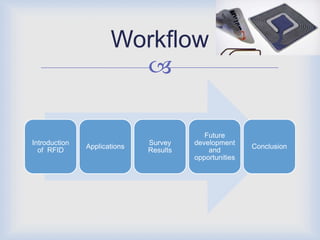
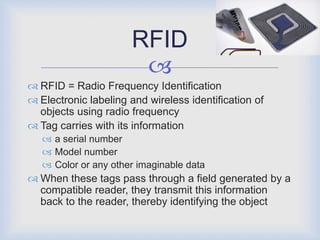
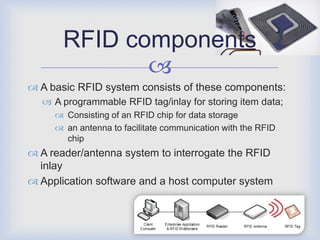
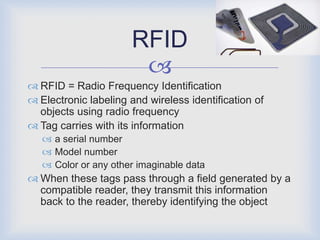
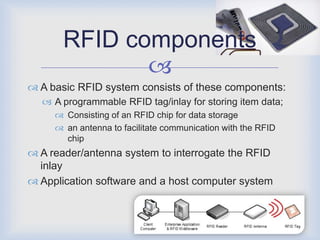
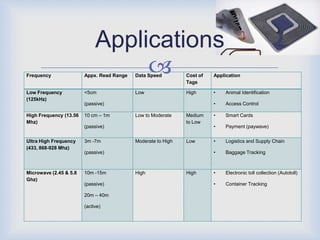
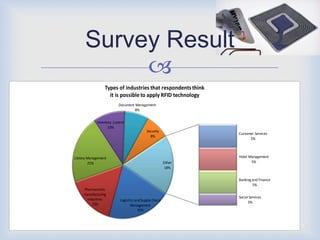
RFID technology has many promising applications. Overall, respondents were positive about RFID's potential. Most saw opportunities in inventory control, logistics/supply chain management and library management. Some concerns remain around cost and standardization, but further development is expected in medical uses and other industries. With refinements, RFID may provide significant benefits for tracking, access control and customer services.