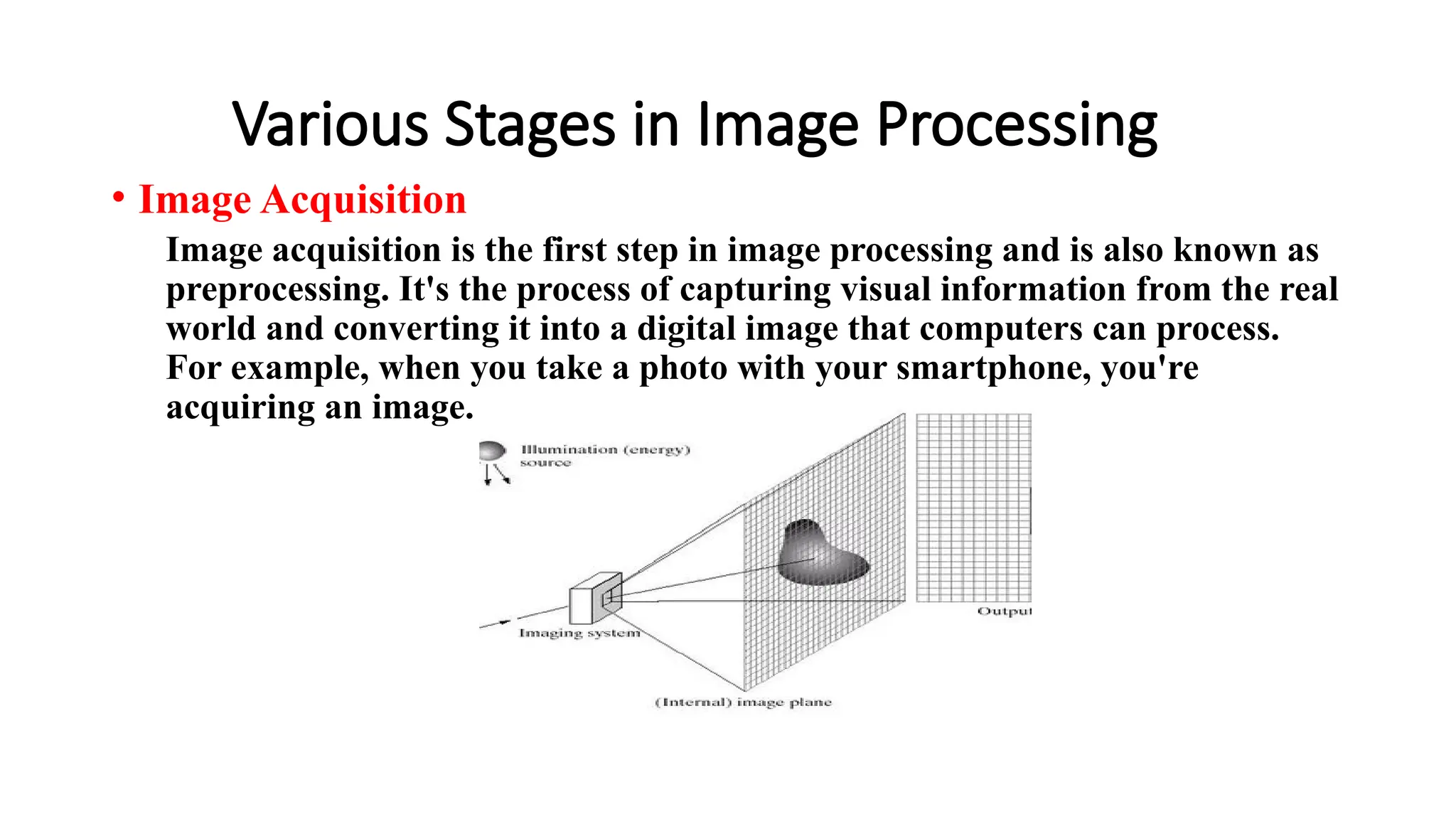
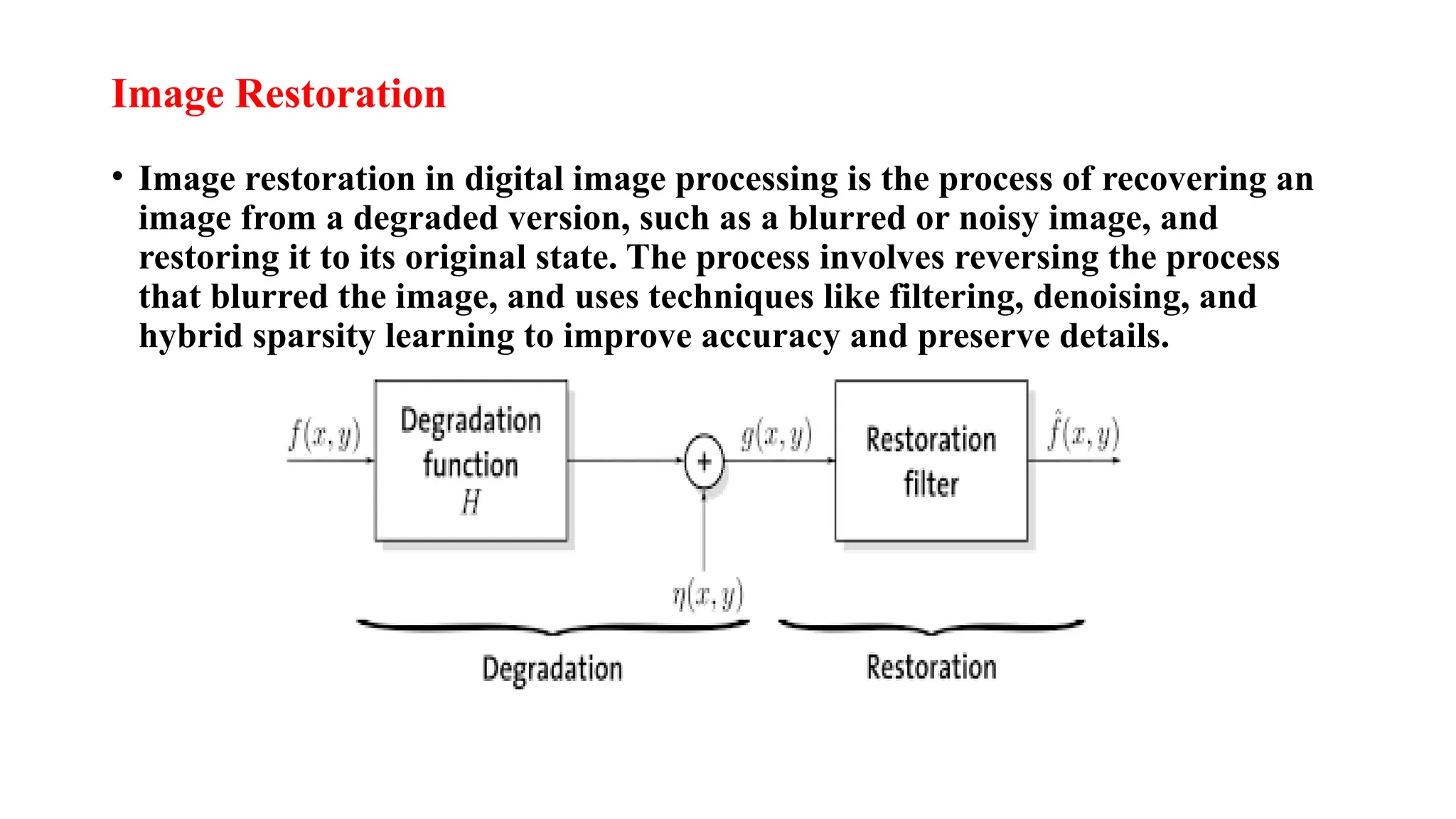
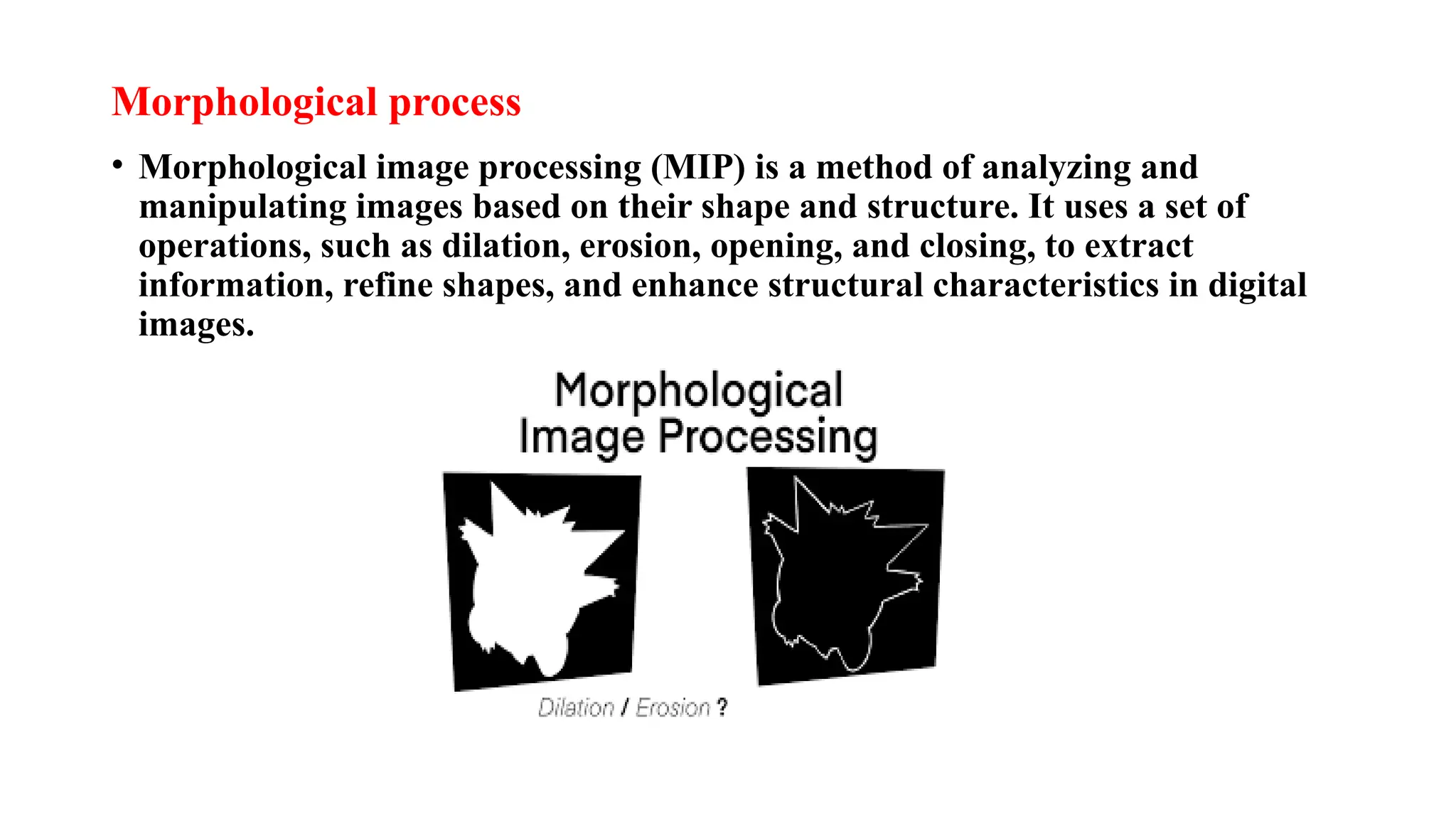
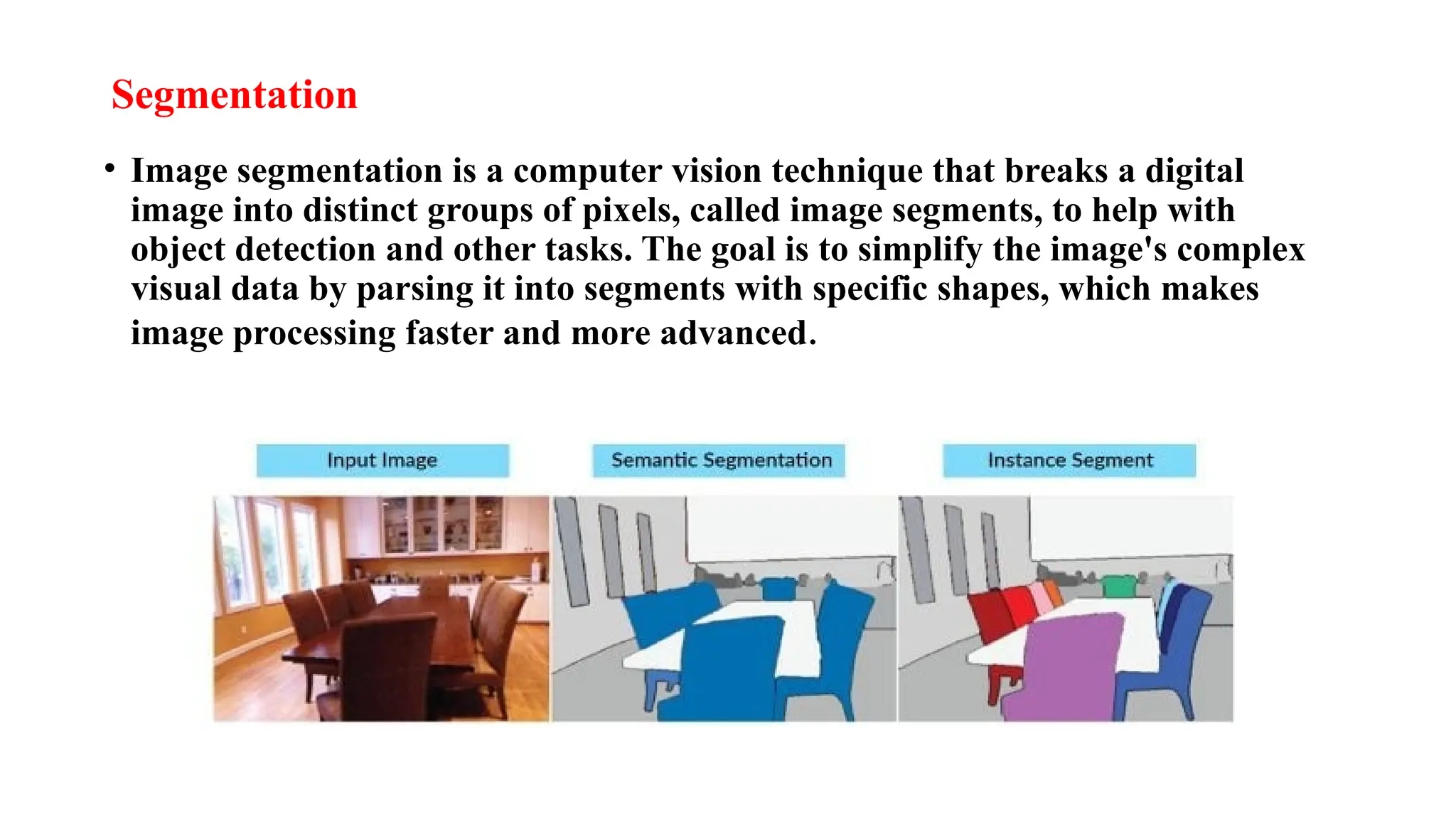
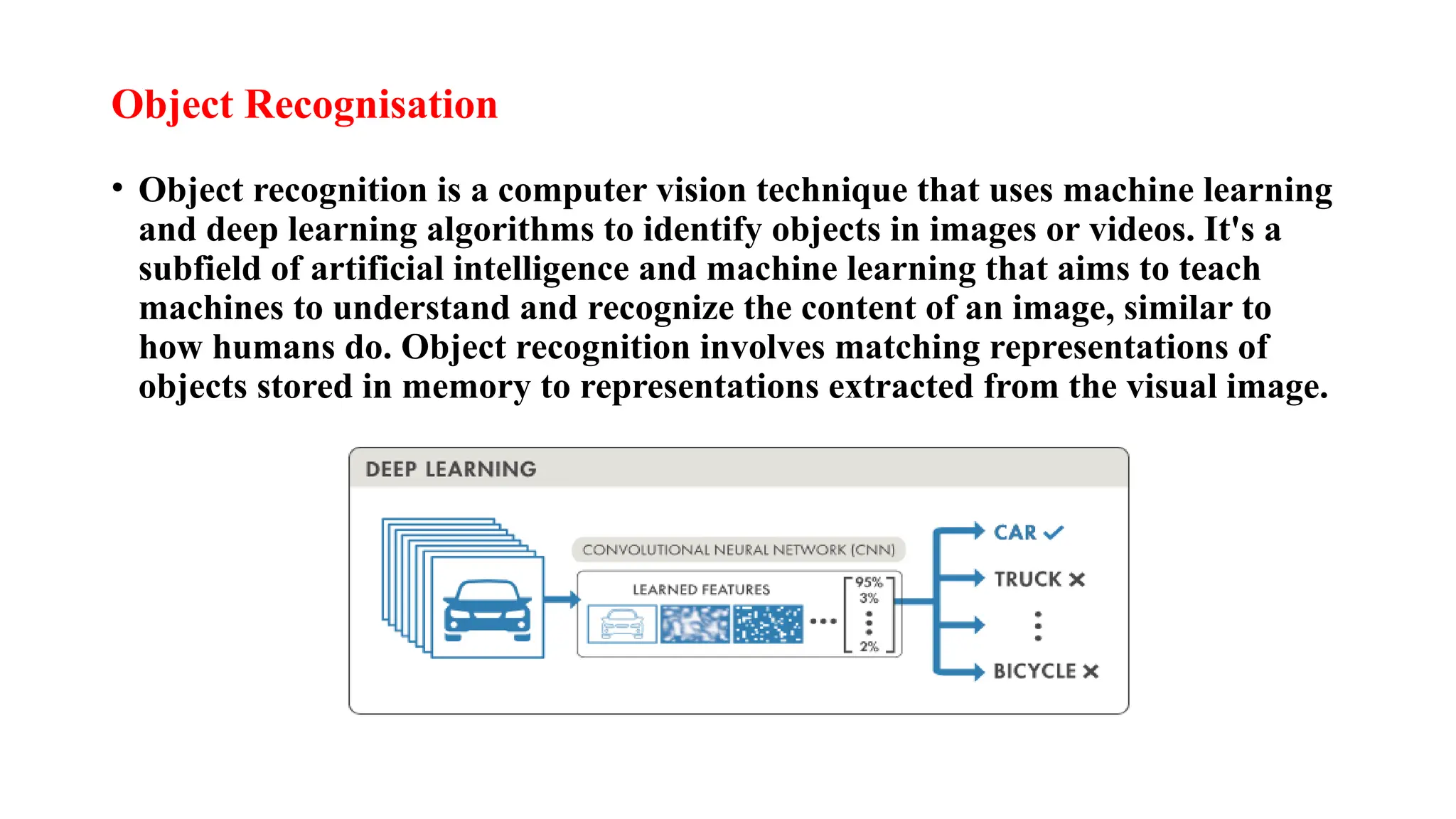
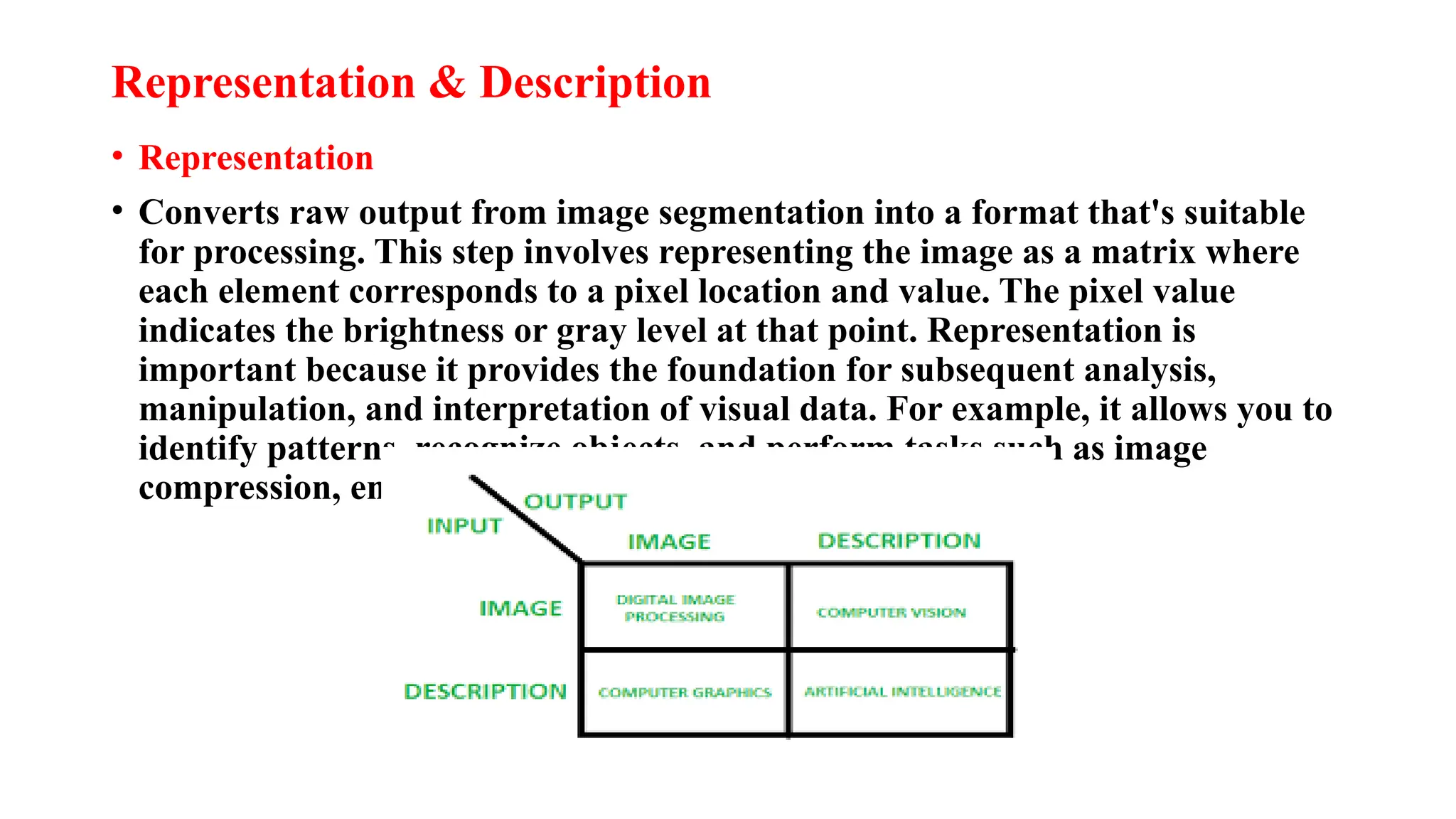
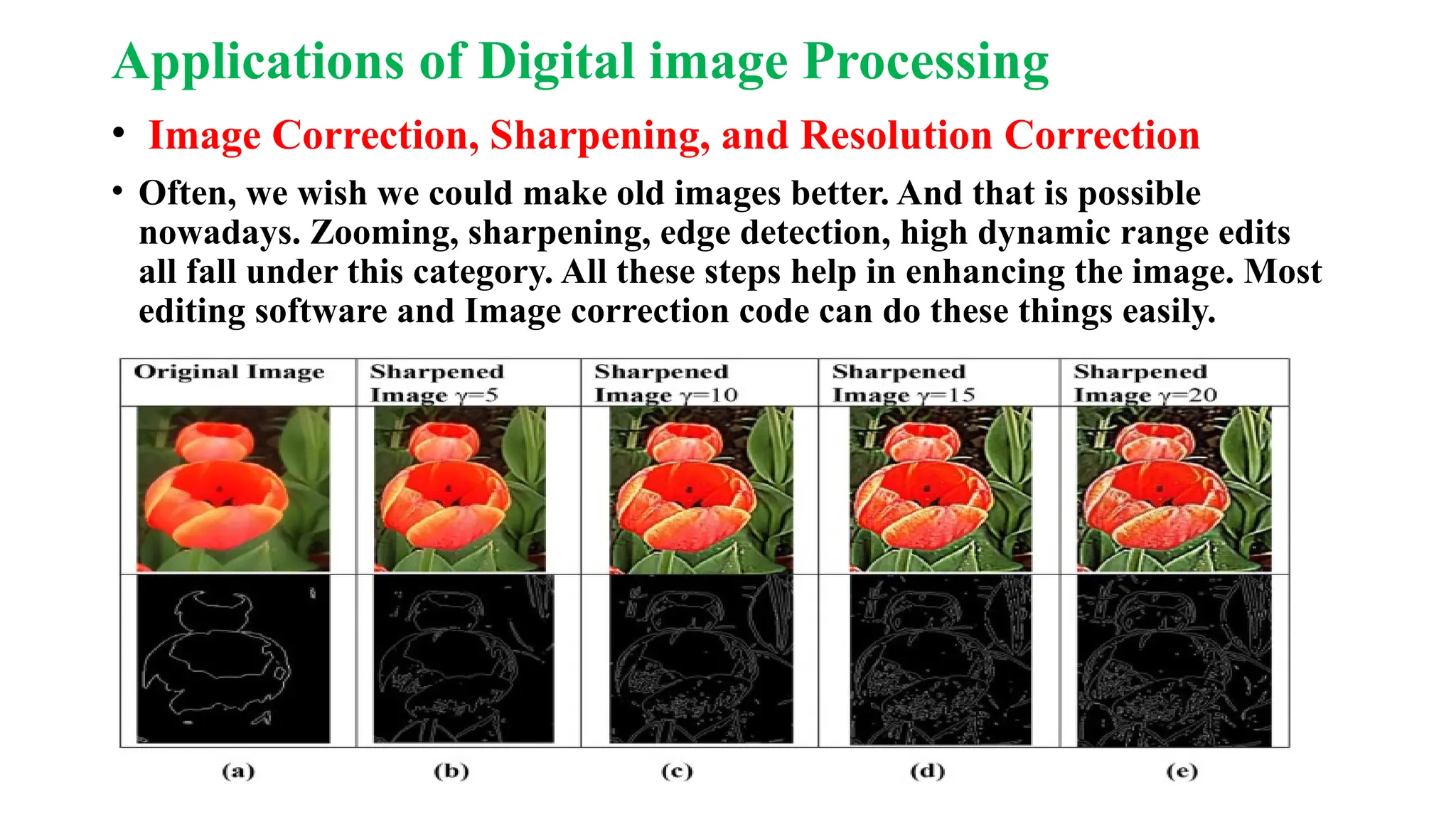
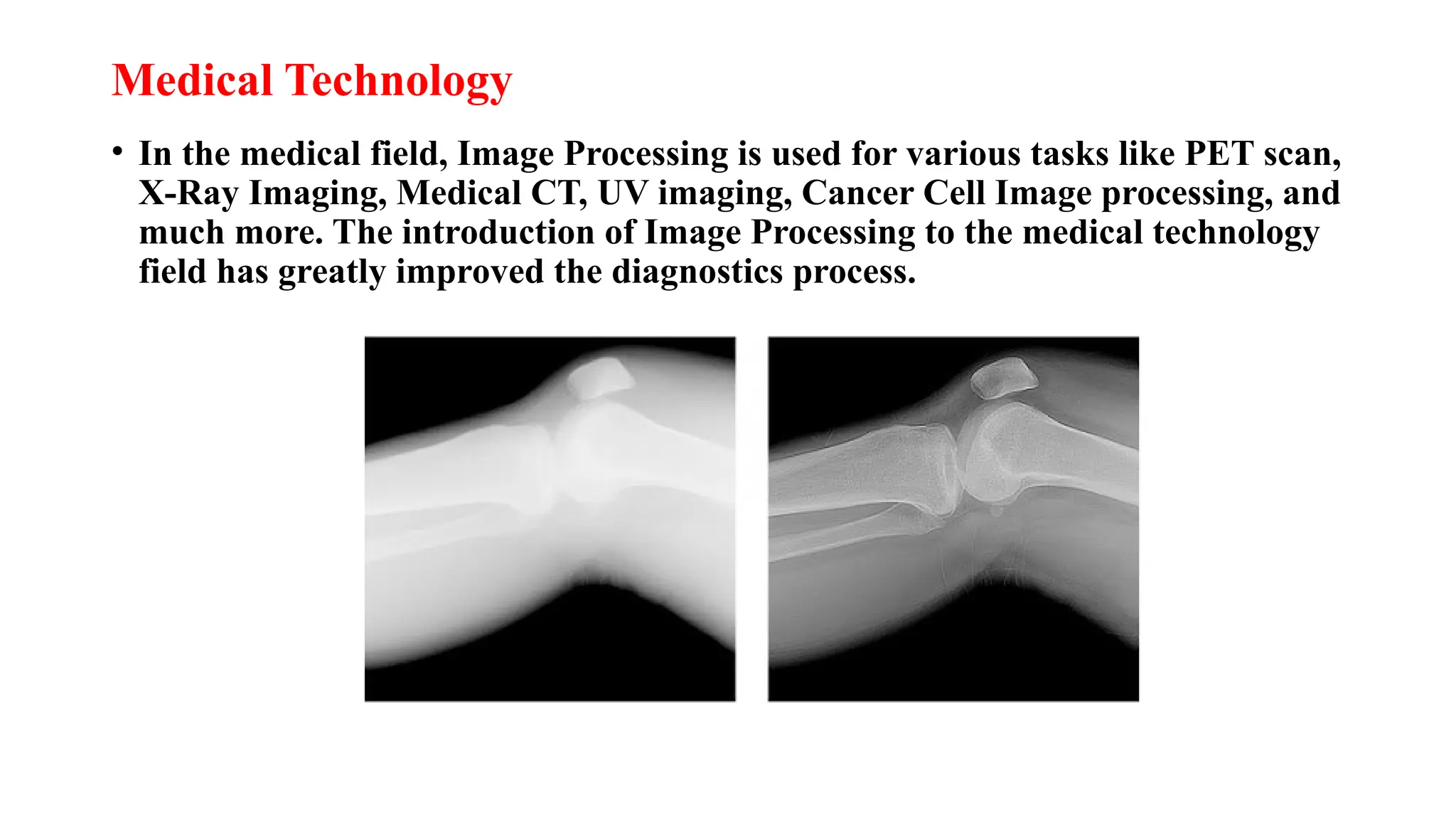
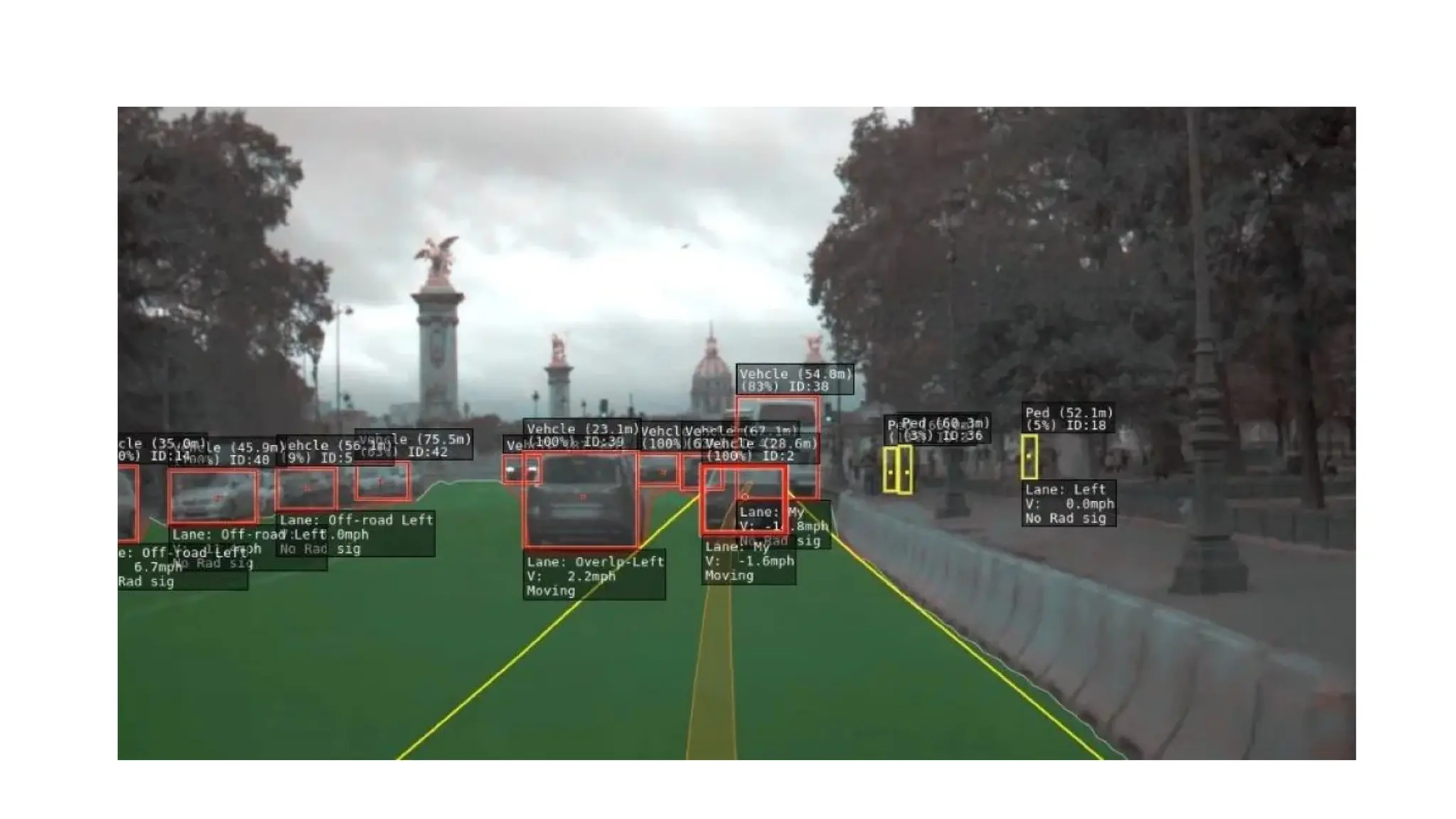
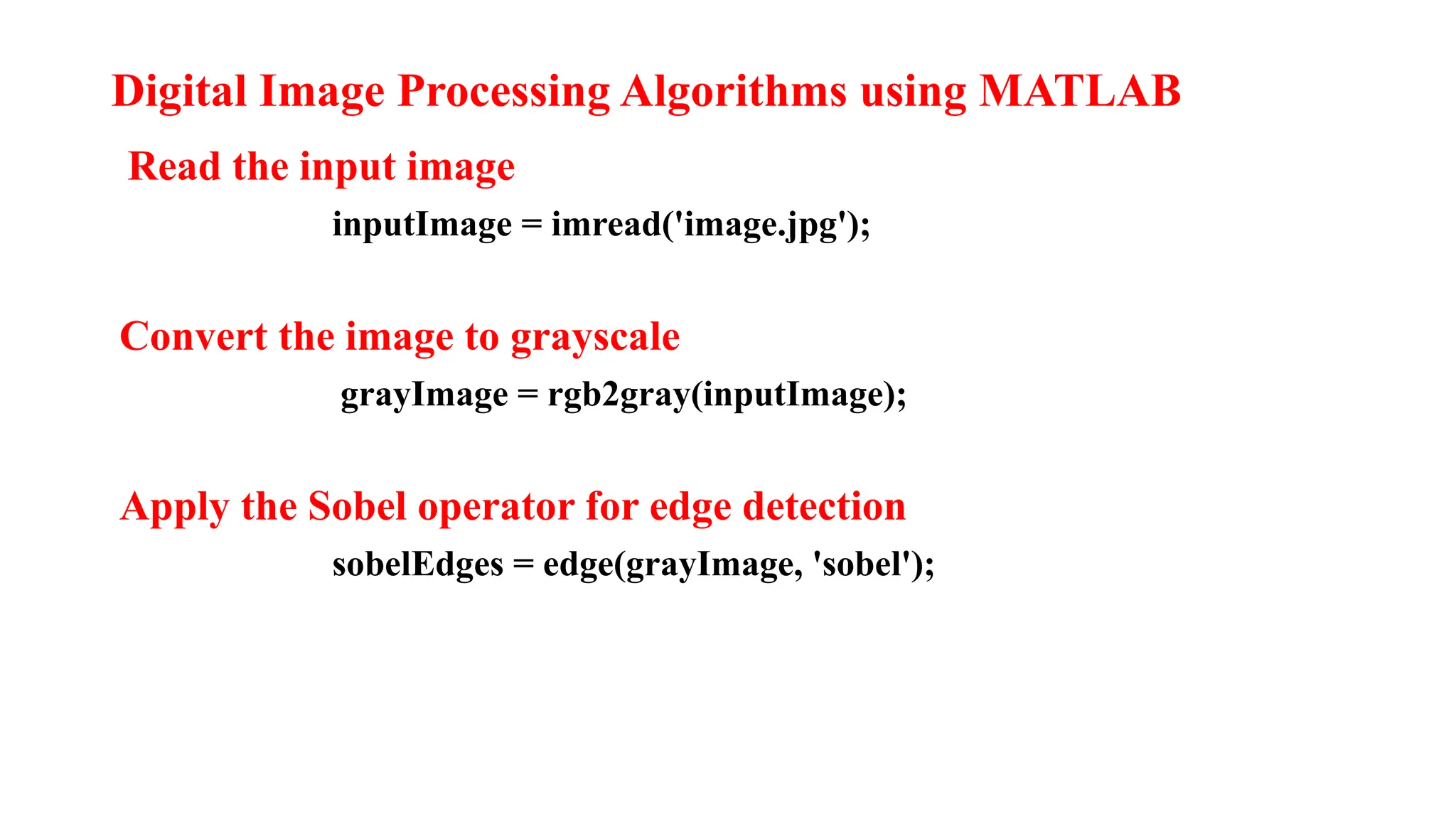
Digital image processing involves transforming images into a digital format and performing operations to extract information. Key stages include image acquisition, enhancement, restoration, morphological processing, segmentation, object recognition, and representation. Applications range from medical imaging and computer vision to video processing and image correction, utilizing algorithms for various enhancement and analysis tasks.