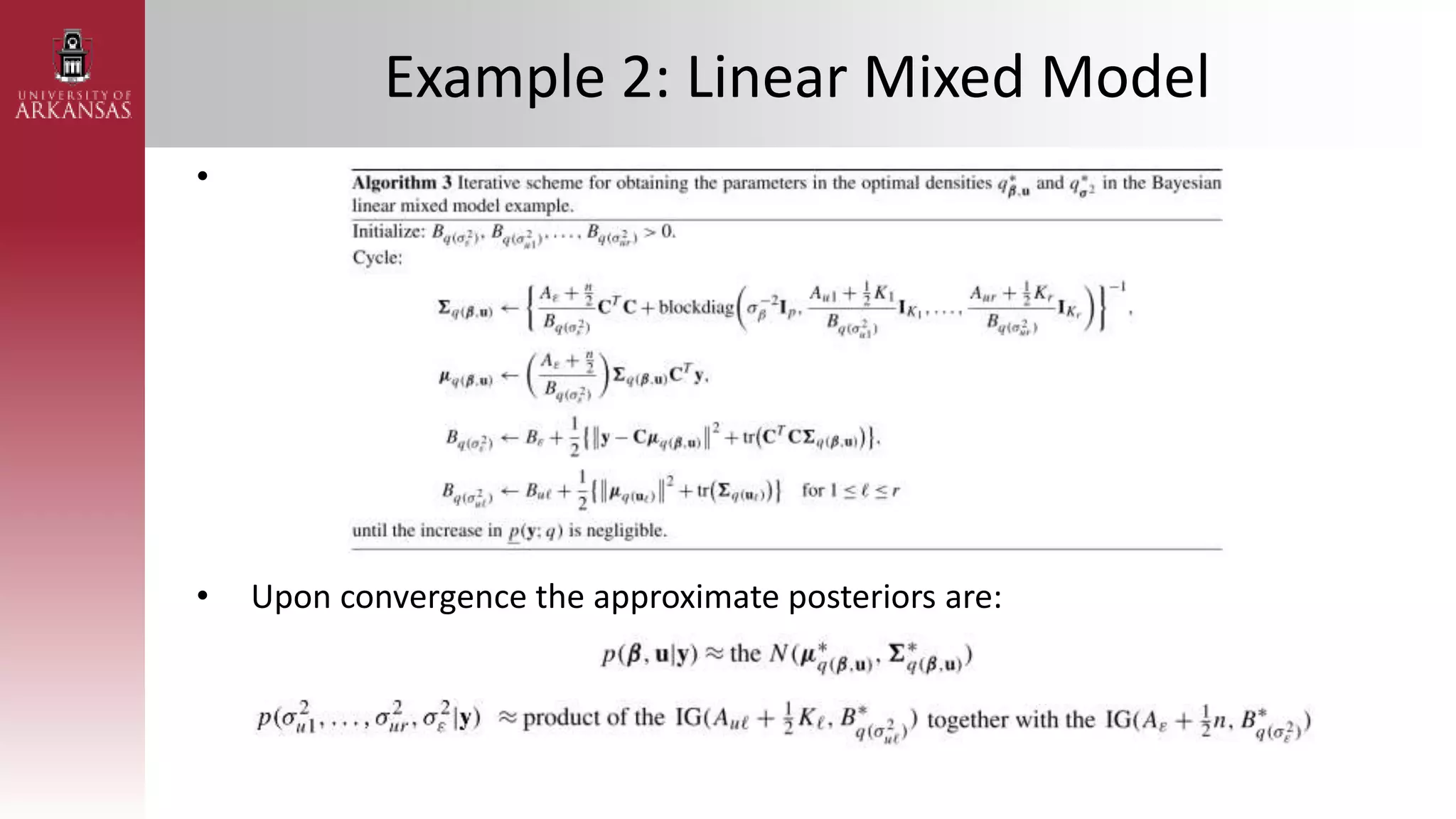
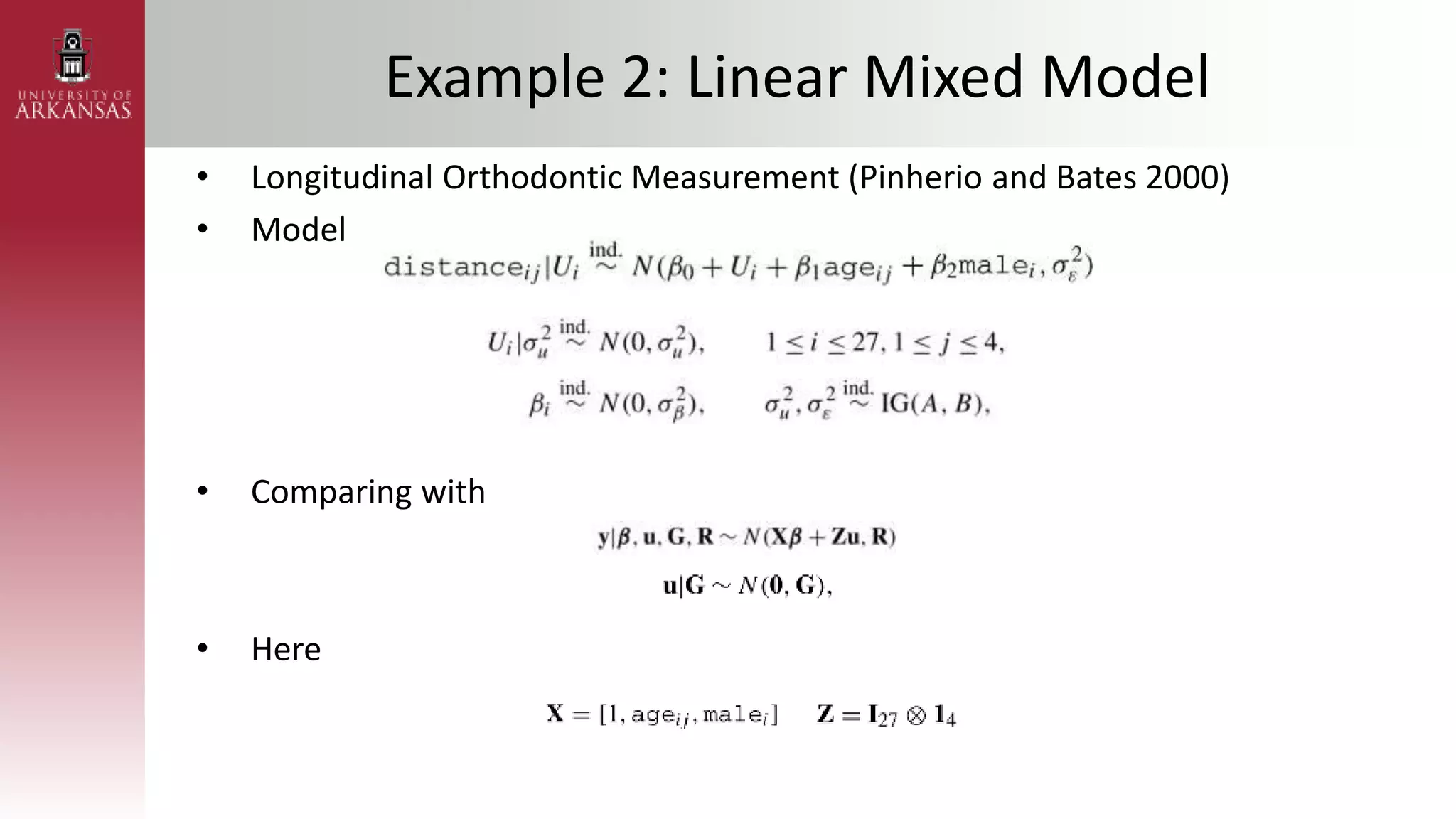
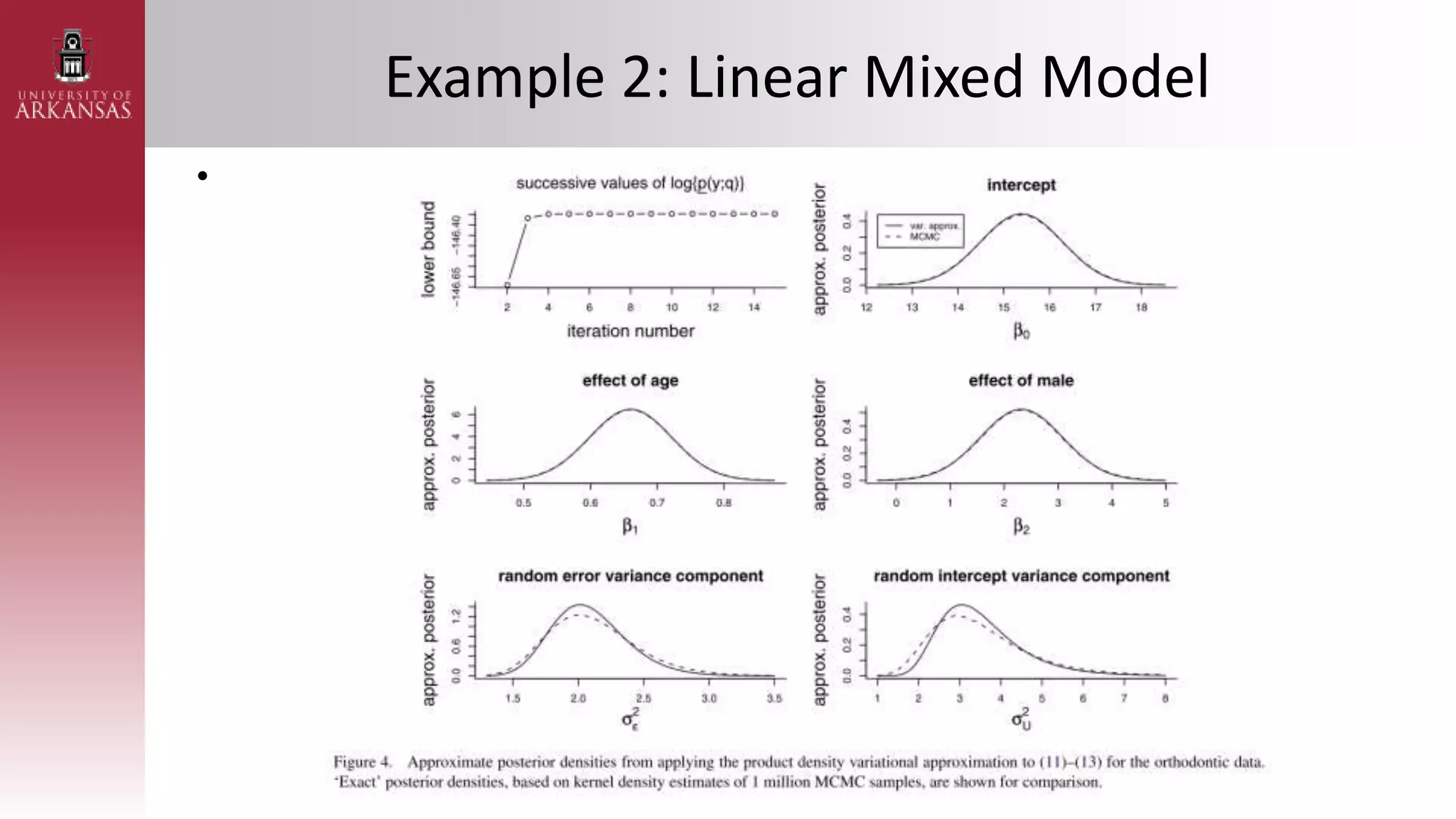
2) Explaining variational approximations, describing the idea, algorithm, and examples of both density transform and tangent transform approaches. Variational approximations provide fast deterministic alternatives to Monte Carlo methods.
3) A question and answer section.





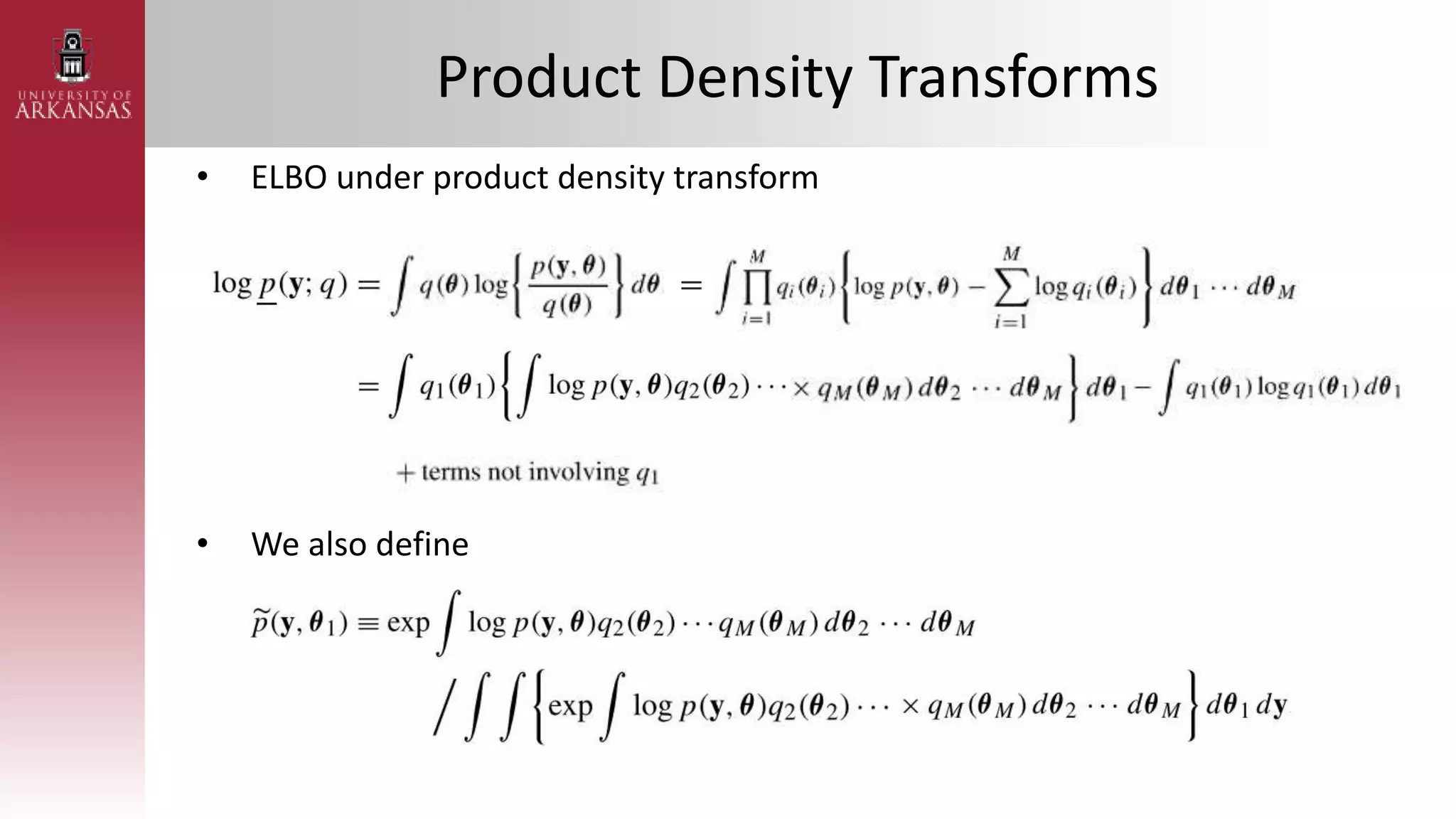
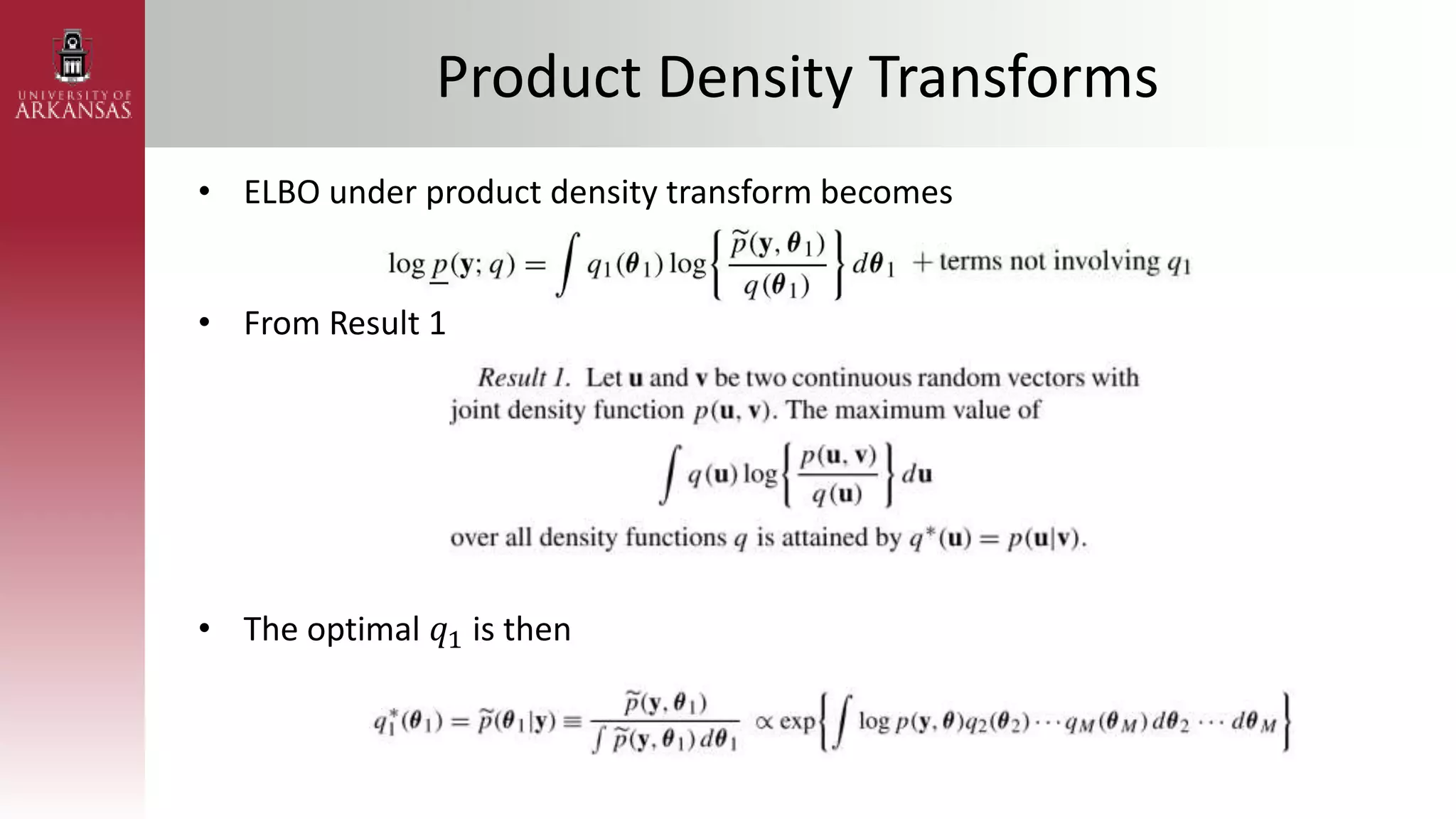
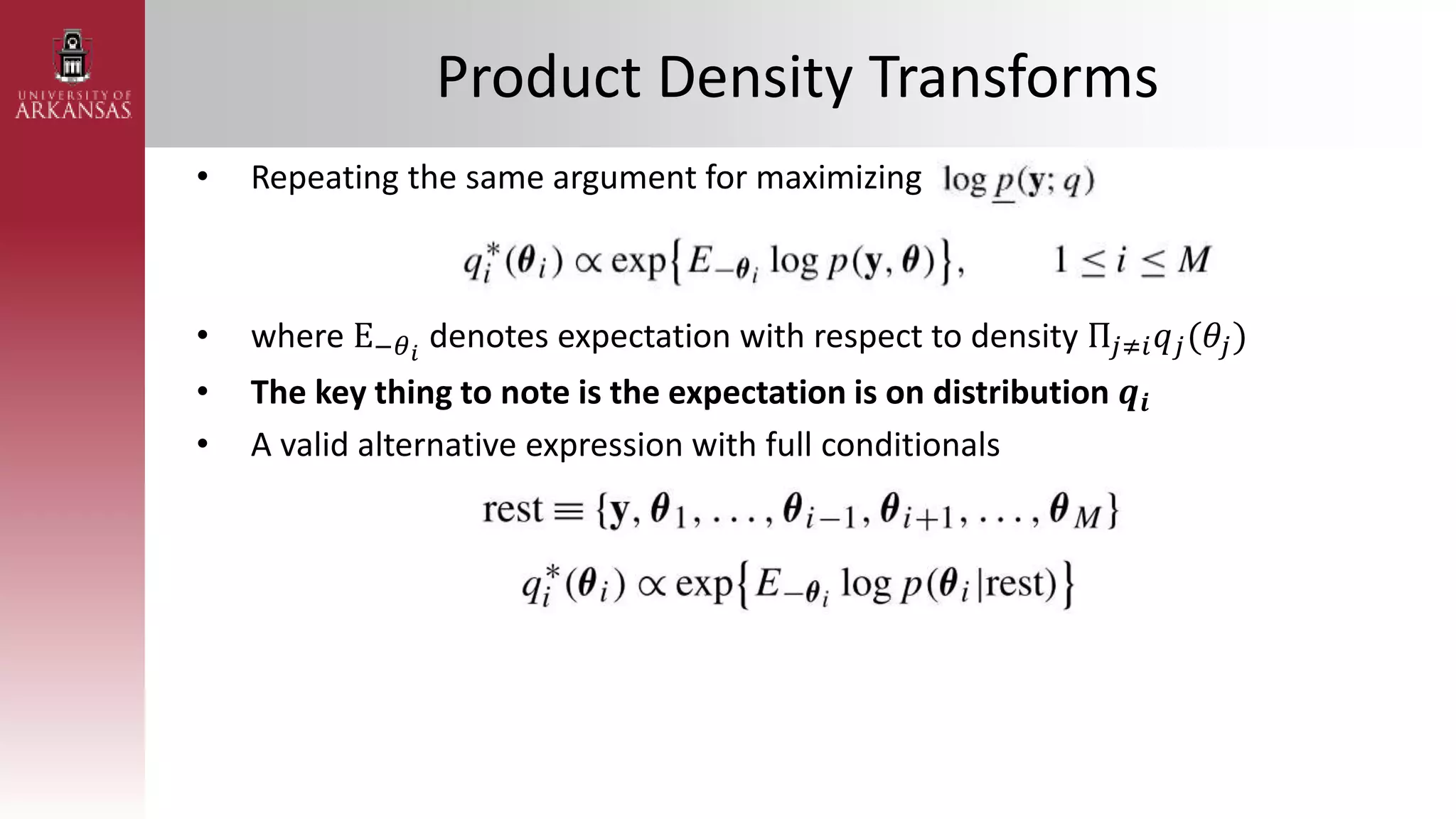
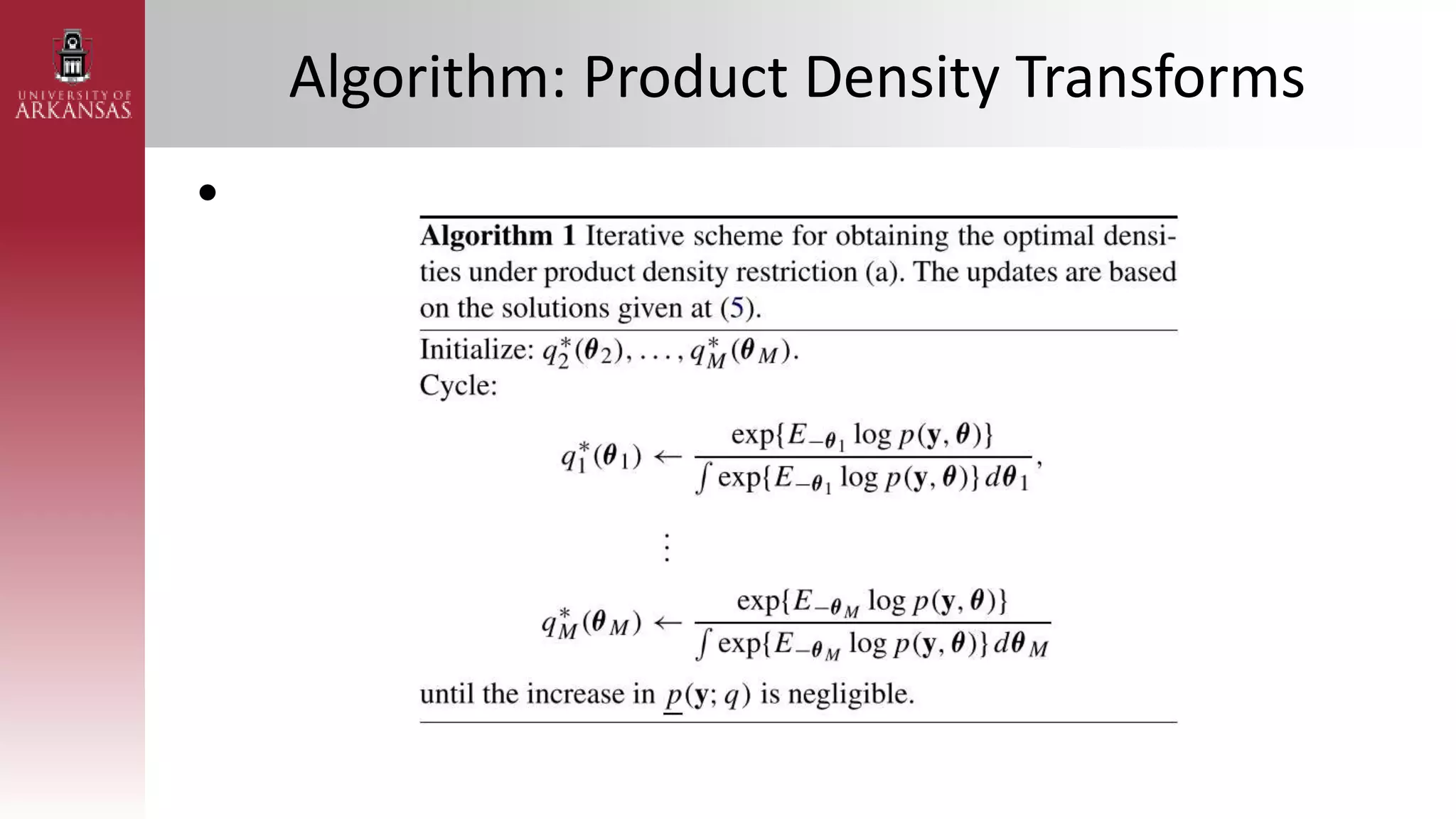


![Parametric Density Transform
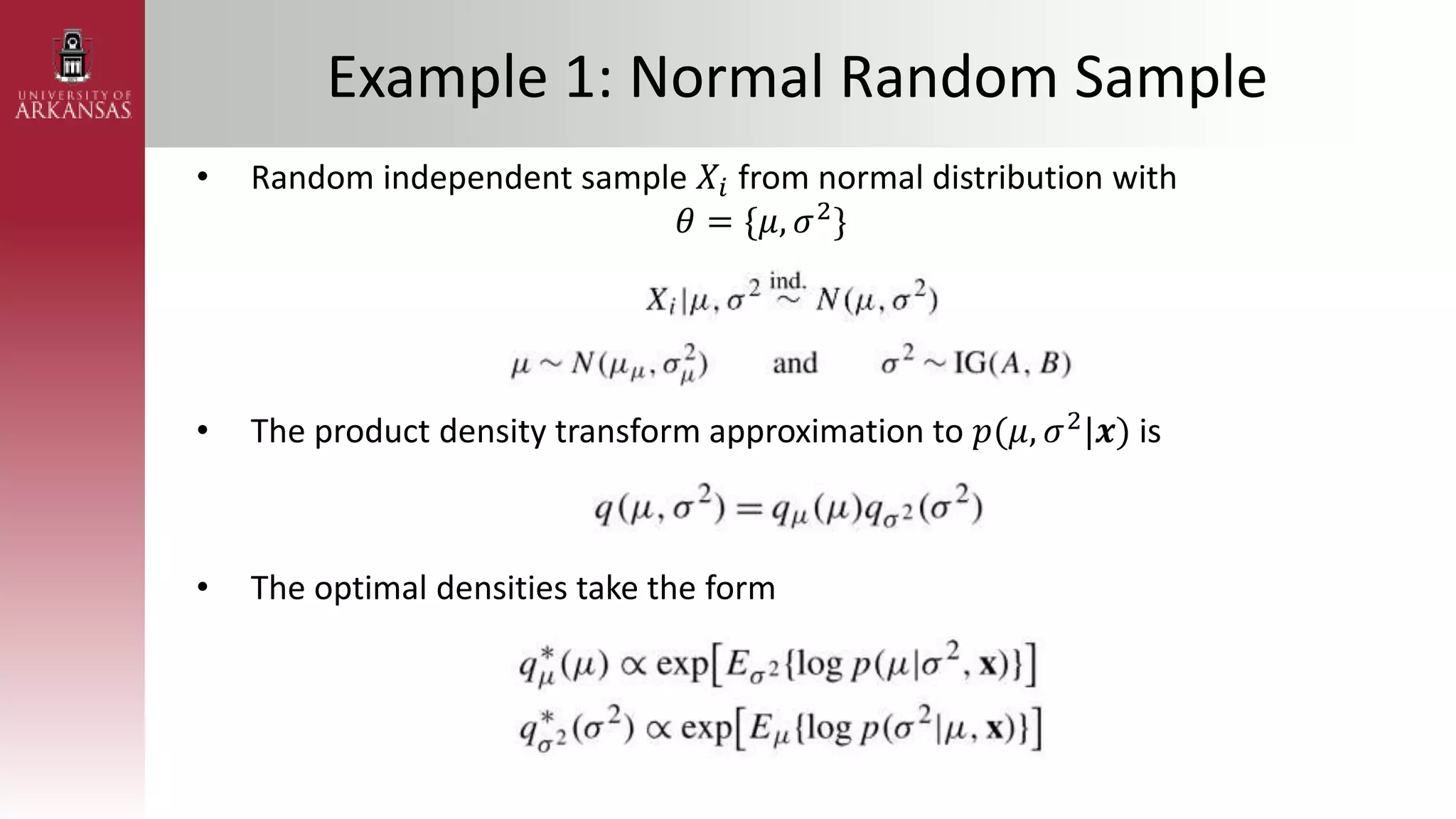
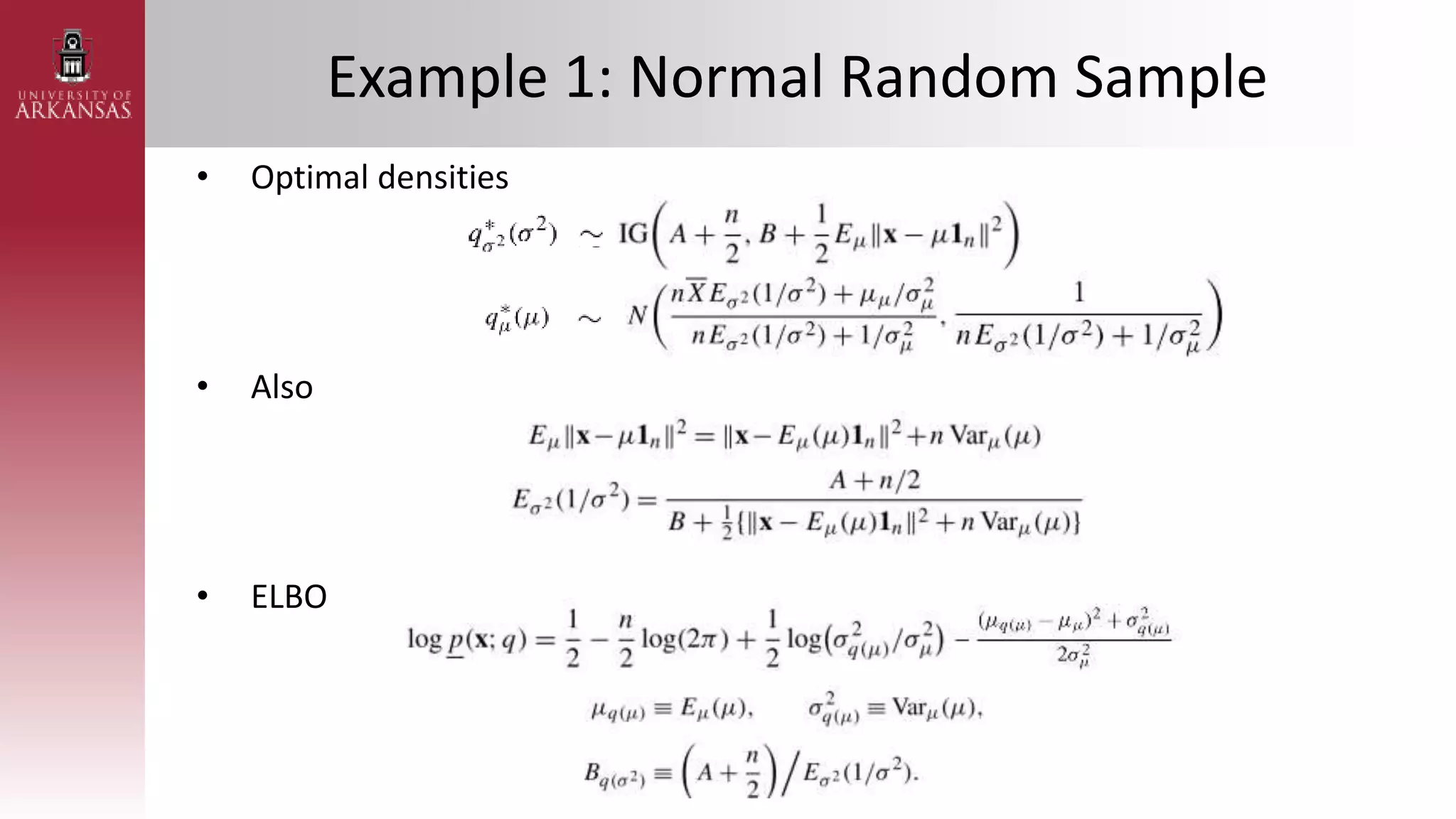
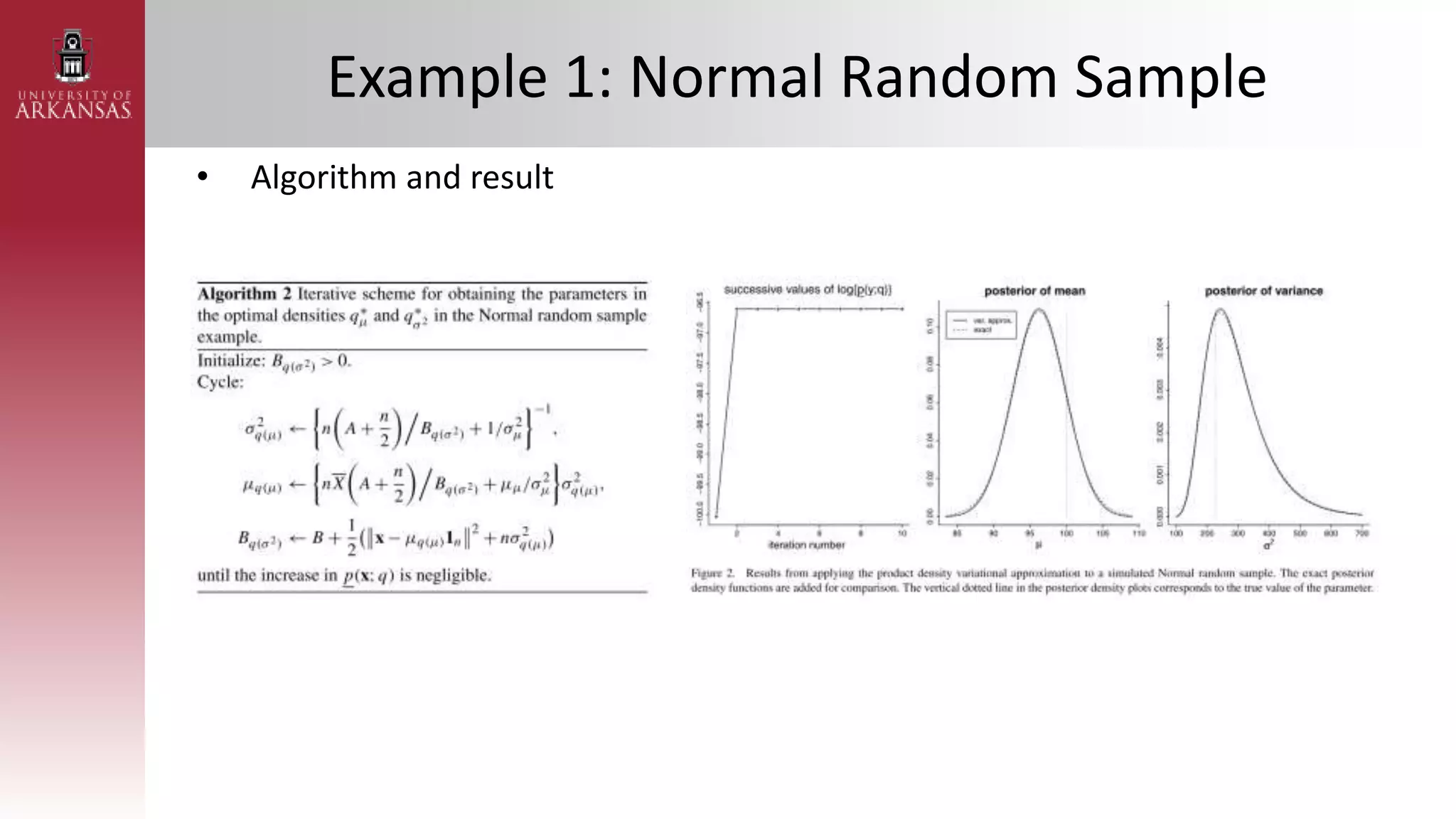
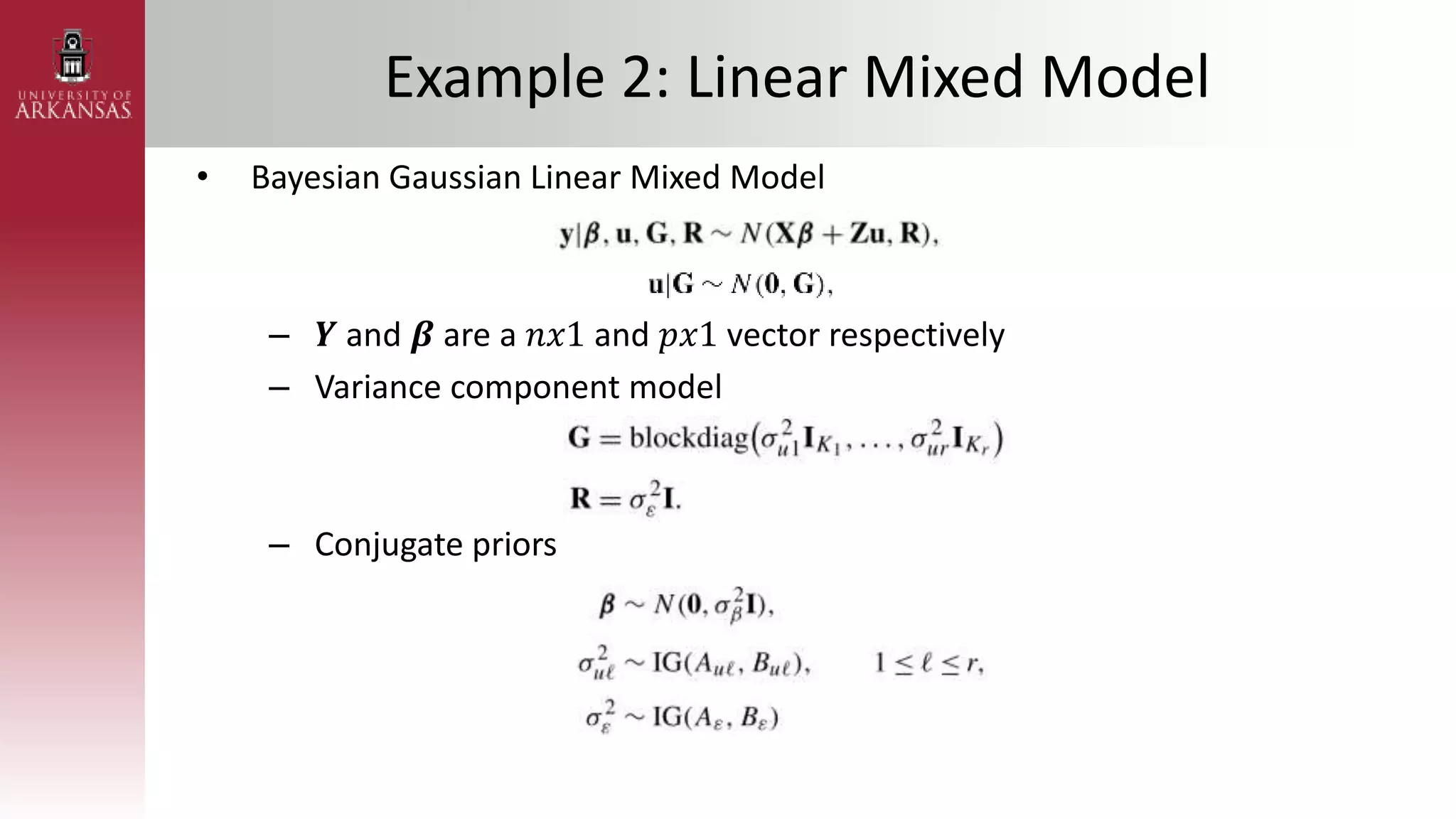
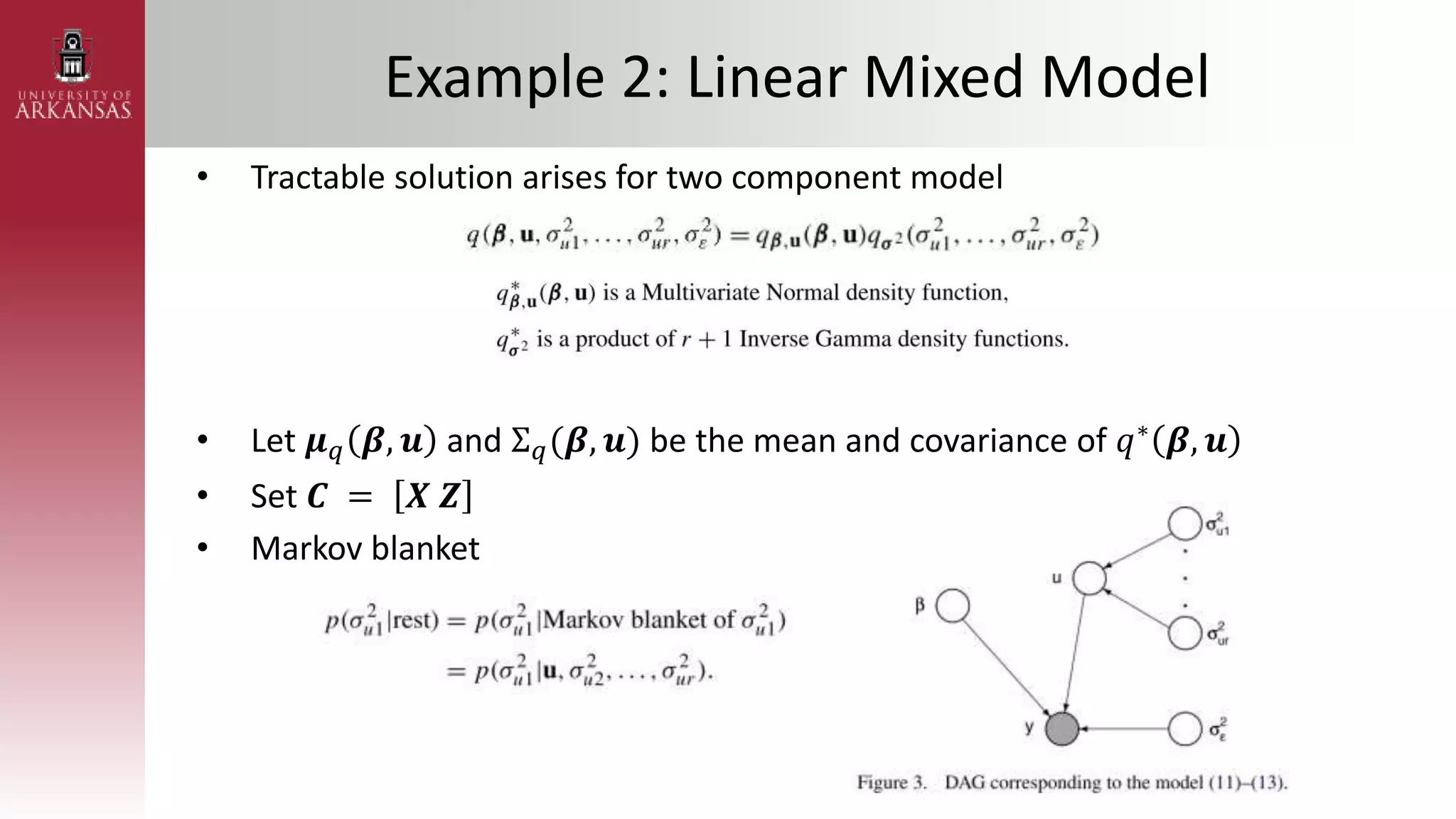
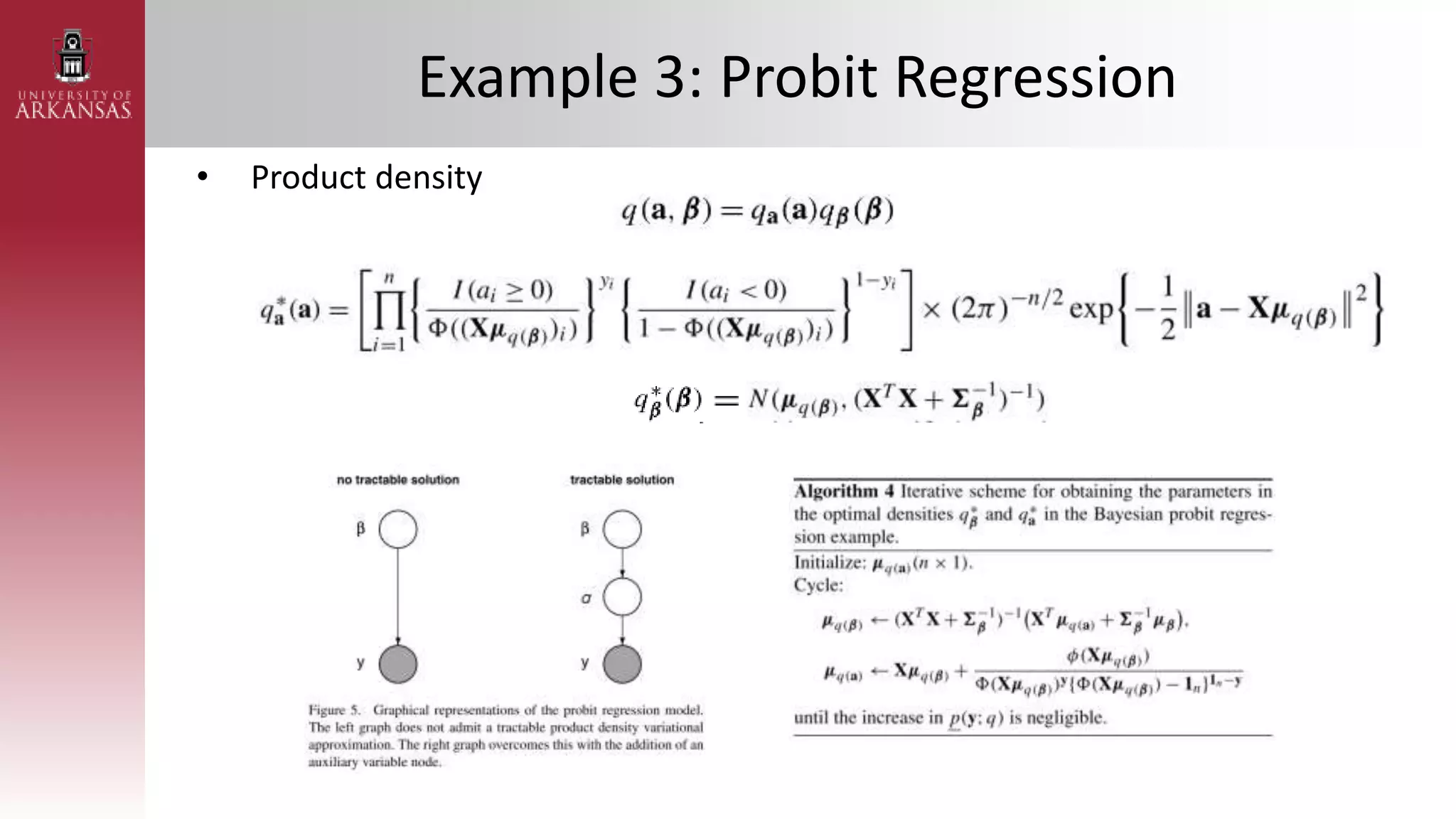
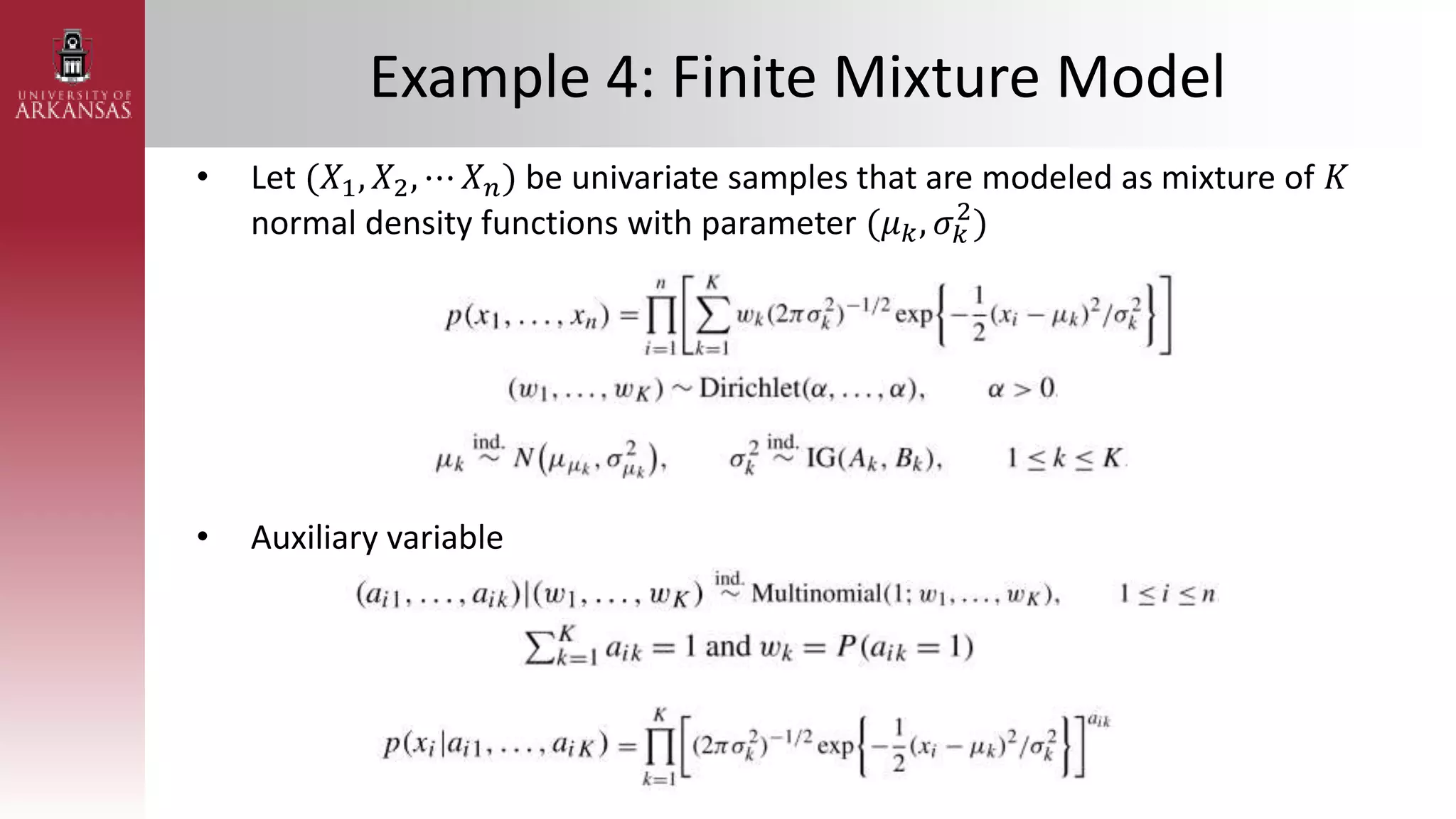
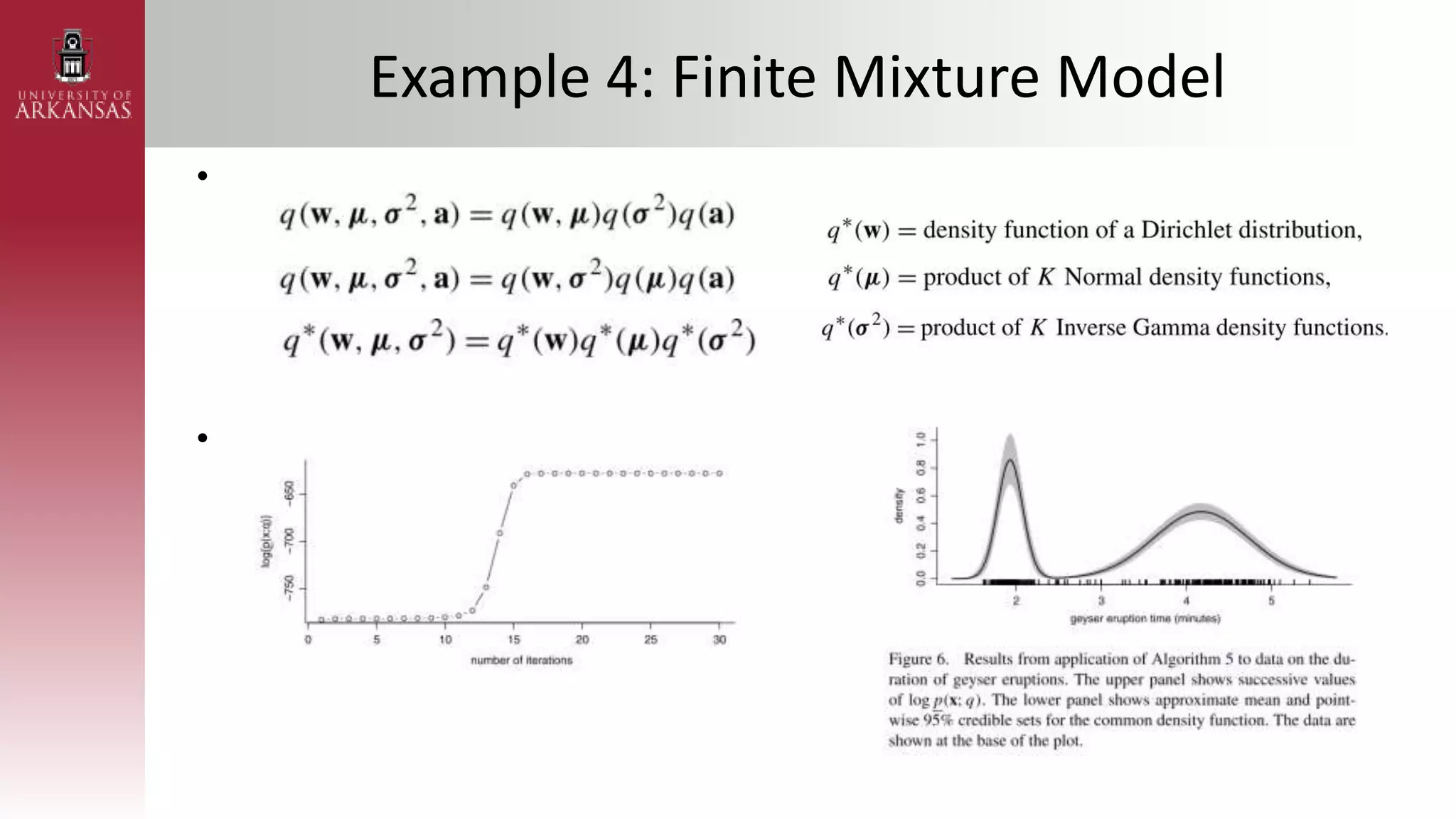
• Poisson Regression with Gaussian Transform
– Assuming 𝜷 ∼ (𝝁𝜷, 𝚺𝜷) and 𝑿 = [1 𝑥1𝑖 ⋯ 𝑥𝑘𝑖]
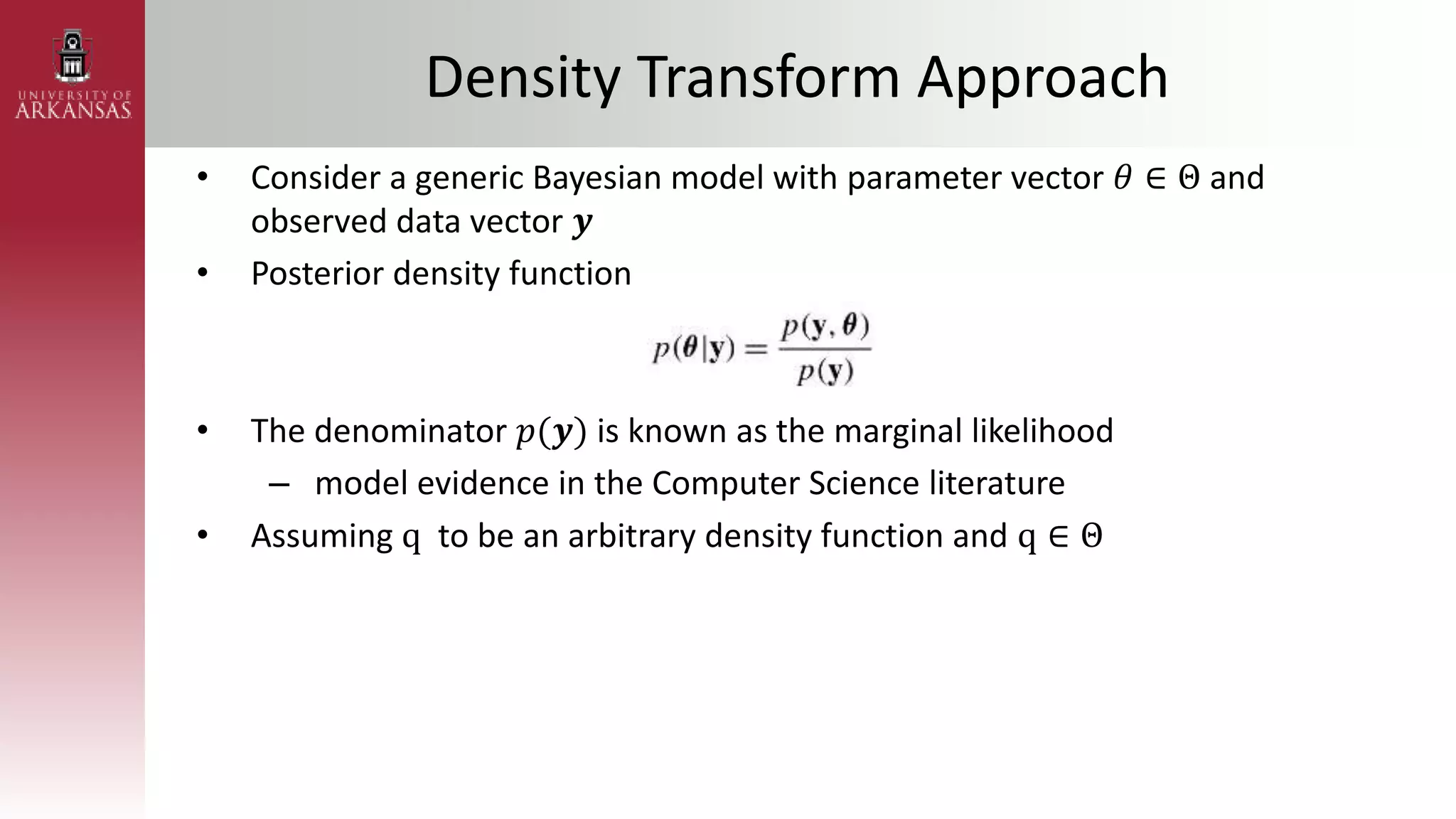
• Likelihood
• Marginal likelihood
• Take the 𝑞 𝛽 = 𝑁(𝝁𝑞 𝛽 , 𝚺𝑞(𝛽)) density](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stanmscompexam-230408162909-3d3d74a8/75/STAN_MS_PPT-pptx-36-2048.jpg)