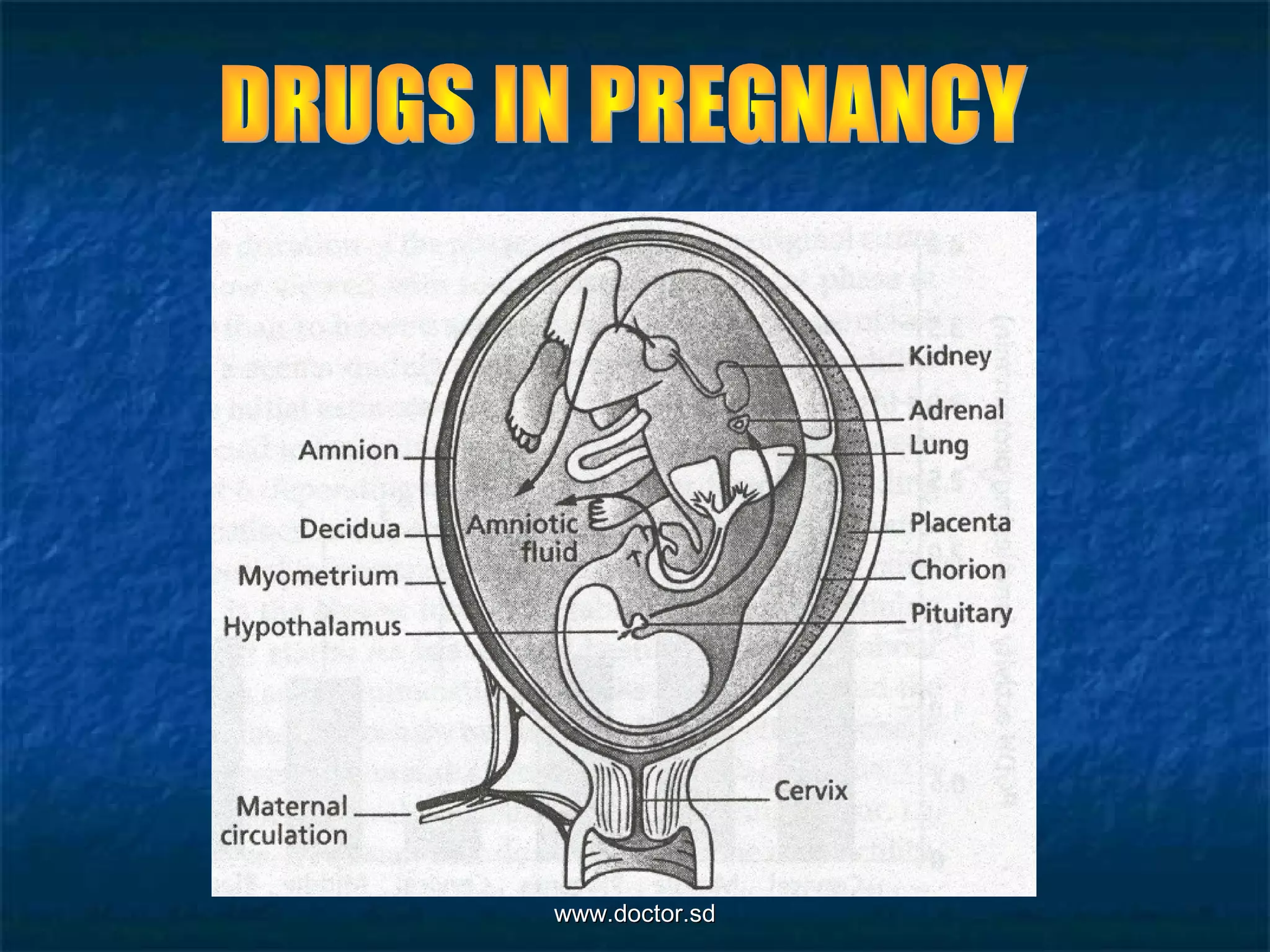
The document provides guidance on prescribing medications during pregnancy. It recommends using a small armamentarium of drugs with proven efficacy and minimal side effects. All drugs may affect the fetus, except heparin and insulin. Patients are often exposed to over-the-counter medications in the first trimester, which carries potential risks. The risks of therapy must be weighed against the risks of not treating diseases. Pharmacokinetics in the mother and fetus are affected by physiological changes in pregnancy. Dietary deficiencies can impact fetal growth and development. Supplementation aims to reduce congenital malformations. Past obstetric history including fertility drugs, hormones, and anticoagulants is important. Screening for STDs like HIV is crucial
![ INTRODUCTION:INTRODUCTION:
ONE SHOULD USE A SMALL ARMAMENTARIUM OFONE SHOULD USE A SMALL ARMAMENTARIUM OF
DRUGS THAT HAVE A PROVEN VALUE WITH KNOWNDRUGS THAT HAVE A PROVEN VALUE WITH KNOWN
AND RECORDED MINIMAL SIDE EFFECTS.AND RECORDED MINIMAL SIDE EFFECTS.
CONSIDER THAT ALL DRUGS MAY AFFECT THECONSIDER THAT ALL DRUGS MAY AFFECT THE
FETUS "EXCEPT HEPARIN & INSULIN".FETUS "EXCEPT HEPARIN & INSULIN".
MANY PATIENTS ARE EXPOSED TO ' OVER-THE-MANY PATIENTS ARE EXPOSED TO ' OVER-THE-
COUNTER' MEDICINES DURING THE FIRSTCOUNTER' MEDICINES DURING THE FIRST
TRIMESTER WITH POTENTIAL RISKS.TRIMESTER WITH POTENTIAL RISKS.
CONSIDER THAT ALL PATIENTS ARE AT RISK OFCONSIDER THAT ALL PATIENTS ARE AT RISK OF
PREGNANCY DURING THEIR REPRODUCTIVE YEARS.PREGNANCY DURING THEIR REPRODUCTIVE YEARS.
ALWAYS CONSIDER THE RISK OF THERAPY AGAINSTALWAYS CONSIDER THE RISK OF THERAPY AGAINST
THE POTENTIAL FOR NOT TREATING THE DISEASE.THE POTENTIAL FOR NOT TREATING THE DISEASE.
[1]
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drugs-in-pregnancy224/85/DRUGS-IN-PREGNANCY-2-320.jpg)
![ PHARMACOKINETICS:PHARMACOKINETICS:
A) MATERNAL;A) MATERNAL;
1]1] DRUG ABSORPTION-DRUG ABSORPTION- - IS AFFECTED BY PHYSIOLOGICAL- IS AFFECTED BY PHYSIOLOGICAL
CHANGES IN PREGNANCY,CHANGES IN PREGNANCY,
ALMOST ALL DRUGS CAN CROSS THE PLACENTA,ALMOST ALL DRUGS CAN CROSS THE PLACENTA,
GASTROINTESTINAL TRANSIT IS PROLONGED DUE TO SLOWGASTROINTESTINAL TRANSIT IS PROLONGED DUE TO SLOW
STOMACH EMPTYING.STOMACH EMPTYING.
2]2] DRUG DISTRIBUTION-DRUG DISTRIBUTION-- LIPID SOLUBILITY & PROTEIN- LIPID SOLUBILITY & PROTEIN
BINDING AFFECT THE DISTRIBUTION,BINDING AFFECT THE DISTRIBUTION,
PLASMA ALBUMINS FALL DUE TO INCREASED TOTAL BODYPLASMA ALBUMINS FALL DUE TO INCREASED TOTAL BODY
WATER & PLASMA VOLUMES.WATER & PLASMA VOLUMES.
3]3] DRUG METABOLISM-DRUG METABOLISM-- WATER-SOLUBLE DRUGS ARE- WATER-SOLUBLE DRUGS ARE
ELIMINATED UNCHANGED,LIPID-SOLUBLE ARE METABOLIZEDELIMINATED UNCHANGED,LIPID-SOLUBLE ARE METABOLIZED
BY OXIDATION,OR CONJUGATED IN THE LIVER.BY OXIDATION,OR CONJUGATED IN THE LIVER.
4]4] DRUG EXCRETION-DRUG EXCRETION-- IS INCREASED DUE TO THE- IS INCREASED DUE TO THE
INCREASED RPF,GFR AND CREATININE CLEARANCEINCREASED RPF,GFR AND CREATININE CLEARANCE
[2]
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drugs-in-pregnancy224/85/DRUGS-IN-PREGNANCY-3-320.jpg)
![ B) FETAL;B) FETAL;
DRUG DISTRIBUTION,METABOLISM ANDDRUG DISTRIBUTION,METABOLISM AND
EXCRETIONS OCCUR IN THE FETUS ANDEXCRETIONS OCCUR IN THE FETUS AND
PLACENTA,PLACENTA,
FETAL LIVER AND ADRENAL GLAND METABOLIZESFETAL LIVER AND ADRENAL GLAND METABOLIZES
DRUGS BY OXIDATION,OXIDATIVE DEALKYLATION,DRUGS BY OXIDATION,OXIDATIVE DEALKYLATION,
REDUCTION HYDROXYLATION,HYDROLYSIS ANDREDUCTION HYDROXYLATION,HYDROLYSIS AND
CONJUGATION.CONJUGATION.
LOW-MOLECULAR-WEIGHT DRUGS DIFFUSELOW-MOLECULAR-WEIGHT DRUGS DIFFUSE
EASILY ACROSS THE PLACENTA,AMINO ACIDSEASILY ACROSS THE PLACENTA,AMINO ACIDS
TRANSPORT BY ACTIVE TRANSFER,TRANSPORT BY ACTIVE TRANSFER,
LIPID SOLUBILITY AND PLASMA PROTEIN BINDINGLIPID SOLUBILITY AND PLASMA PROTEIN BINDING
ARE CONTRIBUTORY FACTORS.ARE CONTRIBUTORY FACTORS.
[3]
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drugs-in-pregnancy224/85/DRUGS-IN-PREGNANCY-4-320.jpg)
![BASIC RULES OF PRESCRIBING INBASIC RULES OF PRESCRIBING IN
PREGNANCYPREGNANCY
A) REMEMBER THEA) REMEMBER THE
OBSTETRIC RULES:OBSTETRIC RULES:
1. FIRST DO NO HARM1. FIRST DO NO HARM
2. NEVER BE THE2. NEVER BE THE
FIRST TO USE THEFIRST TO USE THE
NEW,NOR THE LASTNEW,NOR THE LAST
TO USE THE OLDTO USE THE OLD
3. REMEMBER THAT3. REMEMBER THAT
ALL WOMEN AREALL WOMEN ARE
PREGNANT UNTILLPREGNANT UNTILL
PROVED OTHERWISE.PROVED OTHERWISE.
B) PRESCRIBING INB) PRESCRIBING IN
PREGNANCY:PREGNANCY:
1.1.
PRECONCEPTIONALLY;PRECONCEPTIONALLY;
THE PATEINT MAY BETHE PATEINT MAY BE
TAKING DRUGSTAKING DRUGS
2. THE PATIENT MAY BE2. THE PATIENT MAY BE
TAKING DRUGS ANDTAKING DRUGS AND
FIND SHE IS PREGNANTFIND SHE IS PREGNANT
3. THE PATIENT WHO IS3. THE PATIENT WHO IS
PREGNANT MAYPREGNANT MAY
REQUIRE DRUGREQUIRE DRUG
TREATMENT.TREATMENT.
[4]
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drugs-in-pregnancy224/85/DRUGS-IN-PREGNANCY-5-320.jpg)
![Fetal therapy
Teratogenesis
1/3
trimester
2/3
trimester
3/3
trimester
labour
puerperium
Pre-pregnant
Medical disorders
of pregnancy
Prelabour
Induction of labour
Analgesics
Oxytocics
Depression
Contraception
Breast-feeding
Drugs of abuse
Antibiotics
POTENTIAL RISKS AT DIFFERENT MONTHS OF PREGNANCY
[5]
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drugs-in-pregnancy224/85/DRUGS-IN-PREGNANCY-6-320.jpg)
![ DIETARY ADVICE:DIETARY ADVICE:
DEFICIENCIES IN PROTEINS,VITAMINS,MINERALS OR TRACEDEFICIENCIES IN PROTEINS,VITAMINS,MINERALS OR TRACE
ELEMENTS CAN AFFECT FETAL GROWTH& DEVELOPMENT.ELEMENTS CAN AFFECT FETAL GROWTH& DEVELOPMENT.
THE OPTIMAL WEIGHT GAIN IN PREGNANCY ;FOR THINTHE OPTIMAL WEIGHT GAIN IN PREGNANCY ;FOR THIN
WOMEN=12.5 Kg, AND FOR OBESE=5-10 Kg.WOMEN=12.5 Kg, AND FOR OBESE=5-10 Kg.
DIETARY SUPPLEMENTATION:DIETARY SUPPLEMENTATION:
IS AIMED,AMONGST OTHER FACTORS,TO REDUCEIS AIMED,AMONGST OTHER FACTORS,TO REDUCE
CONGENITAL MALFORMATIONS;CONGENITAL MALFORMATIONS;
1) VITAMINS:1) VITAMINS: DAILY DOSE OF 400 U VIT. D=LOWER THE RISKDAILY DOSE OF 400 U VIT. D=LOWER THE RISK
OF NEONATAL RICKETS,DENTAL ENAMEL DISPLACEMENT.OF NEONATAL RICKETS,DENTAL ENAMEL DISPLACEMENT.
VIT. A = EXCESSIVE DOSE >40 OOO IU,CAN BE HAZARDOUS.VIT. A = EXCESSIVE DOSE >40 OOO IU,CAN BE HAZARDOUS.
FOLIC ACIDFOLIC ACID= DAILY DOSE OF 0.4 mg, WILL REDUCE THE= DAILY DOSE OF 0.4 mg, WILL REDUCE THE
INCIDENCE OF NTD.INCIDENCE OF NTD.
2) HAEMATINICS:2) HAEMATINICS: ORALLY= FERROUS SALTS: SULPHATE ,ORALLY= FERROUS SALTS: SULPHATE ,
GLUCONATE AND FUMARATE,GLUCONATE AND FUMARATE,
PARENTERALLY= I.M.,IV. OR AS TOTAL IRON INFUSIONSPARENTERALLY= I.M.,IV. OR AS TOTAL IRON INFUSIONS
[6]
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drugs-in-pregnancy224/85/DRUGS-IN-PREGNANCY-7-320.jpg)
![ PAST OBSTETRIC HISTORY:PAST OBSTETRIC HISTORY:
1) OVULATION-INDUCING DRUGS;1) OVULATION-INDUCING DRUGS;
CLOMIPHENE CITRATECLOMIPHENE CITRATE -- 2 TO 3X RISK OF STD AND OVARIAN-- 2 TO 3X RISK OF STD AND OVARIAN
MALIGNANCY,FOLLOWING EXCESSIVE USE >12/12.MALIGNANCY,FOLLOWING EXCESSIVE USE >12/12.
2) HORMONES;2) HORMONES;
-DES-DES = PRENATAL EXPOSURE,FOR THREATENED ABORTION,= PRENATAL EXPOSURE,FOR THREATENED ABORTION,
MAY CAUSE ADENOCA OF VAGINA.MAY CAUSE ADENOCA OF VAGINA.
-PROGESTOGENS-PROGESTOGENS = USED IN RECURRENT MISCARRIAGES AND= USED IN RECURRENT MISCARRIAGES AND
POOR LUTEAL PHASE. NO NEED TO USE THEM NOW.POOR LUTEAL PHASE. NO NEED TO USE THEM NOW.
-ORAL CONTRACEPTIVES-ORAL CONTRACEPTIVES = SUPPRESS FOLATE AND= SUPPRESS FOLATE AND
PYRIDOXINE LEVELS, NO OTHER HARMS.PYRIDOXINE LEVELS, NO OTHER HARMS.
-ANTICOAGULANTS-ANTICOAGULANTS = ASPIRIN(75 Mg)& HEPARIN – ARE USED IN= ASPIRIN(75 Mg)& HEPARIN – ARE USED IN
CASES OF RECURRENT ABORTIONS DUE TO SLE OR RAISEDCASES OF RECURRENT ABORTIONS DUE TO SLE OR RAISED
APA.APA.
-OTHERS-OTHERS = ASPIRIN & NITRIC OXIDE ARE ALSO USED TO= ASPIRIN & NITRIC OXIDE ARE ALSO USED TO
IMPROVE UTERINE PERFUSION IN RECURRENT MISCARRIAGES.IMPROVE UTERINE PERFUSION IN RECURRENT MISCARRIAGES.
[7]
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drugs-in-pregnancy224/85/DRUGS-IN-PREGNANCY-8-320.jpg)
![ C) STD;C) STD; THE COMMONEST COMMUNICABLETHE COMMONEST COMMUNICABLE
DISEASES GLOBALLY. SCREENING FORDISEASES GLOBALLY. SCREENING FOR
SYPHILIS & AIDS IS IMPORTANT.ABOUT 30%SYPHILIS & AIDS IS IMPORTANT.ABOUT 30%
OF THEIR BABIES WILL BE HIV +VE.OF THEIR BABIES WILL BE HIV +VE.
D) VACCINATION & TRAVELD) VACCINATION & TRAVEL ; FOR YELLOW; FOR YELLOW
FEVER,CHOLERA,POLIOMYEILITIS ANDFEVER,CHOLERA,POLIOMYEILITIS AND
INFLUENZA CAN BE GIVEN ANTENATALLY.INFLUENZA CAN BE GIVEN ANTENATALLY.
RUBELLA VACC. IS ALLOWED ONLY PRE-RUBELLA VACC. IS ALLOWED ONLY PRE-
CONCEPTUALLY OR POSTPARTUM.CONCEPTUALLY OR POSTPARTUM.
[8]
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drugs-in-pregnancy224/85/DRUGS-IN-PREGNANCY-9-320.jpg)
![ GENERAL MEDICAL DISORDERSGENERAL MEDICAL DISORDERS ;;
A) EPILEPSYA) EPILEPSY = A RISK OF FETAL MALFORMATIONS WHICH IS= A RISK OF FETAL MALFORMATIONS WHICH IS
INCREASED ON TAKING ANTIEPILEPTICS – THESE ARE :INCREASED ON TAKING ANTIEPILEPTICS – THESE ARE :
1) MINOR1) MINOR STRUCTURAL WITH NO THREAT TO HEALTH.STRUCTURAL WITH NO THREAT TO HEALTH.
2) MAJOR2) MAJOR = CLEFT LIP,SPINA BIFIDA AND CHD.= CLEFT LIP,SPINA BIFIDA AND CHD.
ANTIEPILEPTICSANTIEPILEPTICS : (: (a)VALPORATEa)VALPORATE—SPINA BIFIDA & CRANIAL +—SPINA BIFIDA & CRANIAL +
FACIAL ANOMALIES.(FACIAL ANOMALIES.( b) CARBAMAZEPINEb) CARBAMAZEPINE – SPINA BIFIDA.– SPINA BIFIDA.
((c) PHENOBARBITONEc) PHENOBARBITONE – CHD & CLEFT PALATE.(– CHD & CLEFT PALATE.(d) PHENYTOINd) PHENYTOIN ––
HYDANTOIN SYNDROME.HYDANTOIN SYNDROME.
MANAGEMENT:(1)MANAGEMENT:(1) ADVICE HIGHER DOSES OF COCS.ADVICE HIGHER DOSES OF COCS.
(2)(2) FOLIC ACID(4-5MG) BEFORE CONCEPTION AND UP TO 12/52FOLIC ACID(4-5MG) BEFORE CONCEPTION AND UP TO 12/52
PREGNANCYPREGNANCY.(3).(3) ADVISE SINGLE DRUG AND LOWEST DOSE.ADVISE SINGLE DRUG AND LOWEST DOSE.
CARBAMAZEPINECARBAMAZEPINE IS THE DRUG OF CHOICEIS THE DRUG OF CHOICE.(4).(4) VITAMIN K TO BEVITAMIN K TO BE
GIVEN AT BIRTH TO PROTECT THE INFANT.GIVEN AT BIRTH TO PROTECT THE INFANT.
B) PSYCHIATRIC ILLNESSB) PSYCHIATRIC ILLNESS = like depression= like depression (a)(a) Meprobamate orMeprobamate or
benzodiazepines --- serious neonatal symptoms.Not teratogenic.benzodiazepines --- serious neonatal symptoms.Not teratogenic.
bb) (Monoamine-oxidase inhibitors– c/i in pregnancy due to) (Monoamine-oxidase inhibitors– c/i in pregnancy due to
anaesthesiaanaesthesia.(c).(c) Tricyclic antidepressants--- babies refusal to feed.Tricyclic antidepressants--- babies refusal to feed.
(d)(d) Lithium salts ;lithium clearance in pregnancy increases.It mayLithium salts ;lithium clearance in pregnancy increases.It may
affect the fetus causing cyanosis,lethargy,hypotonia,poor suckling andaffect the fetus causing cyanosis,lethargy,hypotonia,poor suckling and
CHDCHD.(e).(e) Phenothiazines can cause Parkinsonism .Phenothiazines can cause Parkinsonism .
[10]
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drugs-in-pregnancy224/85/DRUGS-IN-PREGNANCY-10-320.jpg)
![ C)TRANSPLANTATIONC)TRANSPLANTATION ::
INCLUDING RENAL,LUNG,LIVER,BONE MARROW ANDINCLUDING RENAL,LUNG,LIVER,BONE MARROW AND
HEART.SURVIVAL RATE = 70-80%.DRUGS USED;HEART.SURVIVAL RATE = 70-80%.DRUGS USED;
1)ADRENAL STEROIDS1)ADRENAL STEROIDS – PEPTIC– PEPTIC
ULCERATION,ULCERATION,
OSTEOPOROSIS,HYPERTENSION,MATERNALOSTEOPOROSIS,HYPERTENSION,MATERNAL
INFECTION AND POOR TISSUE HEALING.INFECTION AND POOR TISSUE HEALING.
2)AZATHIOPRINE2)AZATHIOPRINE – HEPATIC TOXICITY,BONE– HEPATIC TOXICITY,BONE
MARROW DEPRESSION,INFECTION AND NEOPLASIA.MARROW DEPRESSION,INFECTION AND NEOPLASIA.
3)CYCLOSPORIN3)CYCLOSPORIN – NEPHROTOXICITY,ELEVATED– NEPHROTOXICITY,ELEVATED
SERUM URIC ACID,LYMPHOMAS AND VIRALSERUM URIC ACID,LYMPHOMAS AND VIRAL
INFECTION.INFECTION. D) HYPERTENSIOND) HYPERTENSION: MOST DRUGS: MOST DRUGS
HAVE A FAVOURABLE BENEFIT. ANGIOTENSIN-HAVE A FAVOURABLE BENEFIT. ANGIOTENSIN-
CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS ARECONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS ARE
CONTRAINDICATED.CONTRAINDICATED. E)DIABETESE)DIABETES
MELLITUSMELLITUS: ORAL HYPOGLYCAEMICS ARE: ORAL HYPOGLYCAEMICS ARE
CONTRAINDICATED.CONTRAINDICATED.
[11]
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drugs-in-pregnancy224/85/DRUGS-IN-PREGNANCY-11-320.jpg)
![ INDUSTRIAL HISTORYINDUSTRIAL HISTORY
A)OPERATING THEATRESA)OPERATING THEATRES: VOLATILE GASES: VOLATILE GASES
MAY CAUSE SPON. ABORTIONS ANDMAY CAUSE SPON. ABORTIONS AND
CONGENITAL ANOMALIES. SCAVENGERCONGENITAL ANOMALIES. SCAVENGER
SYSTEMS SHOULD BE INSTALLED.SYSTEMS SHOULD BE INSTALLED.
B) LAUNDRIESB) LAUNDRIES: ORGANIC: ORGANIC
SOLVENTS CAN CAUSE ANENCEPHALY ORSOLVENTS CAN CAUSE ANENCEPHALY OR
FETAL DYSMORPHOLOGY.FETAL DYSMORPHOLOGY. C) COMPUTERSC) COMPUTERS::
NO RISK.NO RISK. D) SAUNASD) SAUNAS: NO: NO
HARM .HARM .
FAMILY HISTORYFAMILY HISTORY
GENDER CHOICEGENDER CHOICE: DIETS HIGH IN SODIUM &: DIETS HIGH IN SODIUM &
POTASSIUM AND LOW IN CALCIUM &POTASSIUM AND LOW IN CALCIUM &
MAGNESIUM ARE REPORTED TO GIVE ANMAGNESIUM ARE REPORTED TO GIVE AN
80% CHANCE OF A MALE FETUS.80% CHANCE OF A MALE FETUS.
[12]
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drugs-in-pregnancy224/85/DRUGS-IN-PREGNANCY-12-320.jpg)
![ TERATOGENESISTERATOGENESIS
A TERATOGEN: IS AN AGENT THAT CAUSES PHYSICALA TERATOGEN: IS AN AGENT THAT CAUSES PHYSICAL
AND/OR DEVELOPMENTAL ABNORMALITIES IN THE EMBRYOAND/OR DEVELOPMENTAL ABNORMALITIES IN THE EMBRYO
OR THE FETUS.OR THE FETUS.
TIMING OF FETAL LIFE:TIMING OF FETAL LIFE:
[[11]PRE-EMBRYONIC PHASE = 1–17 DAY POSTCONCEPTION]PRE-EMBRYONIC PHASE = 1–17 DAY POSTCONCEPTION
[[22] EMBRYONIC = 18-55 DAY.] EMBRYONIC = 18-55 DAY.
[[33]ORGANOGENESIS.]ORGANOGENESIS.
TERATOGENIC MECHANISMSTERATOGENIC MECHANISMS::
(a)(a) DIRECT EMBRYO TOXICITY.DIRECT EMBRYO TOXICITY.
(b) INDIRECT TOXICITY– BY ALTERATION OF(b) INDIRECT TOXICITY– BY ALTERATION OF
METABOLIC FACTORS.METABOLIC FACTORS.
(c)(c) GENETIC FACTORS– DETERMINING THEGENETIC FACTORS– DETERMINING THE
SUSCEPTIBILITY TO TERATOGENESIS (WARFARIN !).SUSCEPTIBILITY TO TERATOGENESIS (WARFARIN !).
CLASSIFICATION:CLASSIFICATION: {1}{1}
MAJOR TERATOGENS = WITH PROVEN RISKSMAJOR TERATOGENS = WITH PROVEN RISKS
[THALIDOMIDE,CYTOTOXICS AND RADIOCHEMICALS].[THALIDOMIDE,CYTOTOXICS AND RADIOCHEMICALS].
{2}{2} DRUGS WITH SMALL RISKS BUT OCCASIONALLY NEEDEDDRUGS WITH SMALL RISKS BUT OCCASIONALLY NEEDED
FOR THE HEALTH OF THE WOMAN.FOR THE HEALTH OF THE WOMAN.
[13]
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drugs-in-pregnancy224/85/DRUGS-IN-PREGNANCY-13-320.jpg)