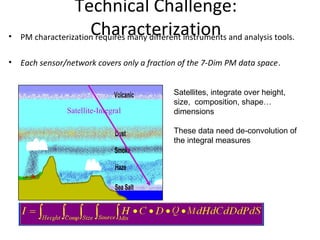
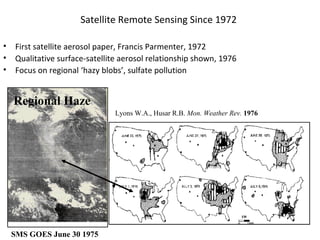
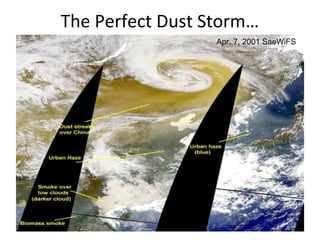
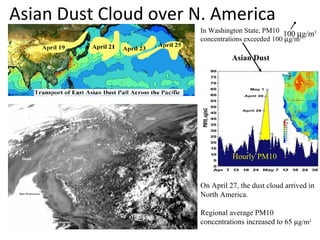
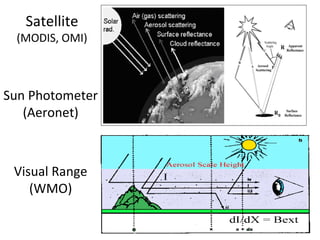
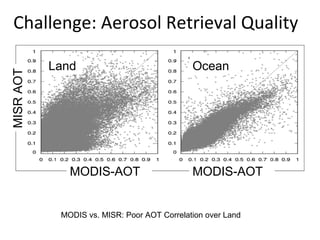
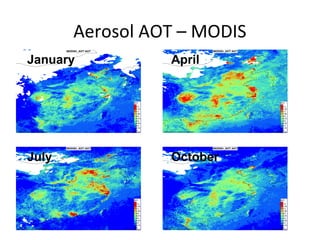
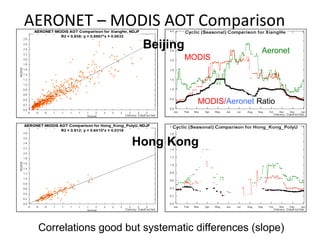
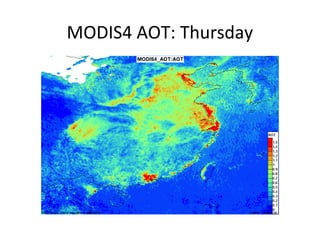
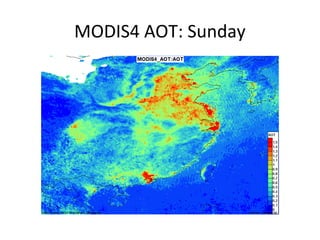
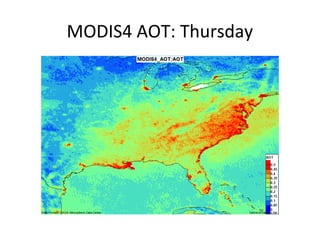
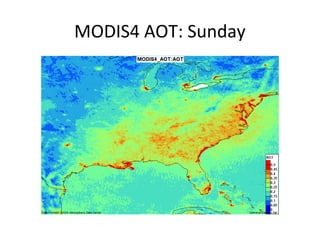
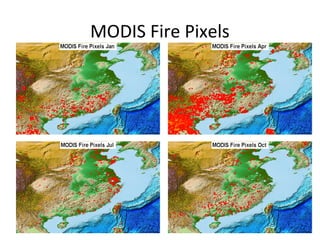
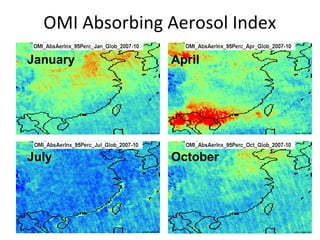
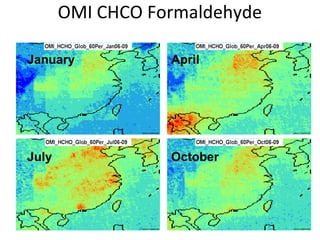
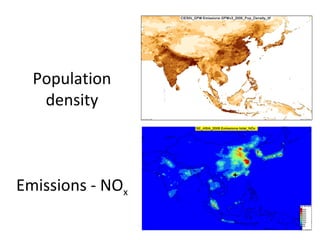
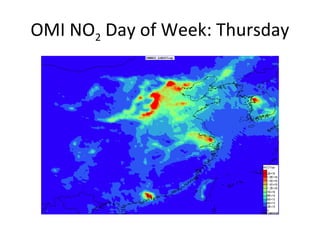
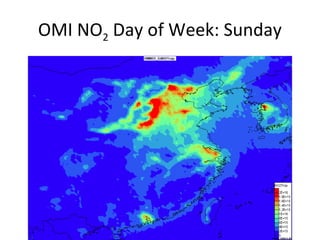
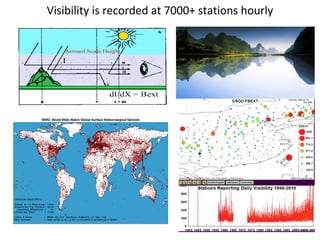
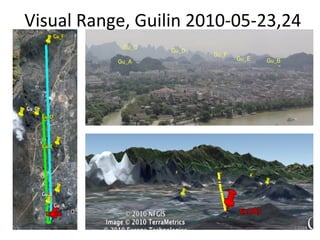
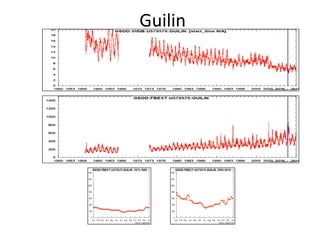
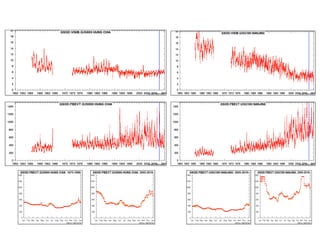
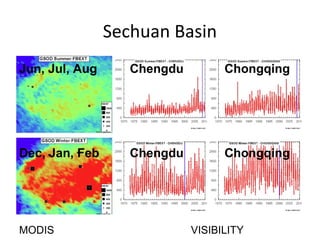
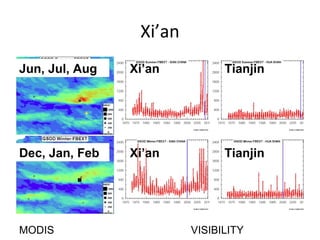
This document discusses the challenges of characterizing air pollution using remote sensing observations over China. It describes the seven dimensions of data - spatial, height, time, particle size, composition, shape, and mixing - needed to fully characterize air pollution. While each individual observation method or data set has limitations, together they can provide consistent global-scale observations. There remain significant challenges to integrating data from multiple sensors to accurately measure air pollution. International collaboration combining global satellite data with detailed local observations in China may help advance progress in addressing this issue.