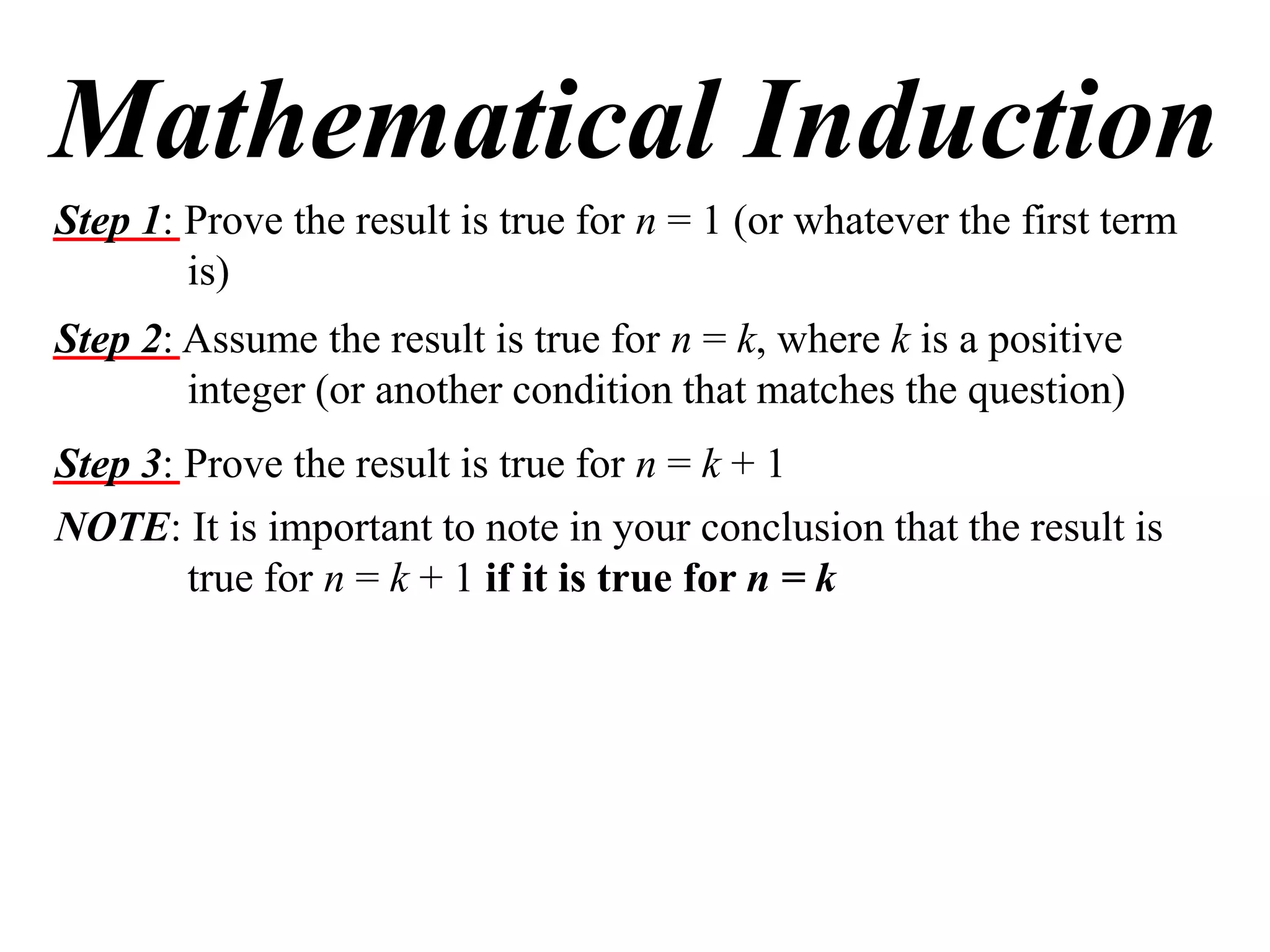
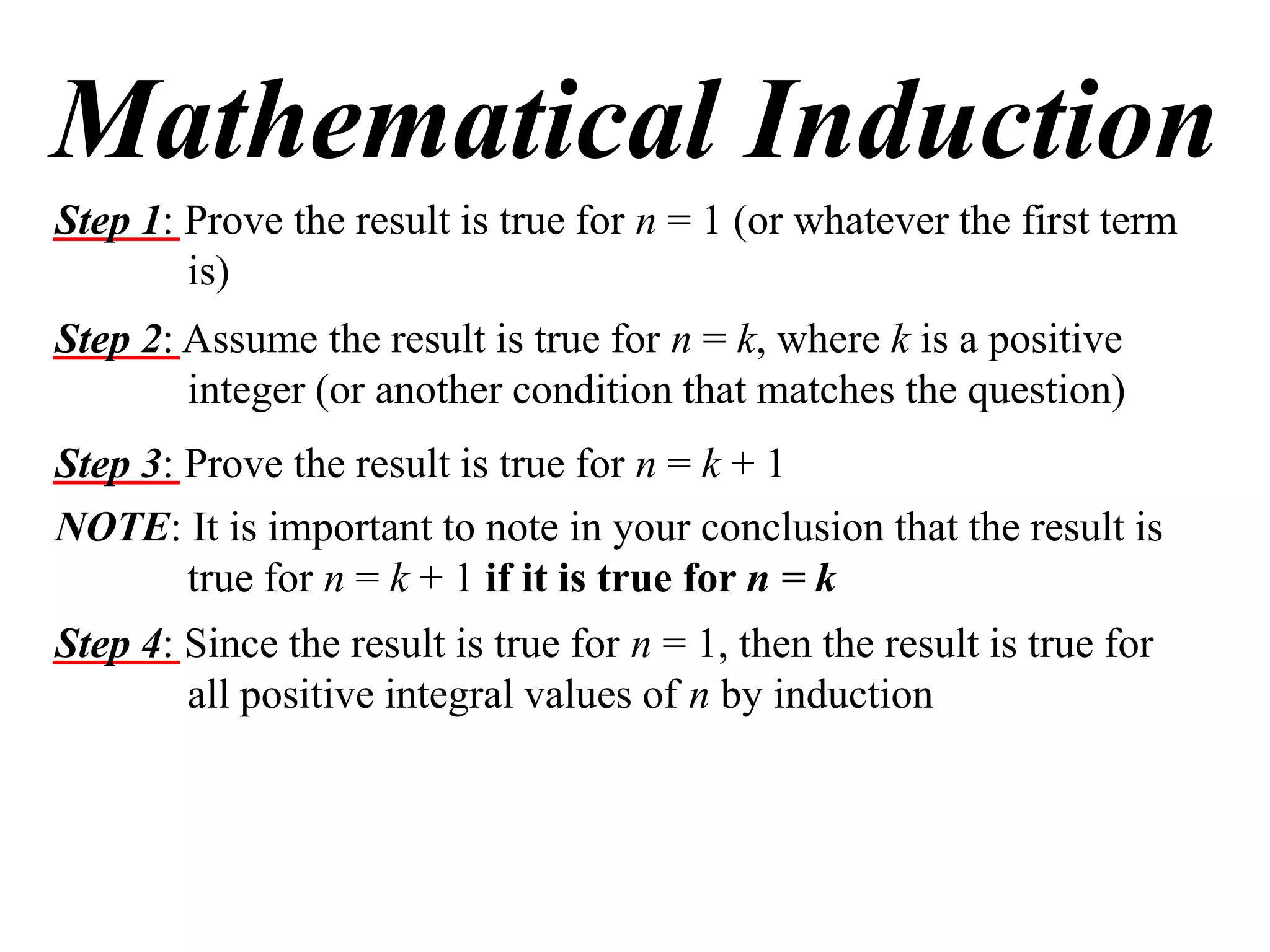
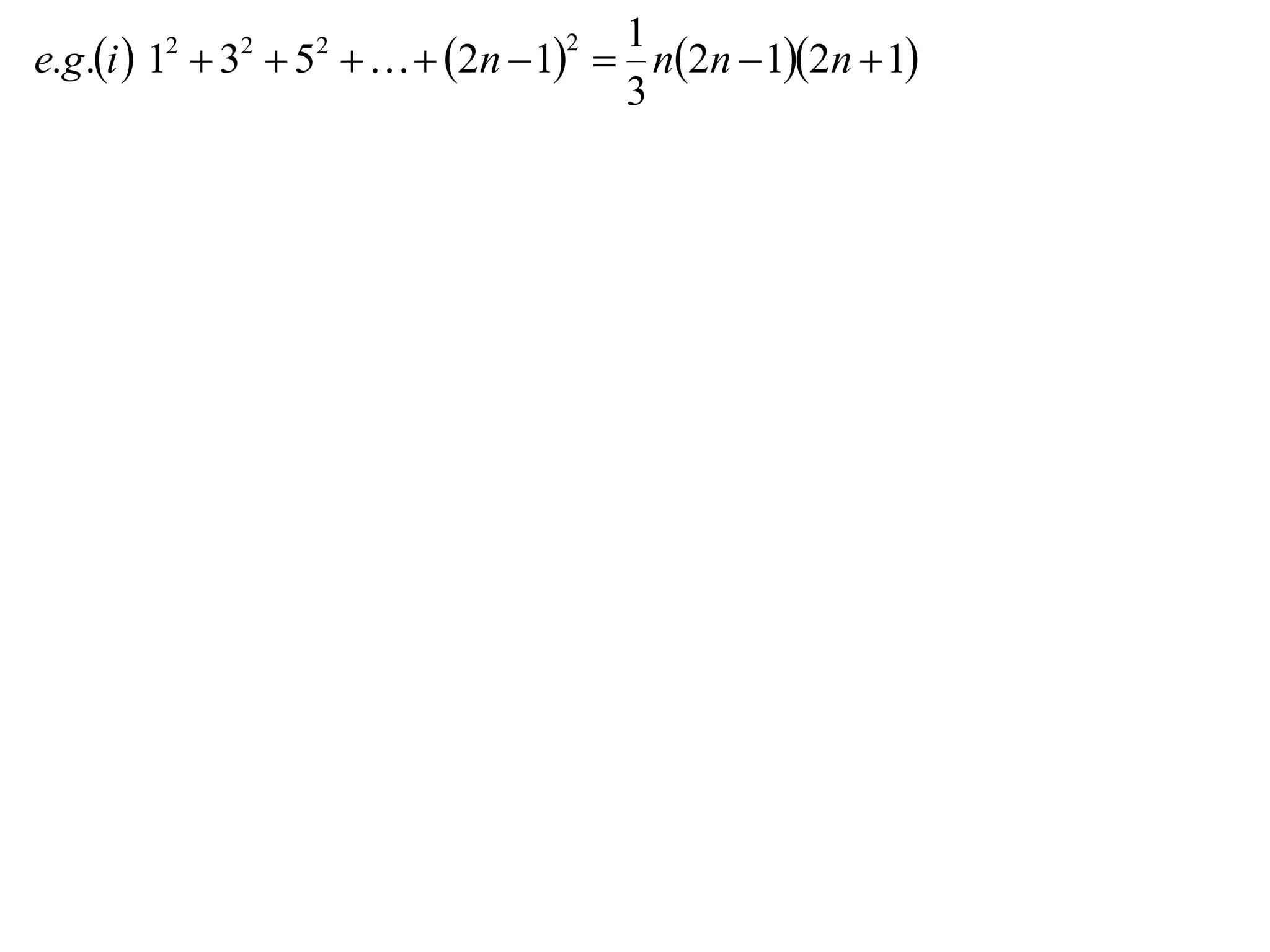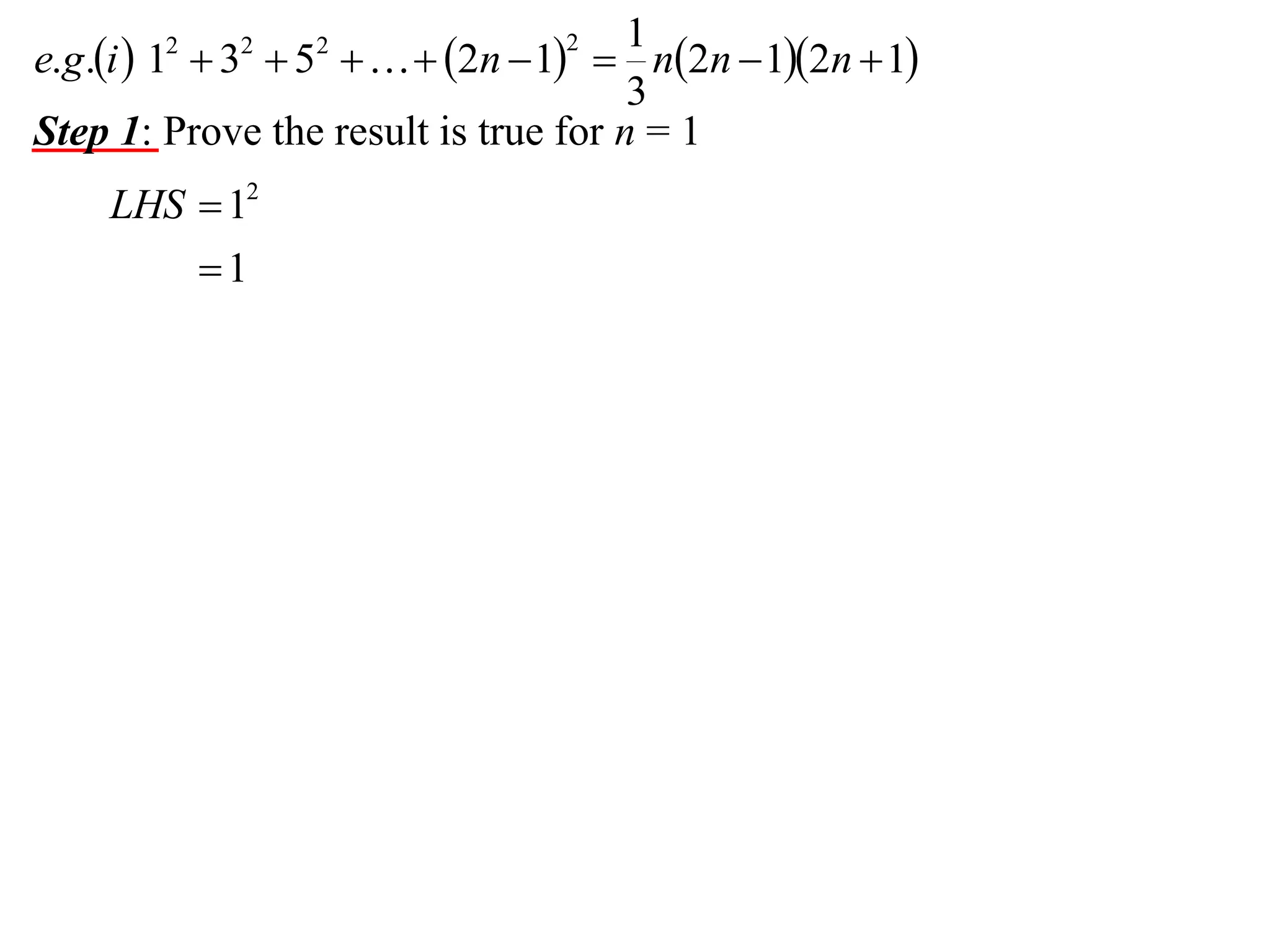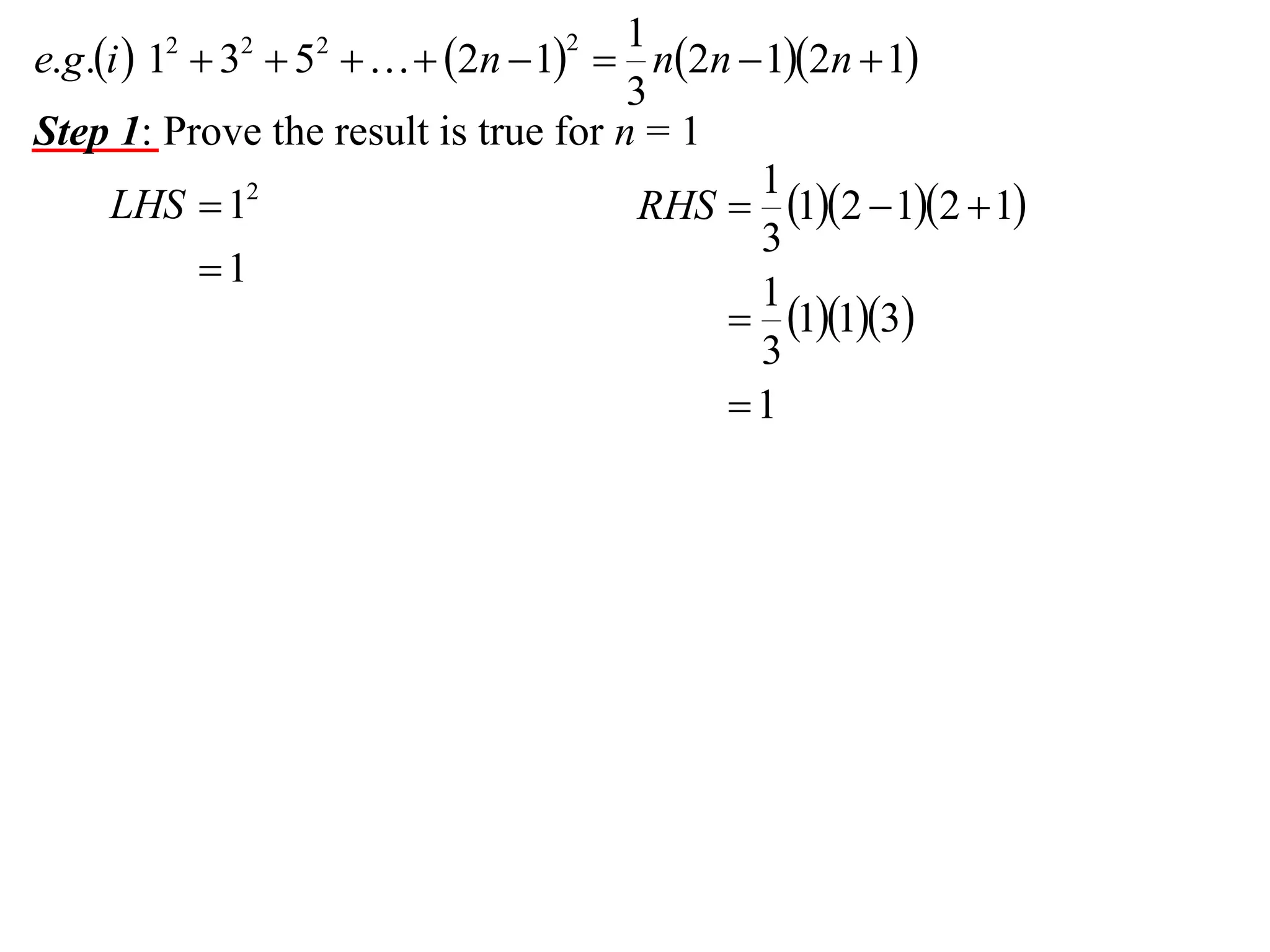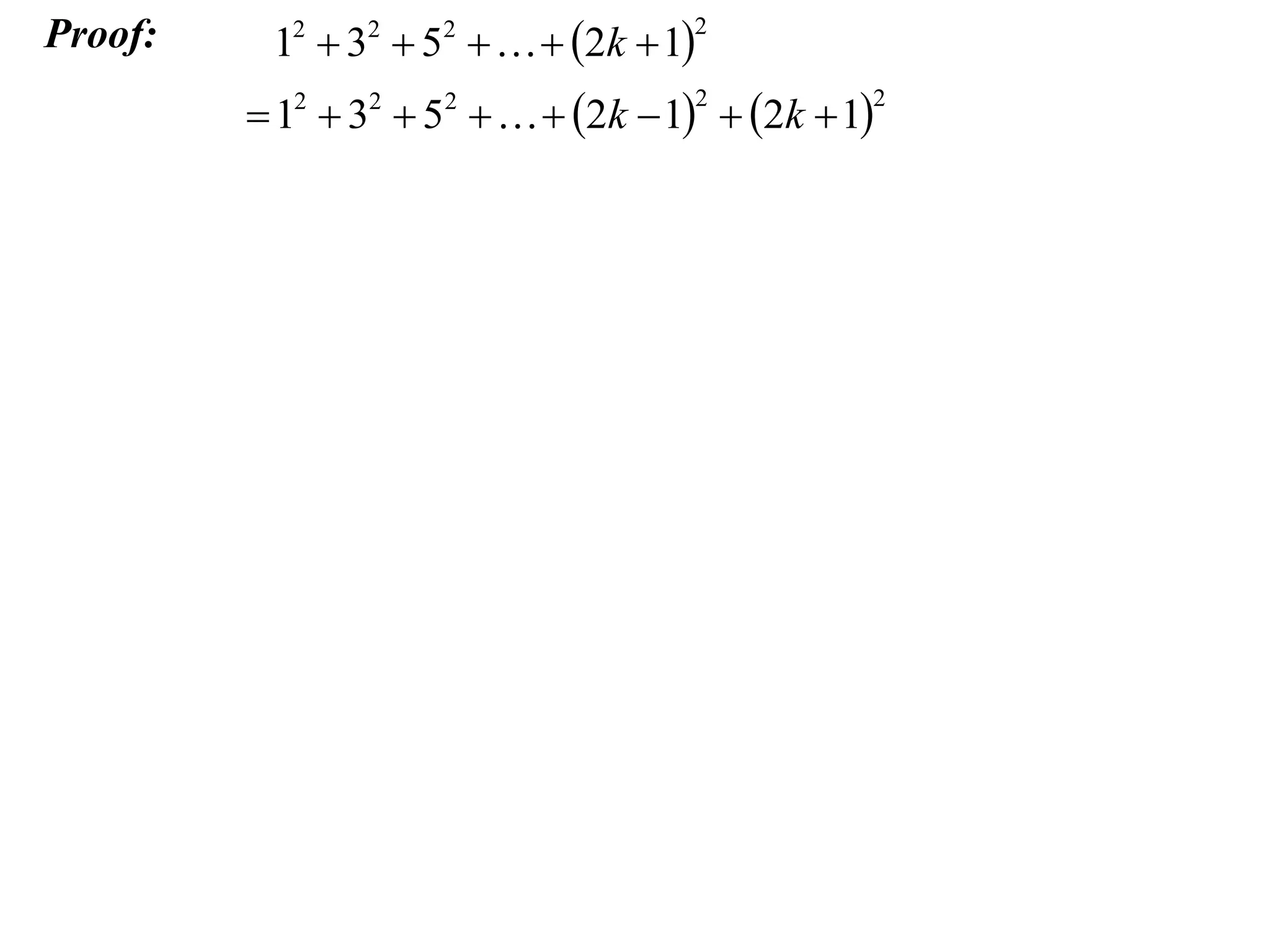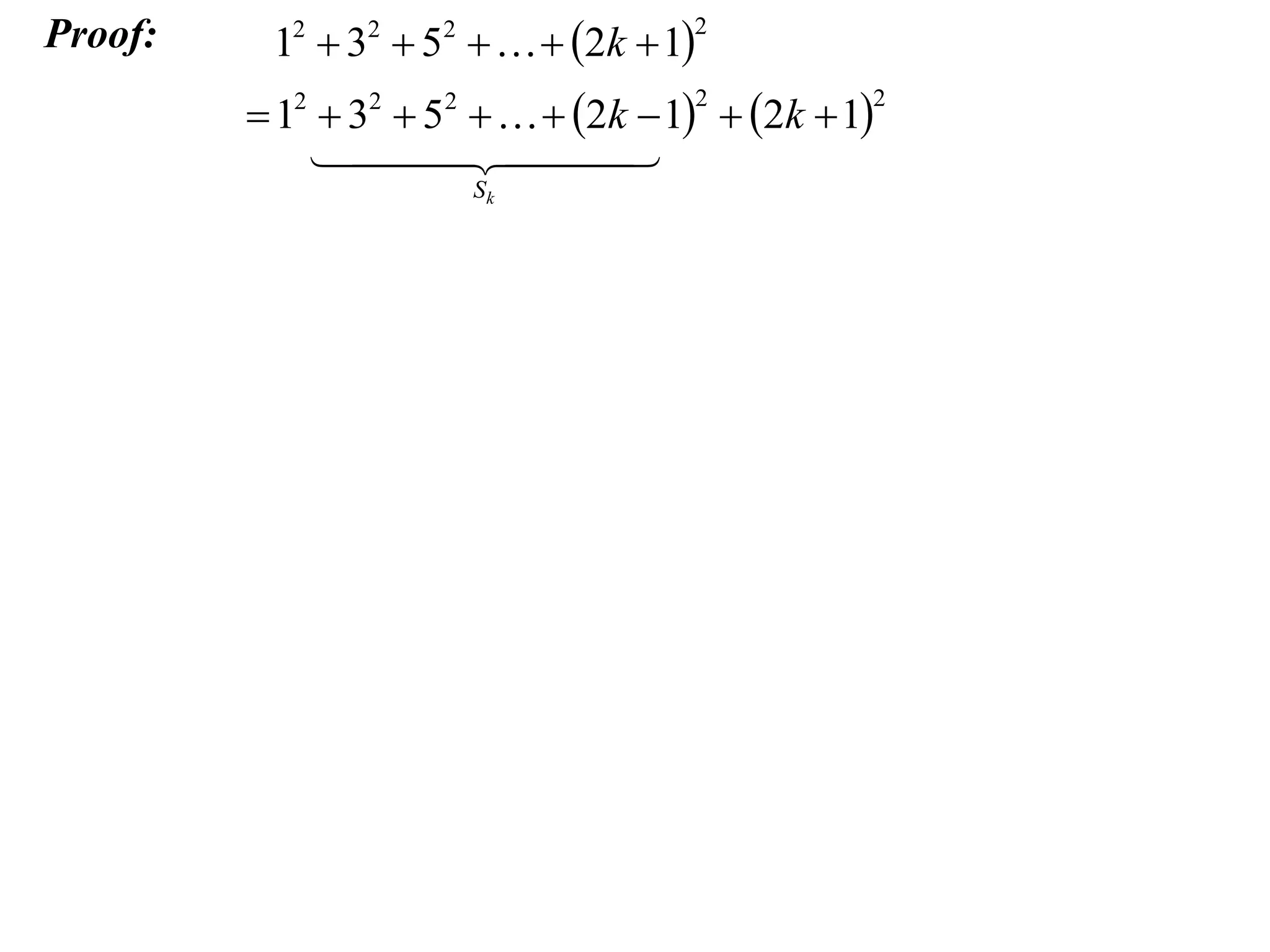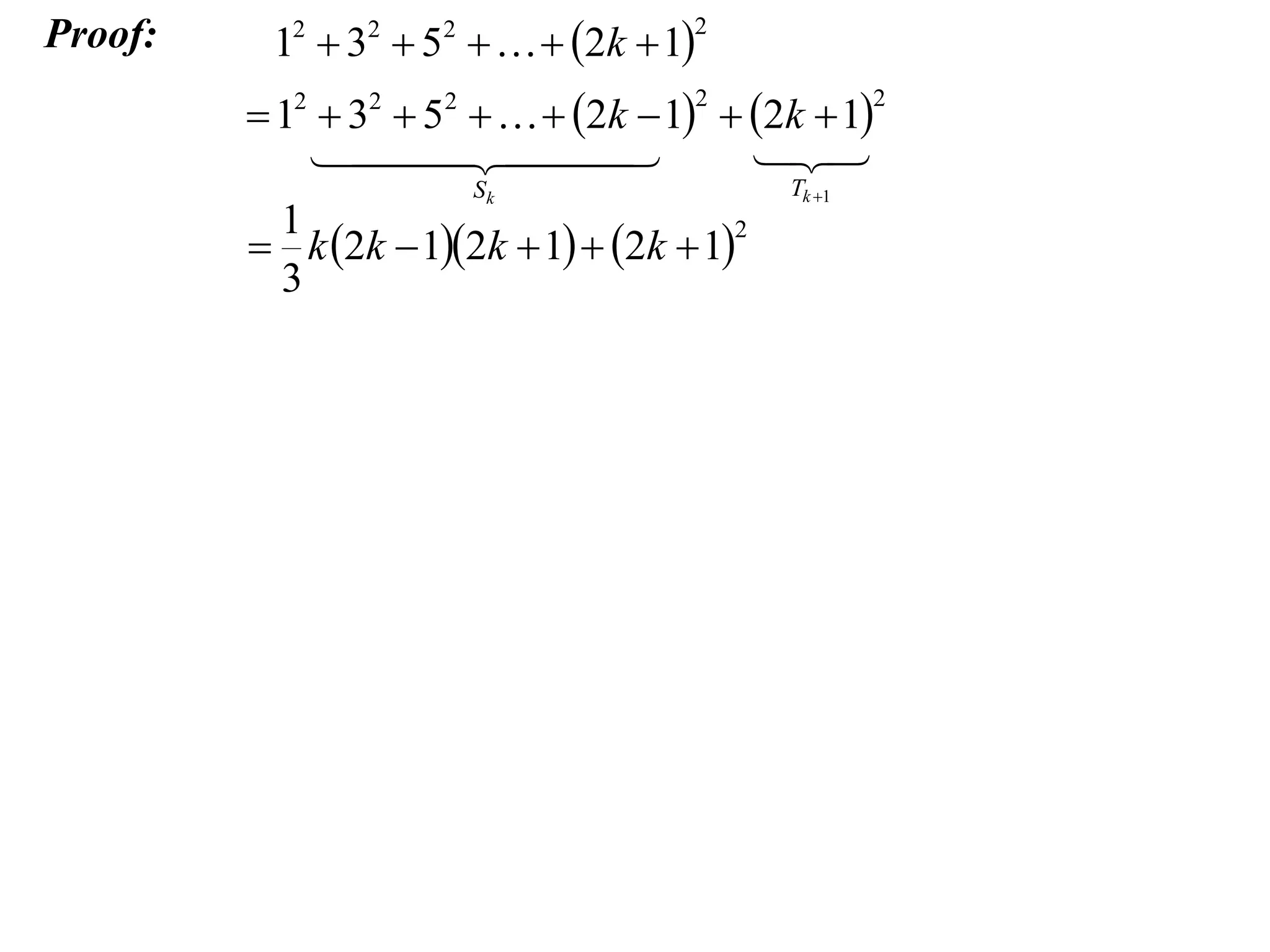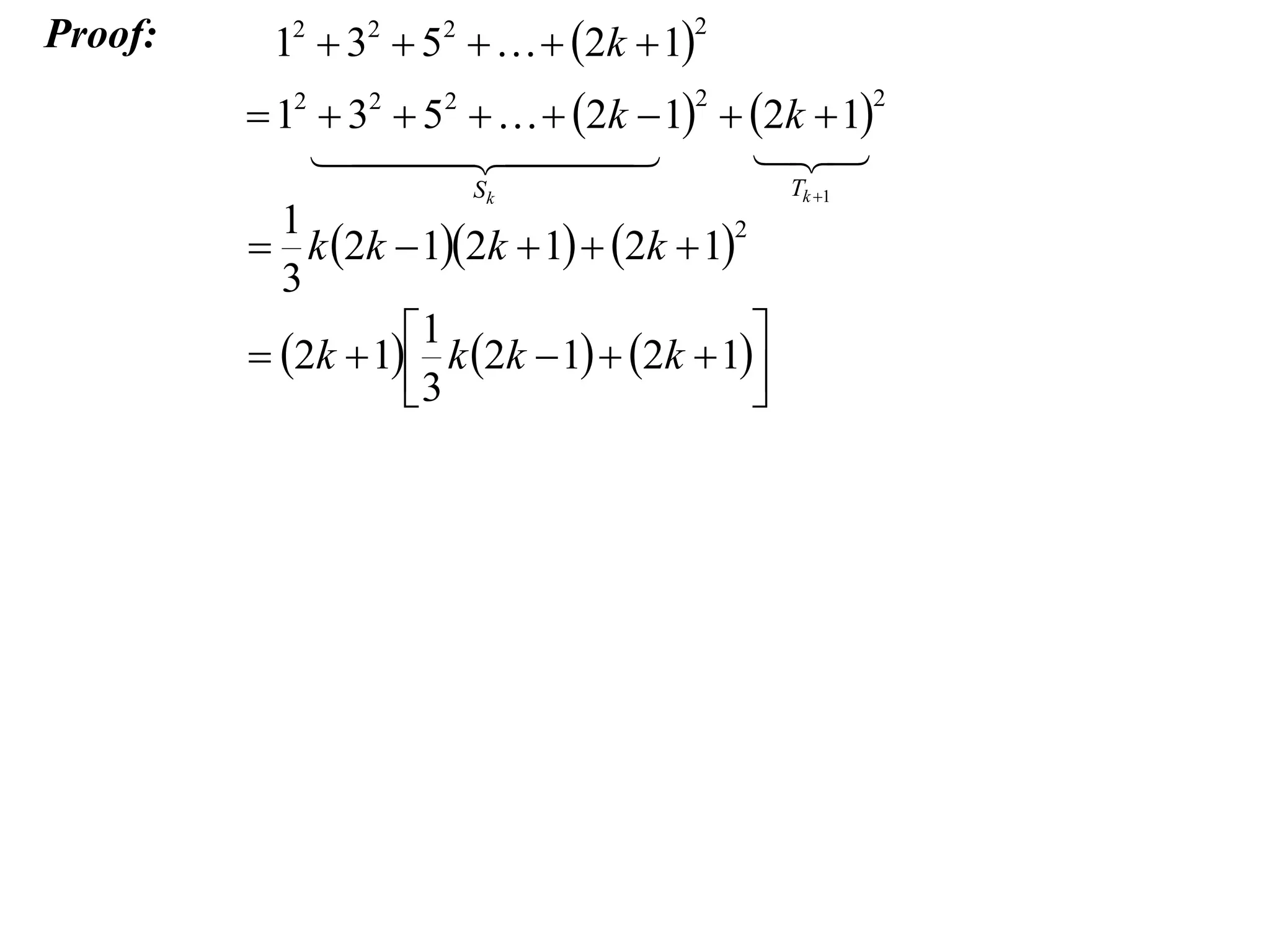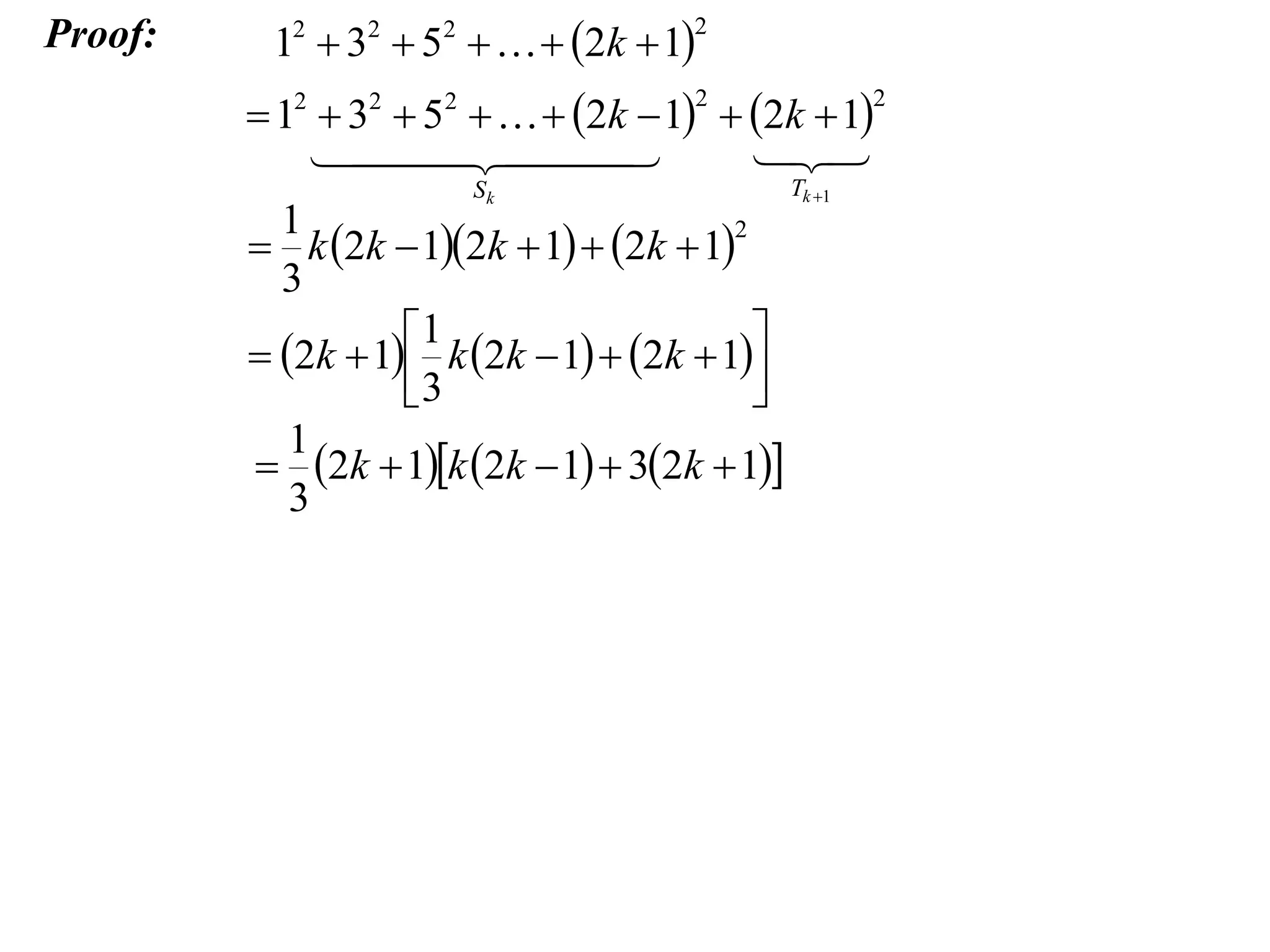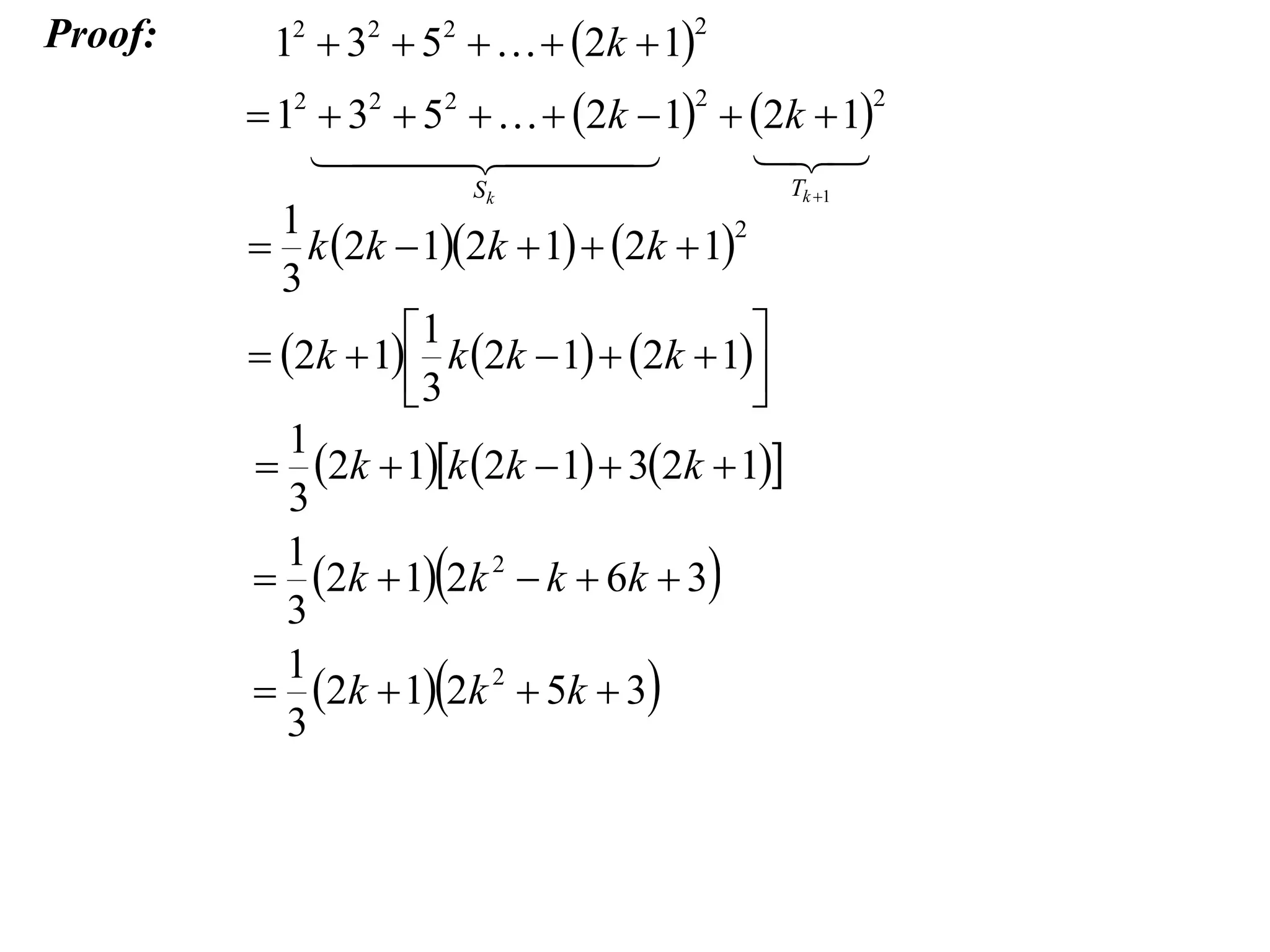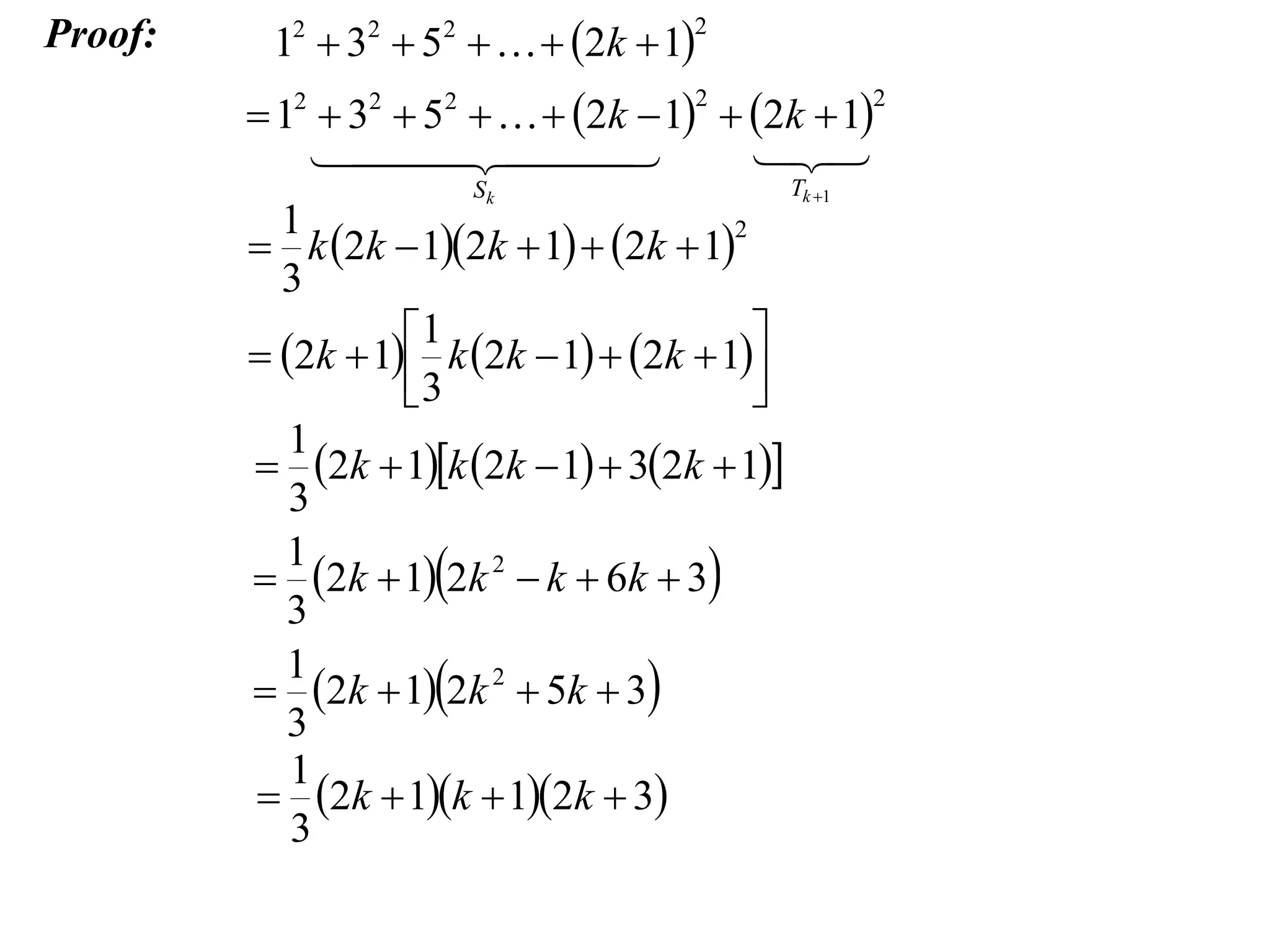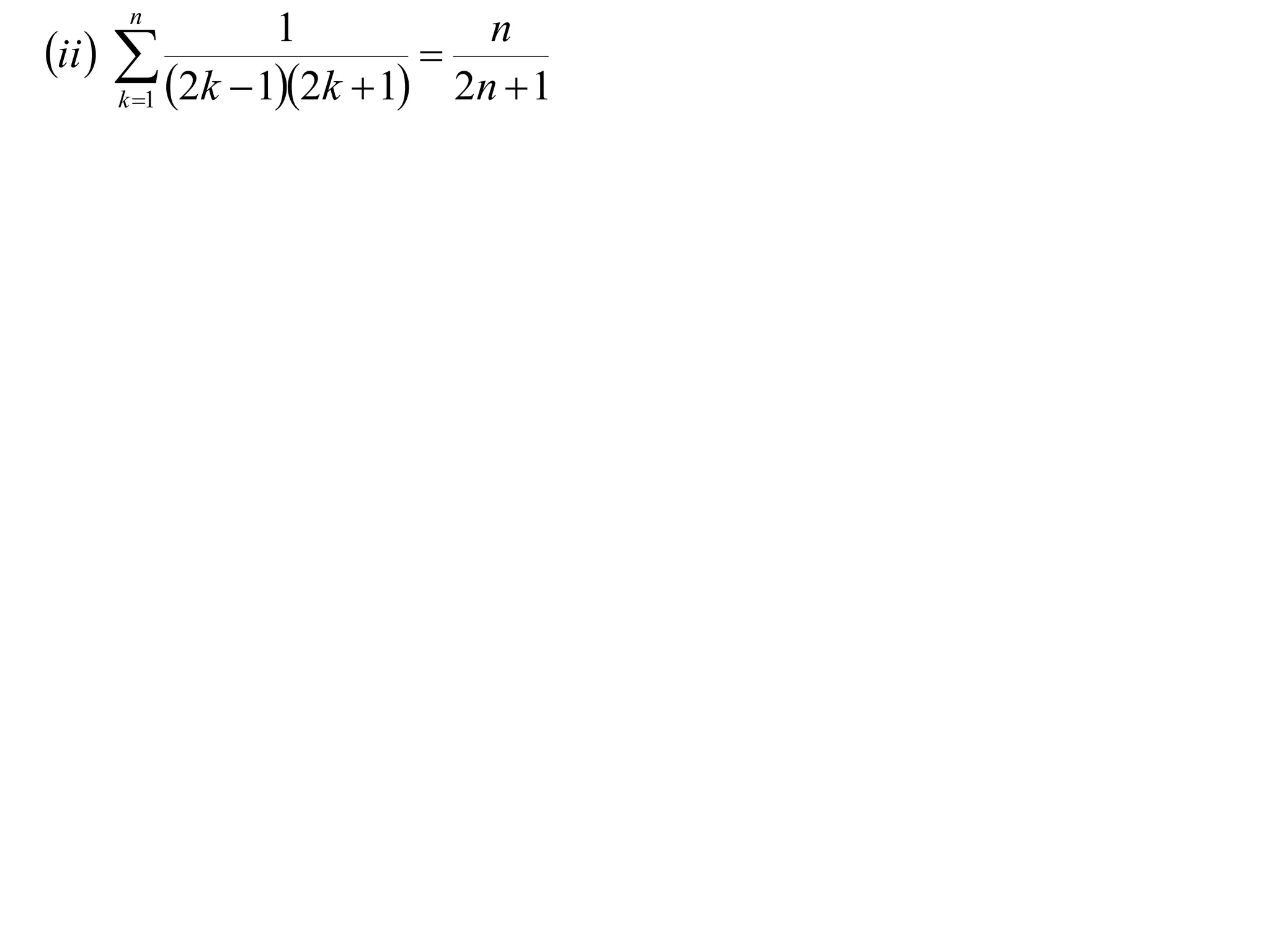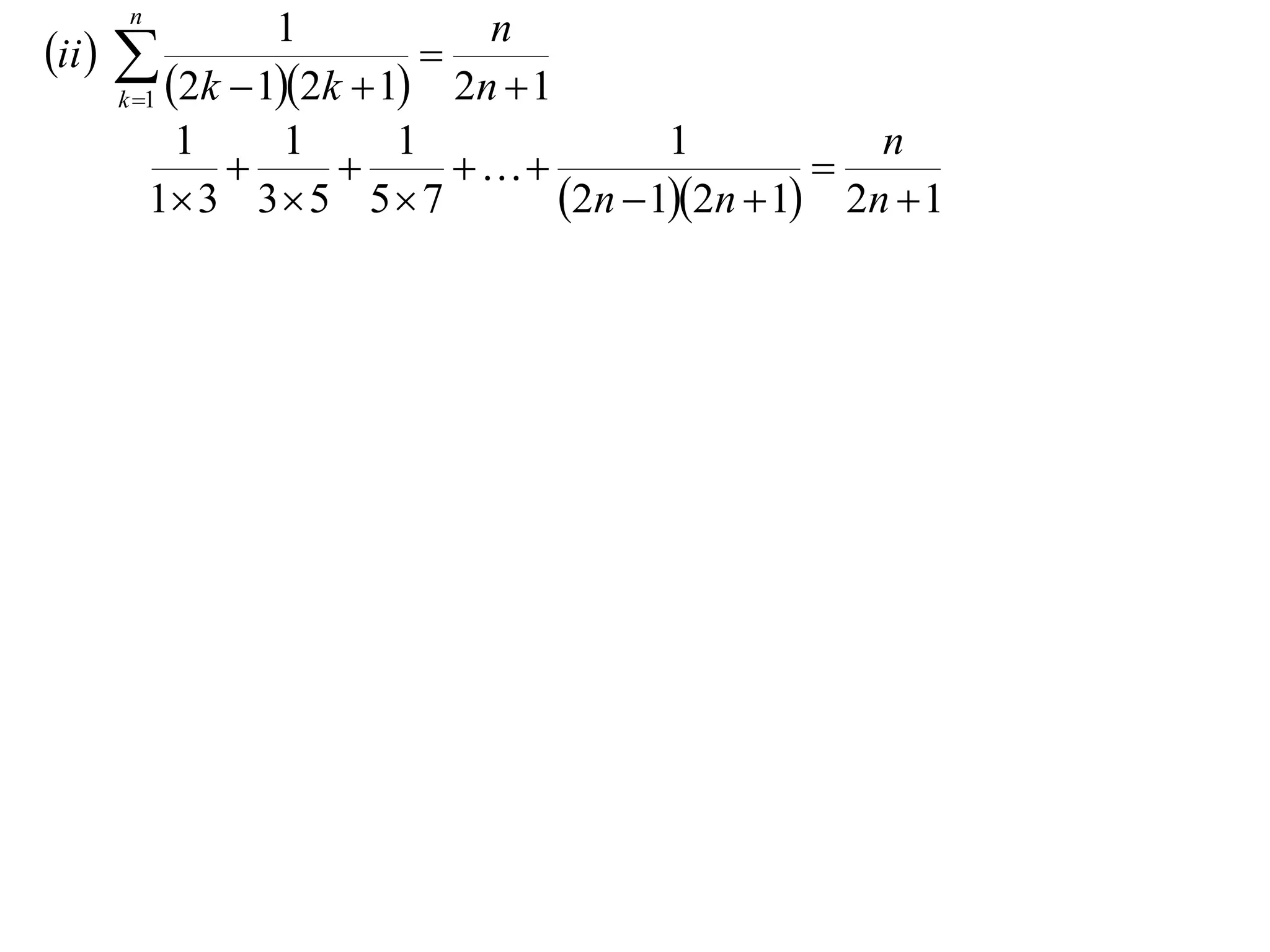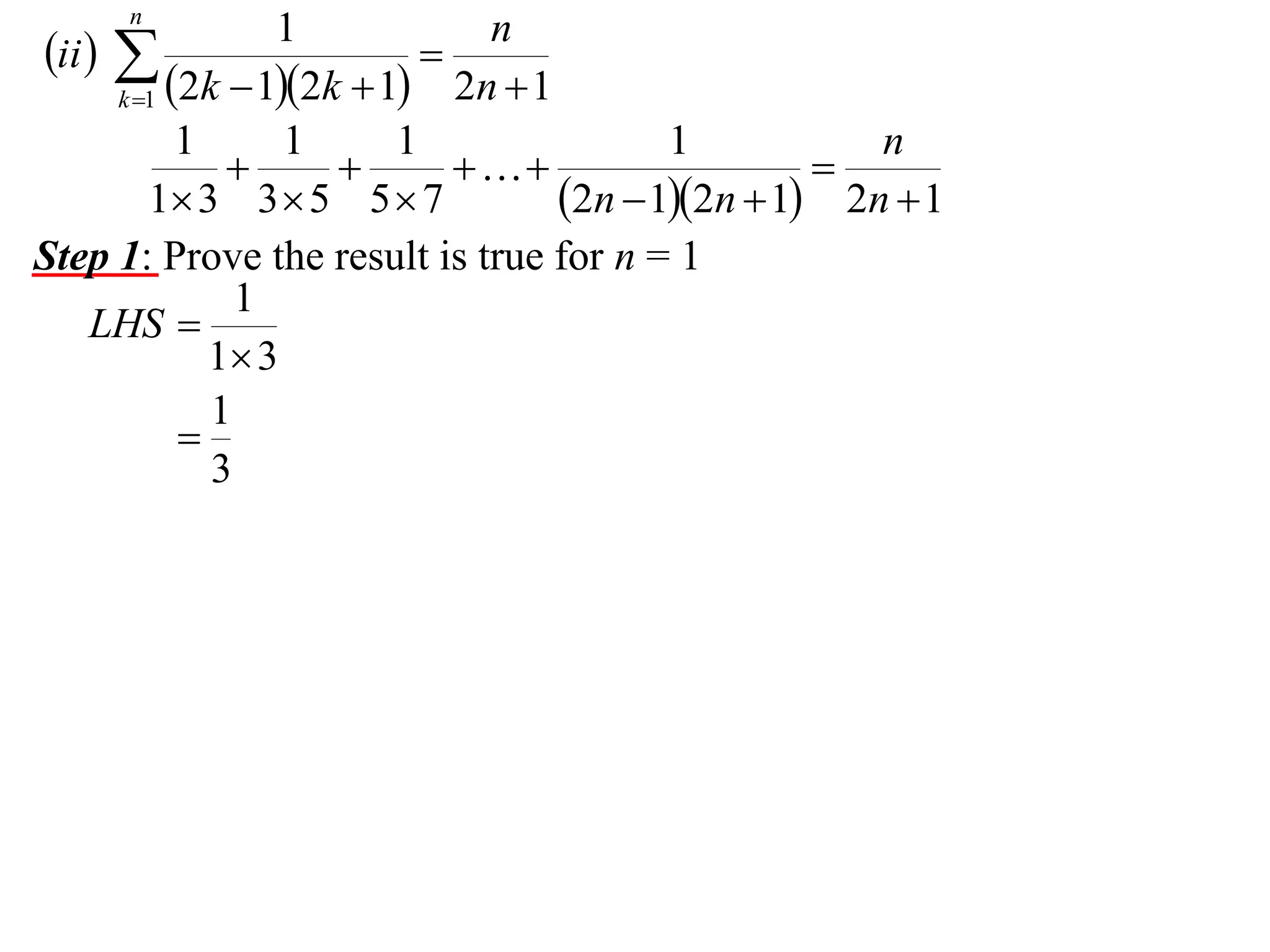The document describes the steps of mathematical induction. It includes:
Step 1: Prove the result is true for the first term, usually n = 1.
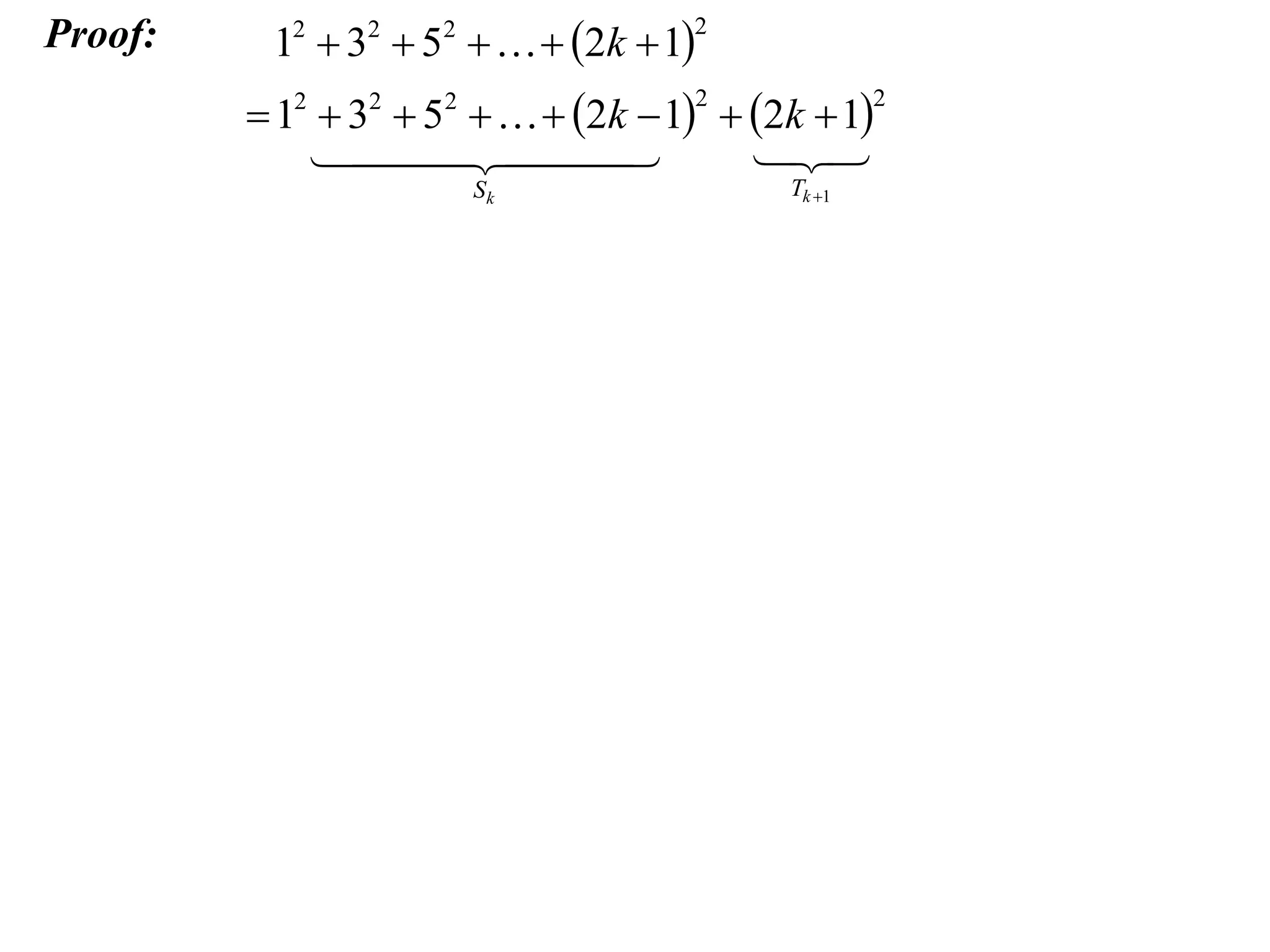
Step 2: Assume the result is true for an integer k.
Step 3: Prove the result is true for k + 1, using the assumption from Step 2.
Step 4: Conclude that since the result is true for n = 1 by Step 1, and true for n = k + 1 by Step 3, it is true for all positive integers n by induction.
The example provided works through an induction proof for the sum of odd integers from 1 to 2n - 1.