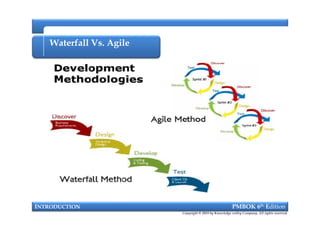
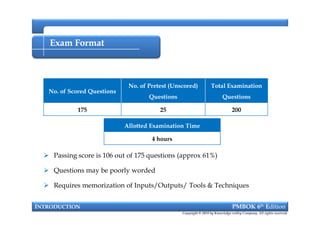
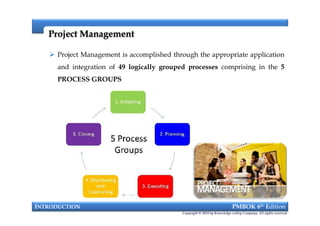
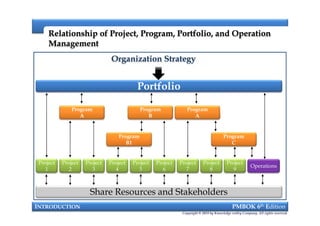
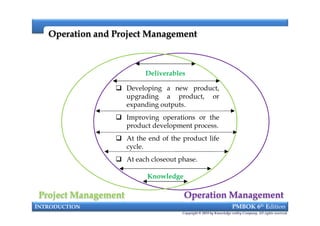
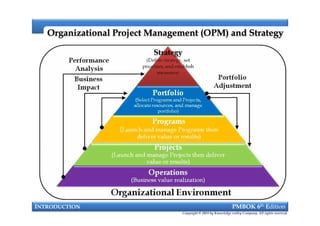
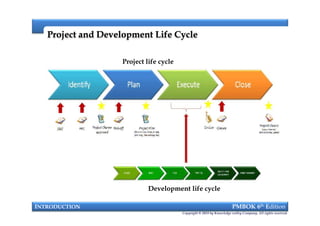
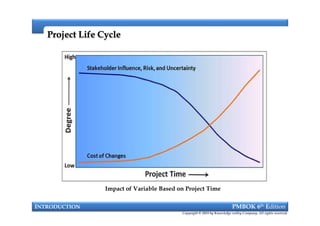
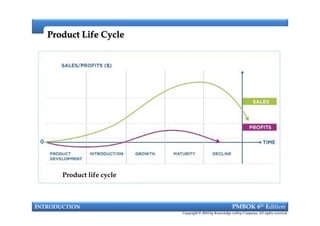
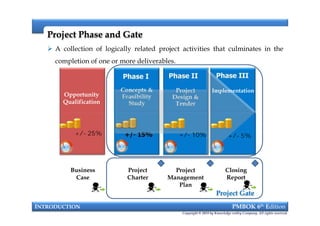
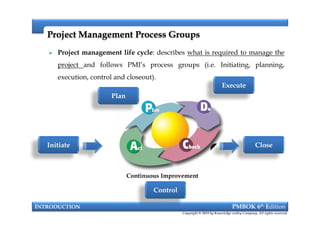
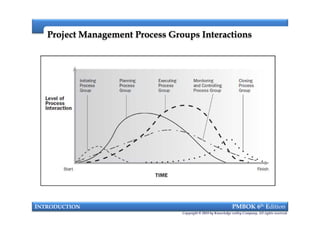
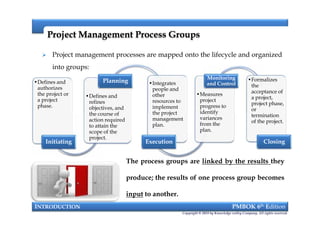
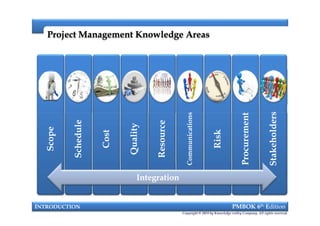
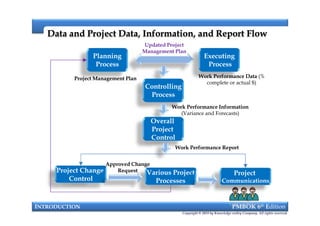
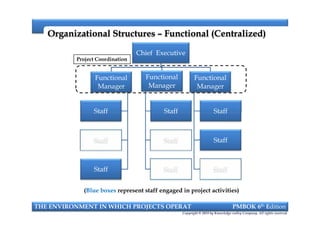
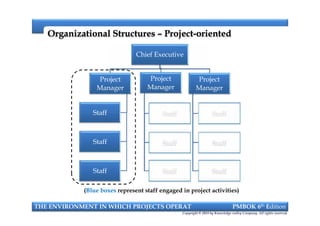
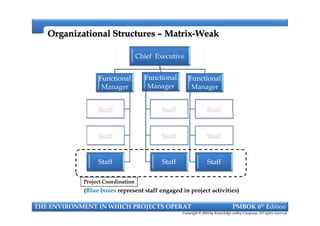
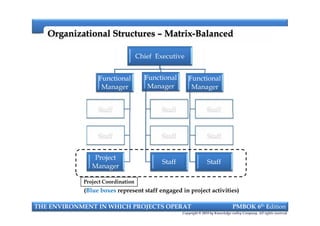
This document provides an introduction to a course on project management based on the PMBOK 6th edition. It outlines the instructor's background and experience in project management. It describes who should attend the course, which is aimed at project managers, team members, and professionals interested in PMP certification. The course will cover all major project management processes defined in PMBOK 6th edition, examine the differences between waterfall and agile approaches, and requirements to sit for the PMP exam.