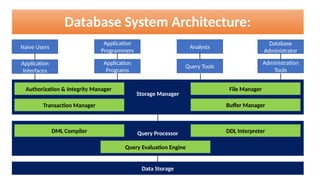
The document provides an overview of database management systems (DBMS), covering essential topics such as the definition of data and information, the structure of a database, and the functionalities of a DBMS. It discusses the features, advantages, and disadvantages of file processing systems compared to DBMS, alongside detailing the architecture of database systems and the importance of data abstraction and independence. Additionally, it includes various short and long questions, as well as multiple choice questions related to the subject matter.