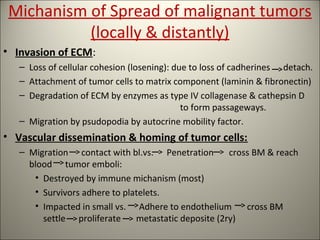
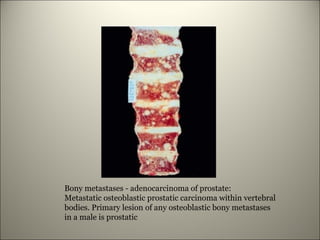
This document discusses neoplasia (tumors). It defines neoplasia as new growth forming an abnormal mass caused by autonomous proliferation of cells independent of stimuli. There are two main components of tumors - transformed neoplastic cells and supporting stroma and vessels from the host. Tumors are classified as benign or malignant based on their behavior and prognosis, and by their tissue of origin histologically. Malignant tumors have characteristics of uncontrolled rapid growth, invasion, ability to spread, recurrence, and causing death. Their structure shows irregular margins, necrosis, and cellular anaplasia. Mechanisms of local and distant spread include invasion of surrounding tissue and vessels, as well as migration of tumor cells through lymphatics and blood