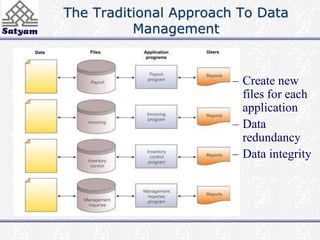
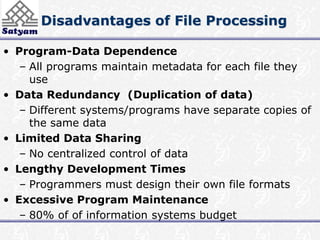
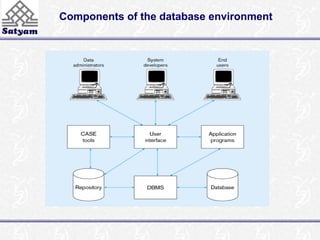
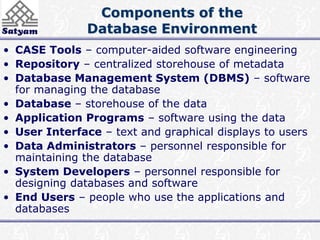
This document provides an introduction to database management systems (DBMS). It discusses the disadvantages of traditional file-based data management approaches, such as data redundancy and lack of data integrity. It then describes the key components of a database system, including the database itself, DBMS software, users, and administrators. Challenges of DBMS include security, data quality, and data integrity issues that must be addressed. The overall system structure partitions responsibilities between query processing and storage management components.