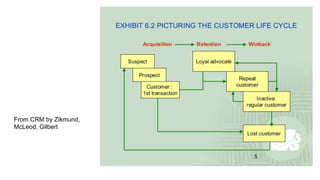
The document discusses customer retention strategies, emphasizing the importance of relationship marketing, loyalty programs, and understanding the customer lifecycle stages. It outlines methods to manage customer complaints, the significance of proactive engagement, and the use of data to personalize experiences. Ultimately, organizations aim to enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty while reducing defections through various incentives and effective communication.