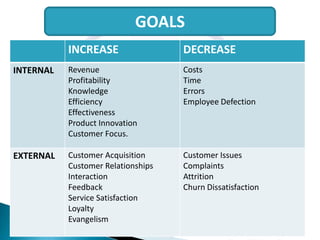
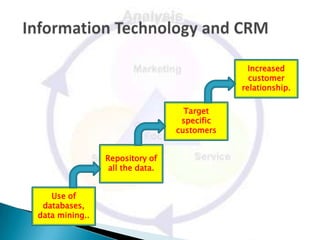
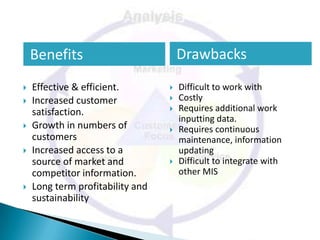
The document discusses customer relationship management (CRM), defining it as a strategy to optimize profitability, revenue, and customer satisfaction by organizing around customer segments and implementing customer-centric processes. It notes that the goals of CRM include increasing customer acquisition and retention while decreasing customer issues and churn. The document also outlines some of the tools and benefits of CRM, as well as potential drawbacks, for organizations.