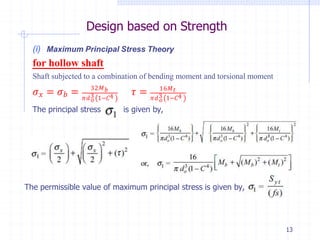
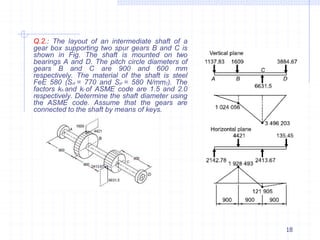
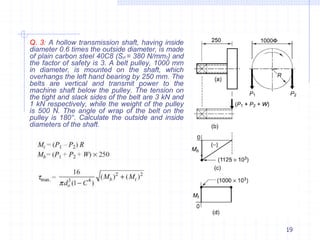
This document discusses the design of solid and hollow shafts subjected to different types of loads. It covers standard shaft sizes and materials, design considerations based on strength and stiffness, stresses due to bending, axial force and torsion, and design according to the ASME code. Example problems are also included to calculate shaft diameters based on strength using factors like load, material properties, and safety factors.