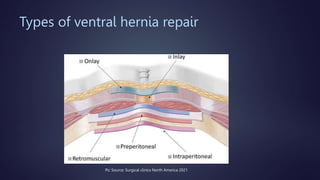
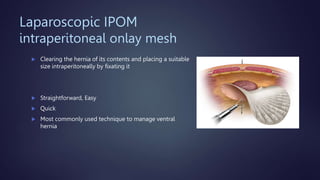
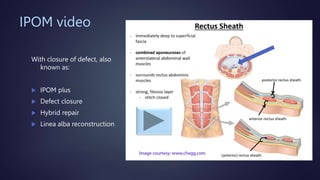
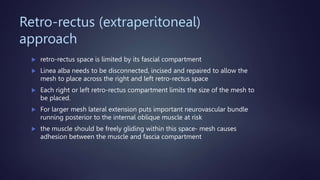
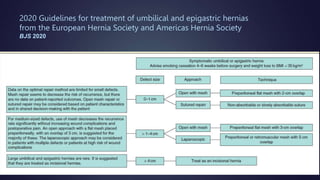
The document discusses various techniques for extraperitoneal ventral hernia repair, especially focusing on IPOM (Intraperitoneal Onlay Mesh) and its advantages and drawbacks. It highlights current guidelines suggesting preperitoneal mesh placement to avoid adhesions and structural disruption, while also mentioning other extraperitoneal techniques. Additionally, it notes the complexities and longer operative time associated with the preperitoneal technique.