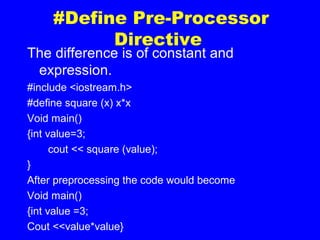
1. The document discusses different ways of creating custom data types in C++, including classes, structures, unions, enumerations, and typedef. Structures are collections of variables that can be referenced under one name.
2. Technically, there is no difference between a structure and a class in C++ - structures are classes with members that are public by default, while classes have private members by default.
3. Structures allow logically related elements to be treated as a single unit, for example to store student information. Arrays can contain elements of a structure type.
![WEL COME
PRAVEEN M JIGAJINNI
PGT (Computer Science)
MCA, MSc[IT], MTech[IT],MPhil (Comp.Sci), PGDCA, ADCA,
Dc. Sc. & Engg.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/13structures-150410073234-conversion-gate01/75/Structures-1-2048.jpg)















![ARRAYS OF STRUCTURE
An array can contain similar elements,the
combination having structures within an array is
an array of structure .To declare an structure tou
must define a structure and then declare an
array variable of that type.
To declare a 100 element array of structure of type
addr men_addr [100] ;
To access a specific structure ex . to print houseno of structure 8
write
cout << mem_add [7].houseno ;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/13structures-150410073234-conversion-gate01/85/Structures-18-320.jpg)