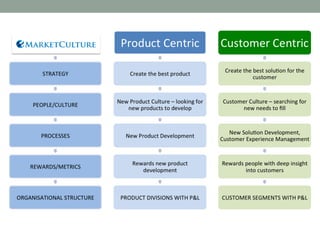
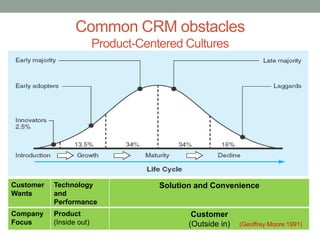
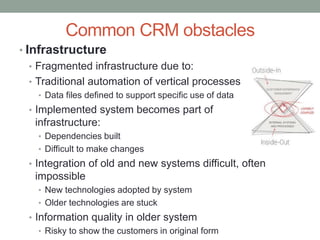
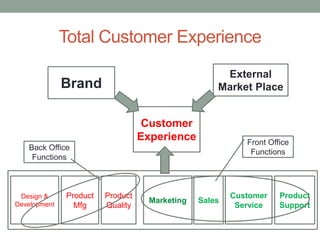
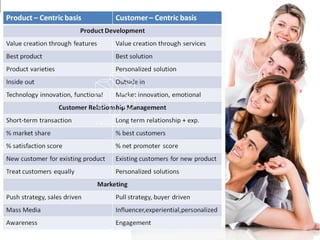
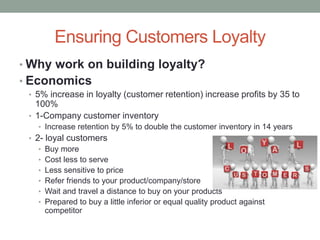
The document discusses common obstacles to customer relationship management (CRM) implementation. It identifies intellectual, cultural, and organizational barriers including unrealistic expectations, wishful thinking, product-centric vs. customer-centric cultures, and fragmented organizational silos. Successfully implementing CRM requires overcoming these barriers by focusing on consistently positive customer experiences over the long-term to build loyalty, rather than expecting immediate results.