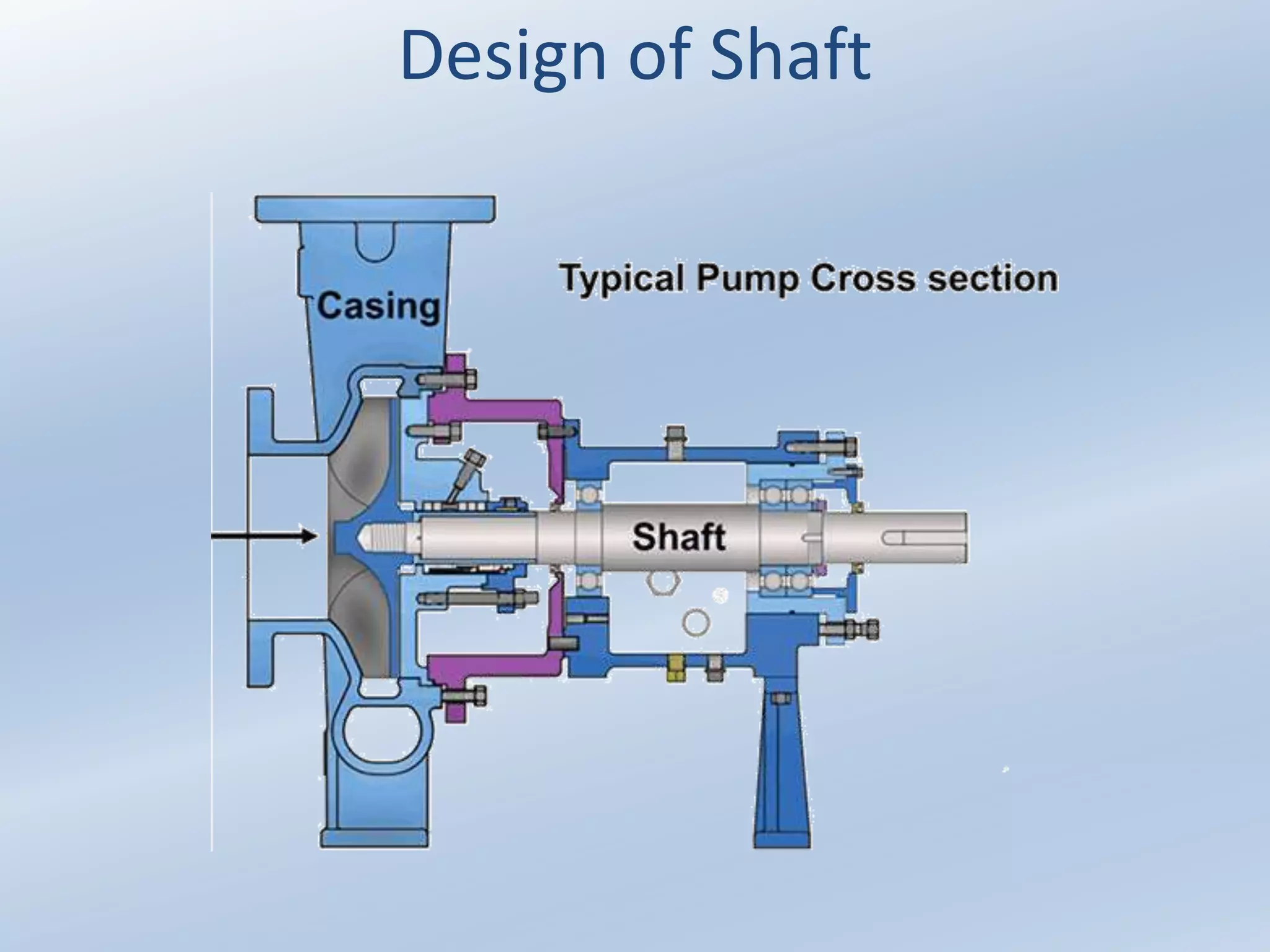
1. A shaft is a rotating cylindrical or cross-shaped member that transmits power and motion. Machine elements like gears and pulleys are mounted on shafts using press fits, keys, or splines.
2. Shafts rotate on bearings and use couplings to transmit power between drive and driven shafts. They experience torsional loading and use features like thrust bearings to handle axial loads.
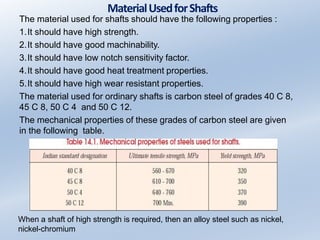
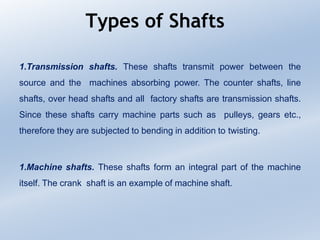
3. Common materials for shafts include carbon steels for strength and machinability. Larger shafts may be forged while smaller shafts are often cold drawn or turned. Shafts can be transmission shafts between power sources and machines or internal machine shafts.