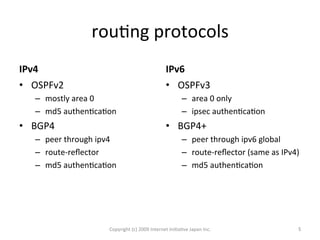
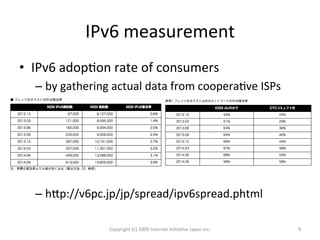
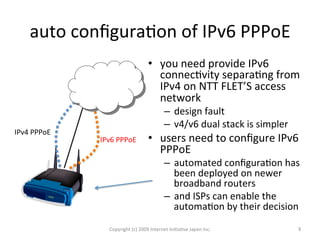
The document outlines IIJ's history and development of IPv6 services, starting from experimental tunnel services in 1999 to dual stack capabilities by 2005. It describes IIJ's business model allowing customers to choose their protocol type and highlights the routing protocols used for both IPv4 and IPv6. Additionally, it addresses the adoption of IPv6 in Japan and the automated configuration efforts for IPv6 over PPPOE.