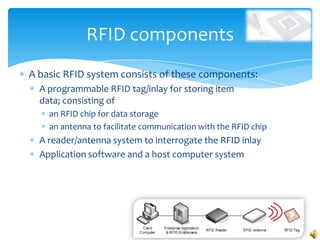
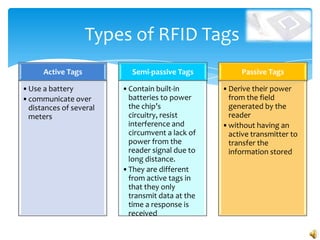
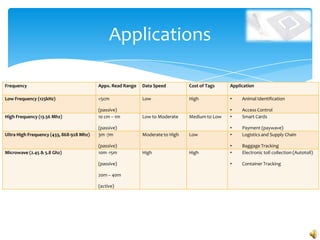
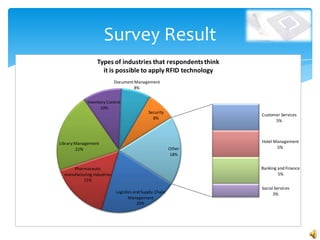
RFID technology uses radio waves to electronically identify objects. It consists of tags that carry data, readers that can interrogate tags, and software. There are active, semi-passive, and passive tags. Common applications include credit cards, toll collection, access control, and supply chain management. A survey found the most common potential applications were in document, library, and logistics management. Further development opportunities exist in medical and library uses. While RFID provides benefits over barcodes, limitations include potential high costs and signal interference from some materials.