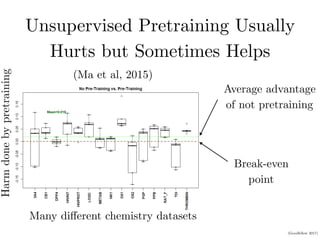
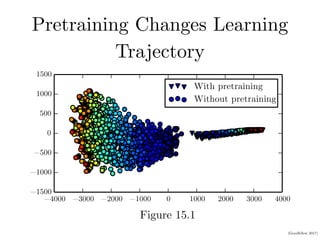
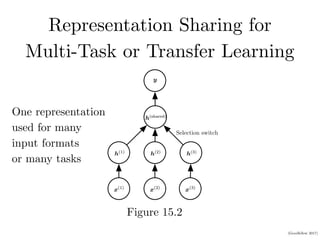
1. Unsupervised pretraining of deep neural networks (DNNs) on multiple datasets usually provides no benefit and sometimes harms performance compared to DNNs trained on individual datasets.
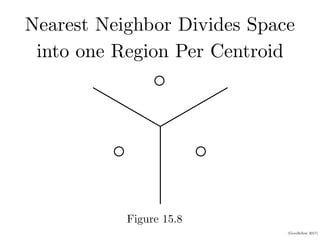
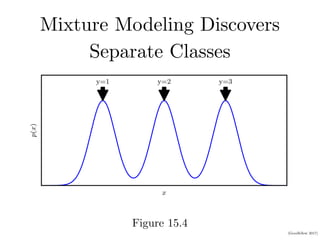
2. Representation learning aims to learn representations of input data that make a task easier by separating explanatory factors of variations. For example, mixture models can discover separate classes in data and distributed representations can divide the input space into uniquely identifiable regions.
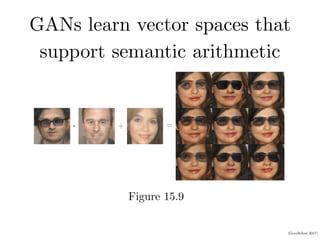
3. Generative adversarial networks (GANs) can learn vector spaces that support semantic operations like representing a woman with glasses by combining vectors for concepts of gender and wearing glasses.


![(Goodfellow 2017)
Binary Distributed Representations Divide
Space Into Many Uniquely Identifiable Regions
CHAPTER 15. REPRESENTATION LEARNING
h1
h2 h3
h = [1, 1, 1]>
h = [0, 1, 1]>
h = [1, 0, 1]>
h = [1, 1, 0]>
h = [0, 1, 0]>
h = [0, 0, 1]>
h = [1, 0, 0]>
Figure 15.7: Illustration of how a learning algorithm based on a distributed representation
breaks up the input space into regions. In this example, there are three binary features
h1, h2, and h3. Each feature is defined by thresholding the output of a learned linear
Figure 15.7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/15representation-220330233744/85/15_representation-pdf-9-320.jpg)
![(Goodfellow 2017)
Binary Distributed Representations Divide
Space Into Many Uniquely Identifiable Regions
CHAPTER 15. REPRESENTATION LEARNING
h1
h2 h3
h = [1, 1, 1]>
h = [0, 1, 1]>
h = [1, 0, 1]>
h = [1, 1, 0]>
h = [0, 1, 0]>
h = [0, 0, 1]>
h = [1, 0, 0]>
Figure 15.7: Illustration of how a learning algorithm based on a distributed representation
breaks up the input space into regions. In this example, there are three binary features
h1, h2, and h3. Each feature is defined by thresholding the output of a learned linear
Figure 15.7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/15representation-220330233744/85/15_representation-pdf-10-320.jpg)