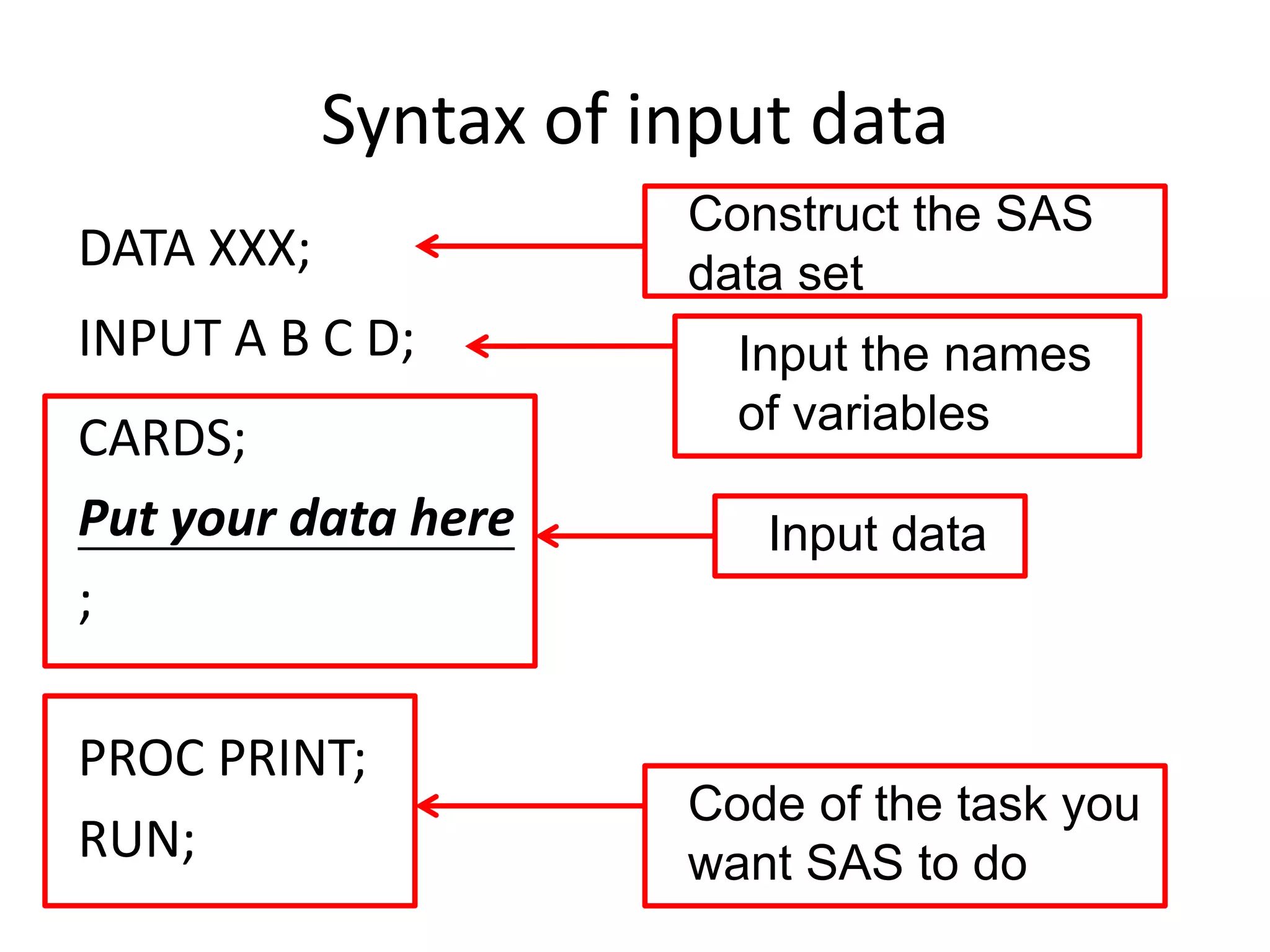
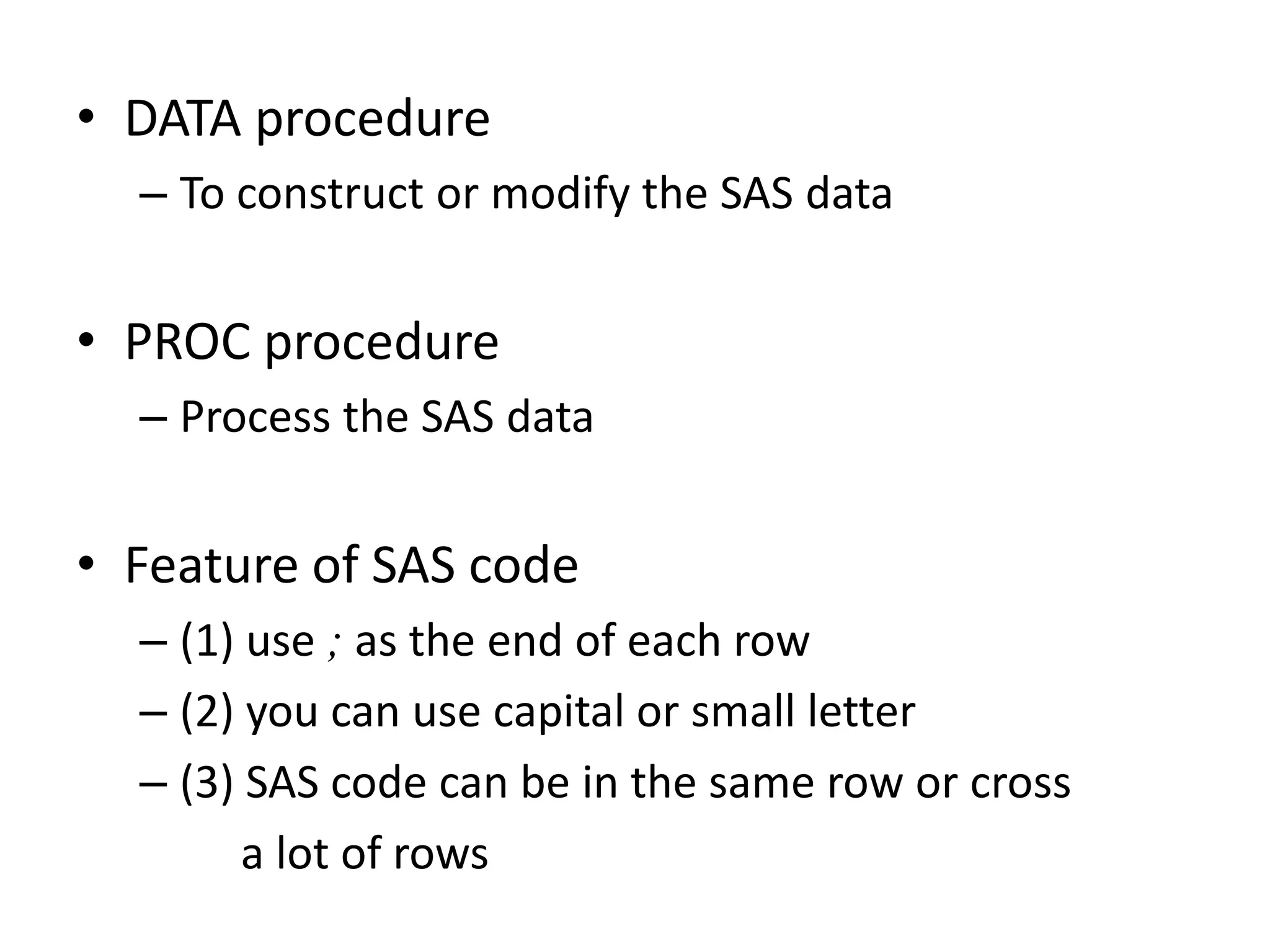
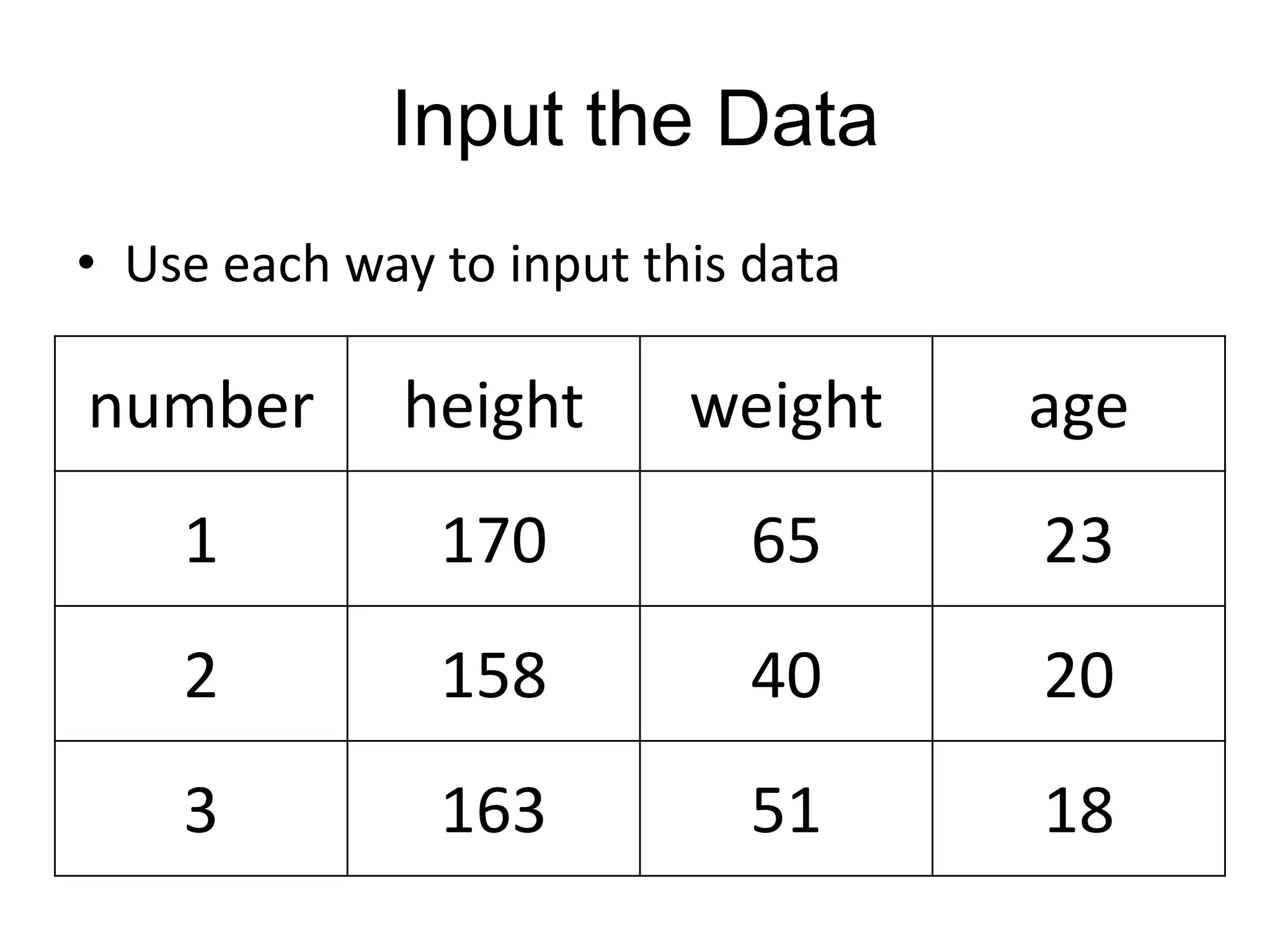
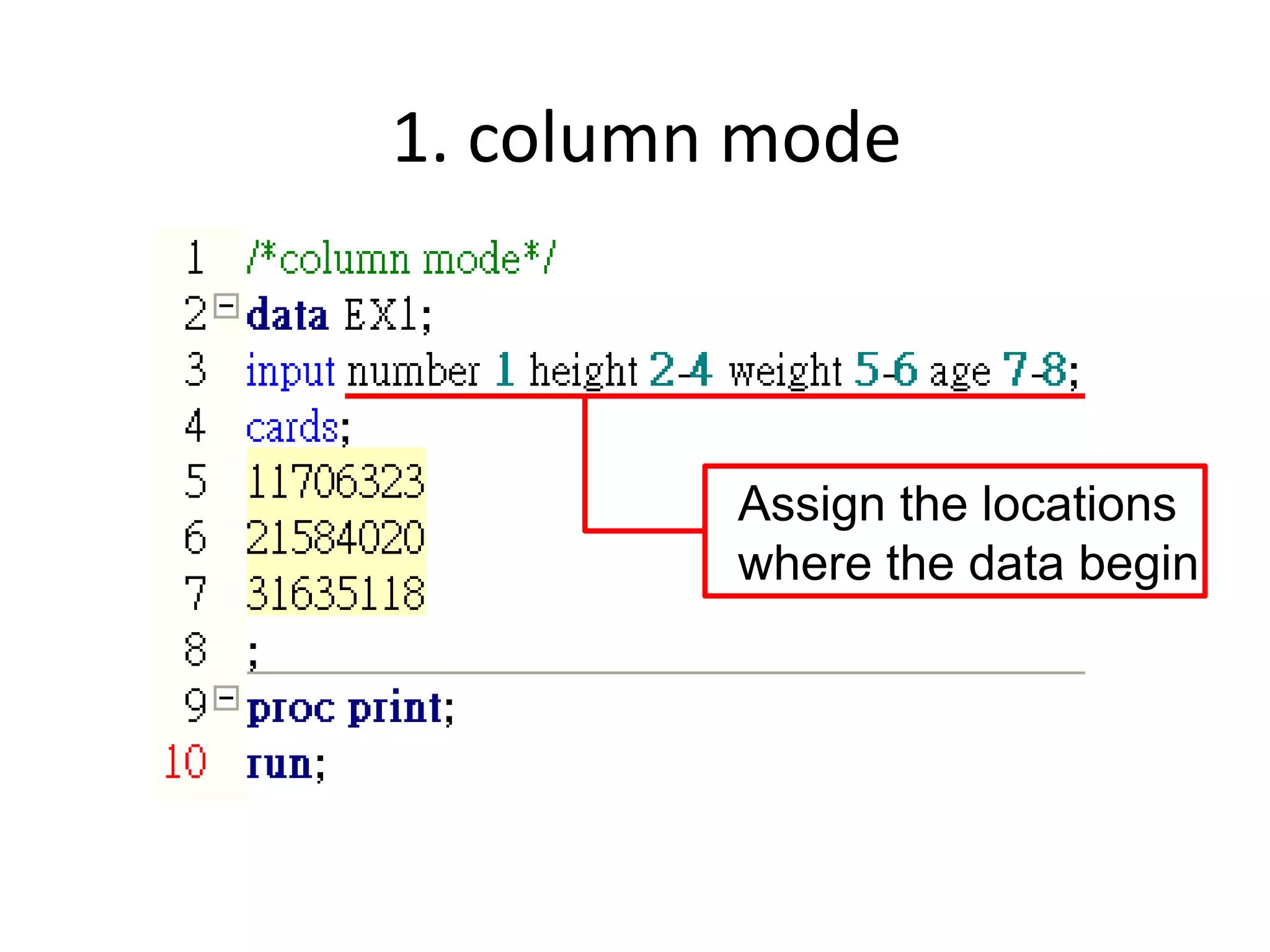
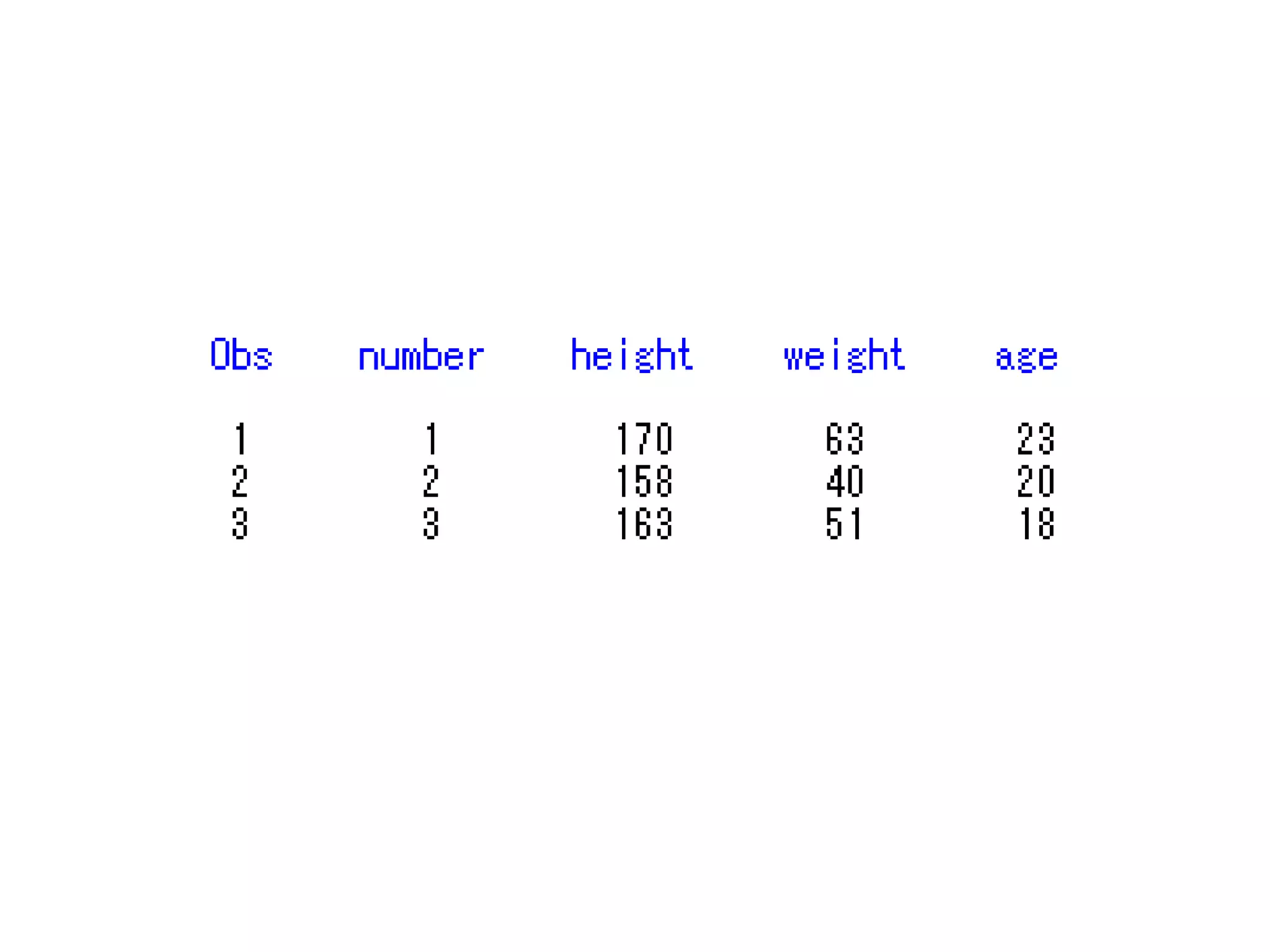
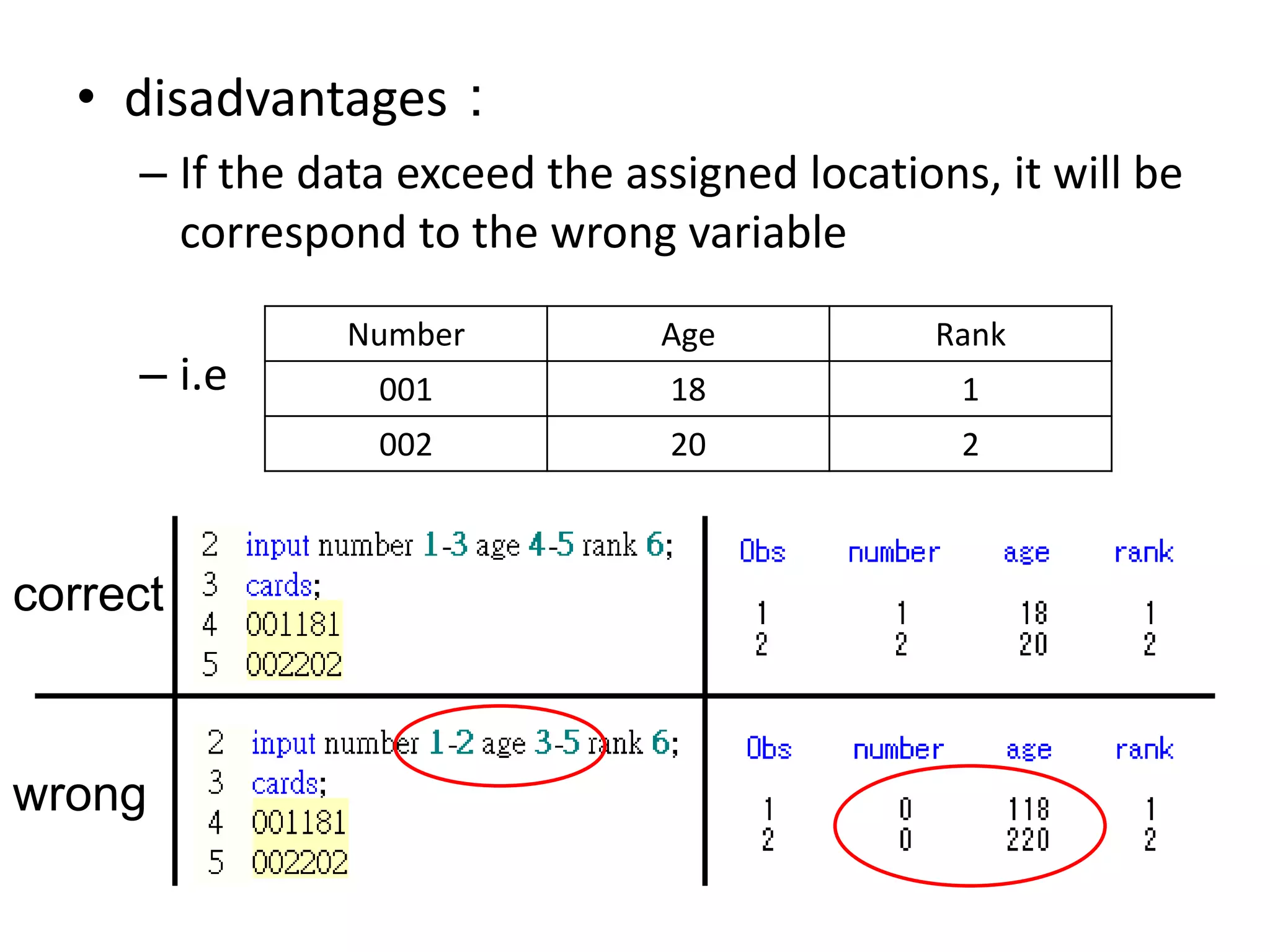
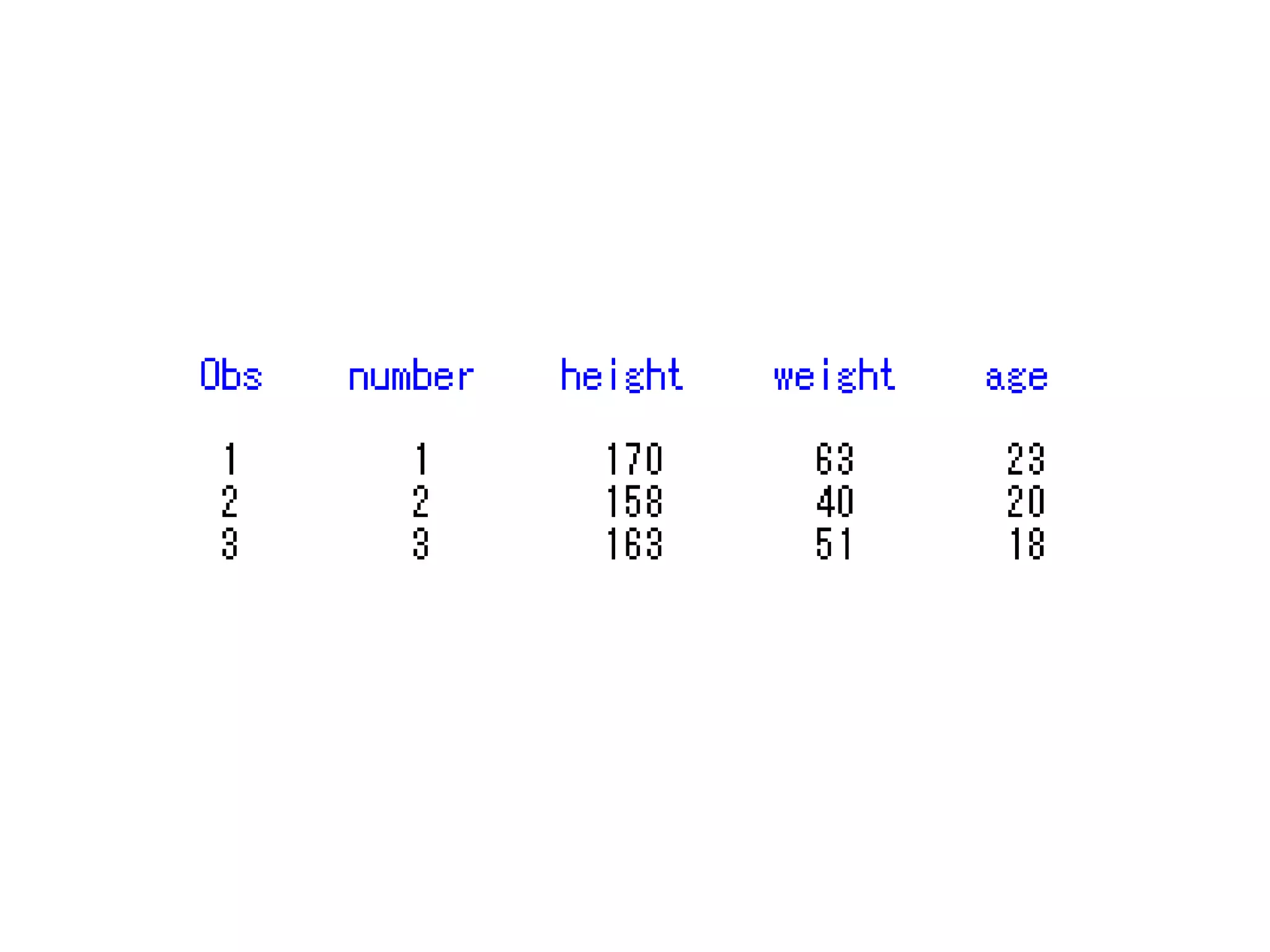
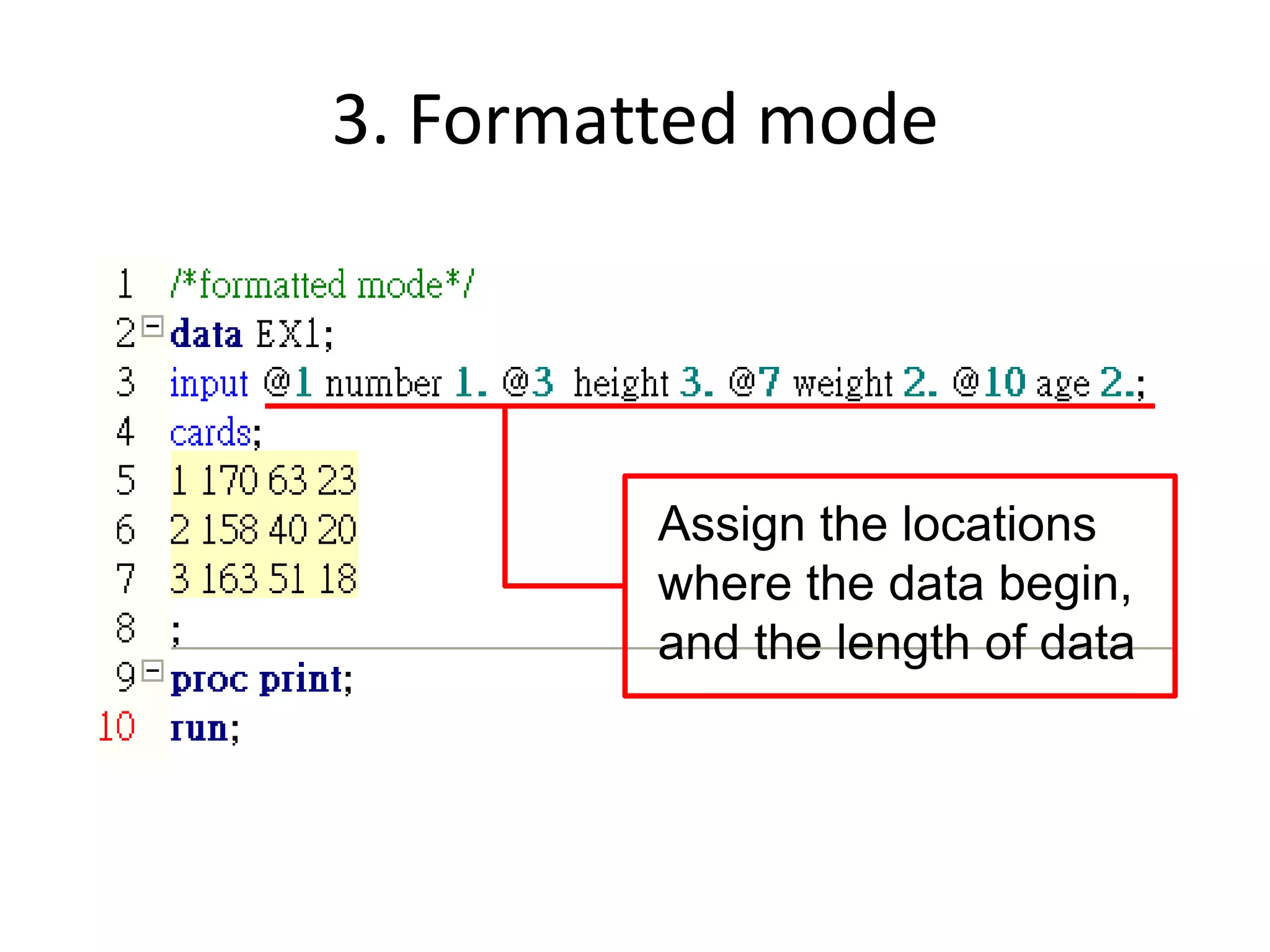
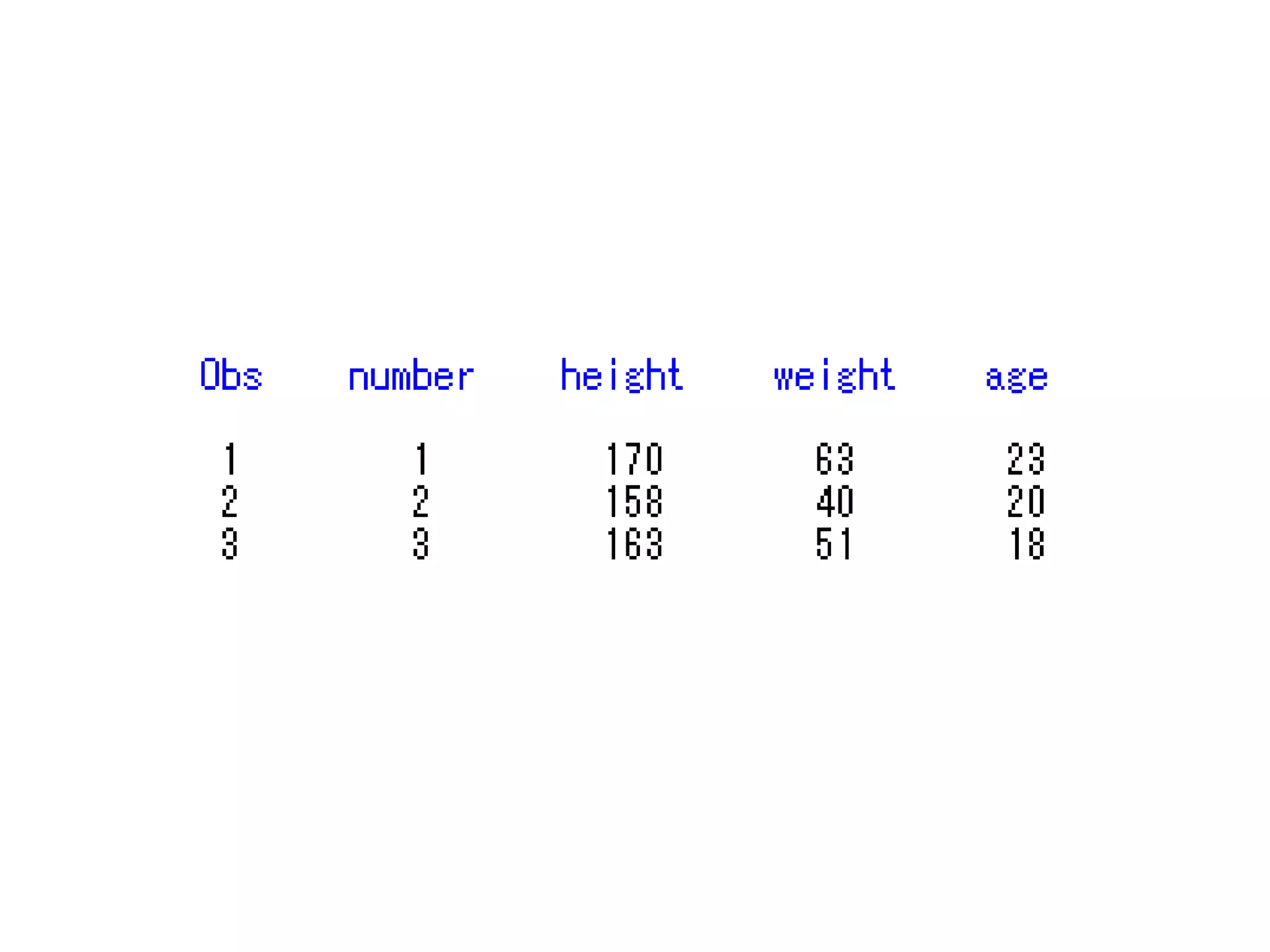
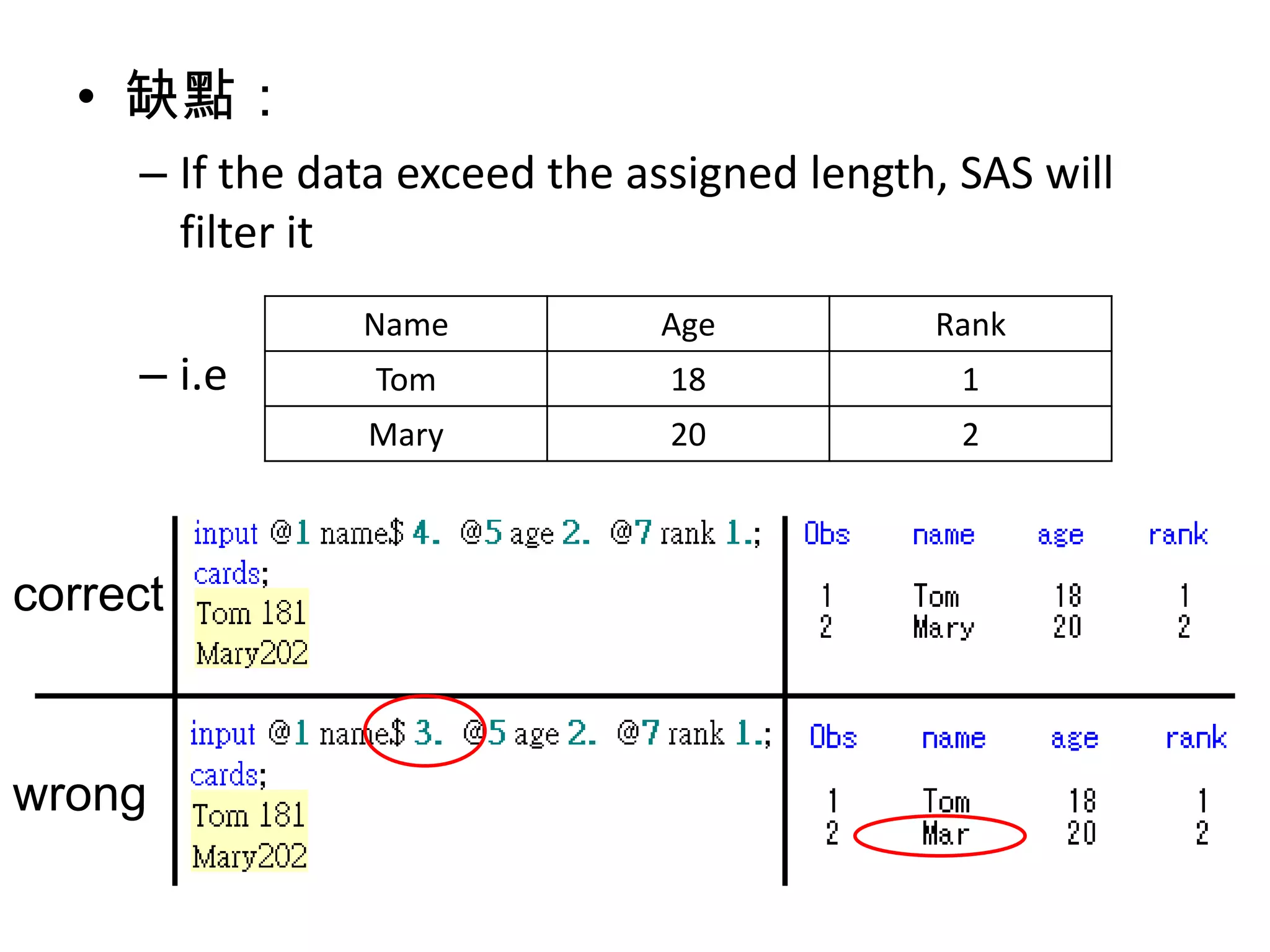
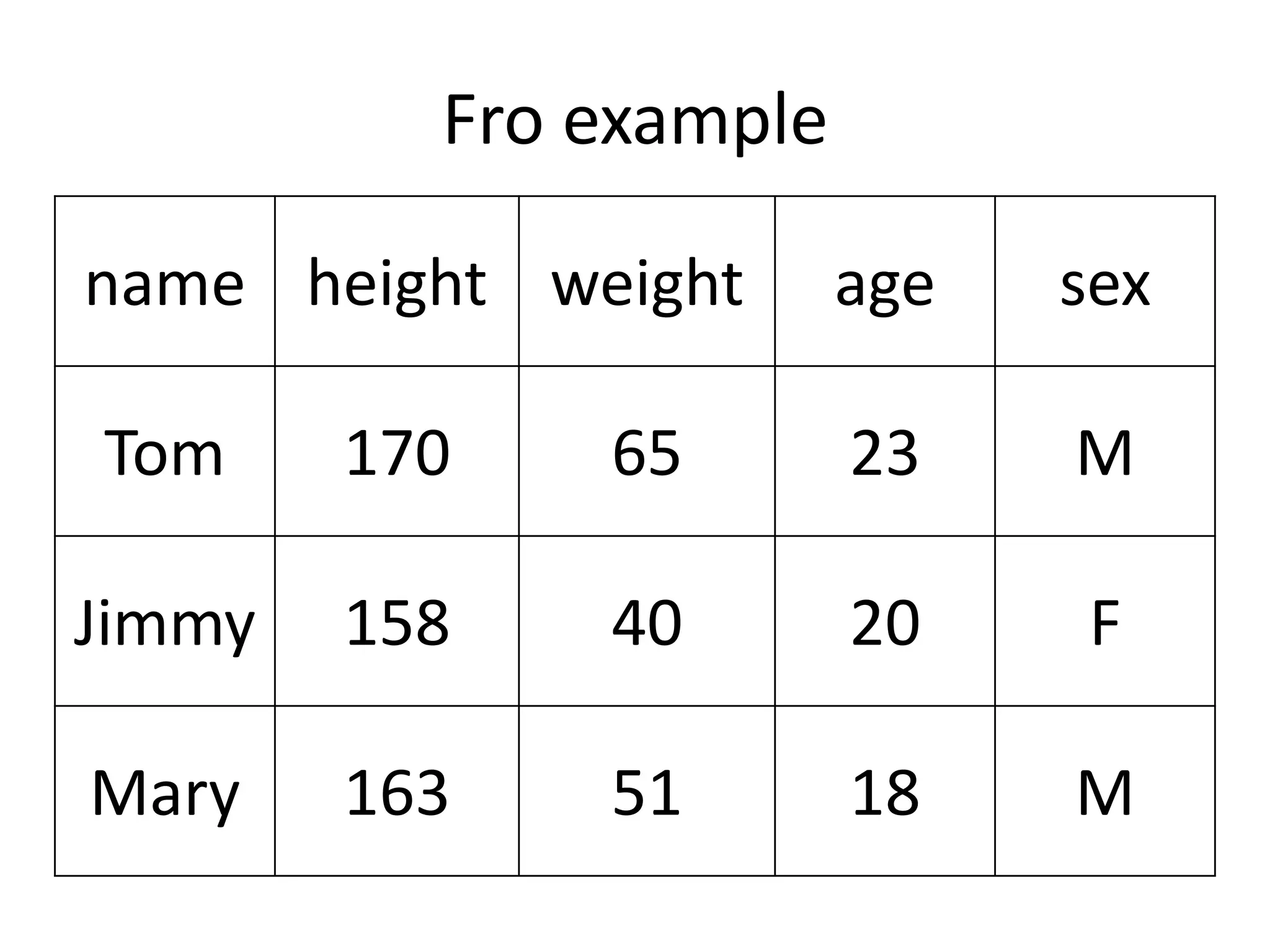
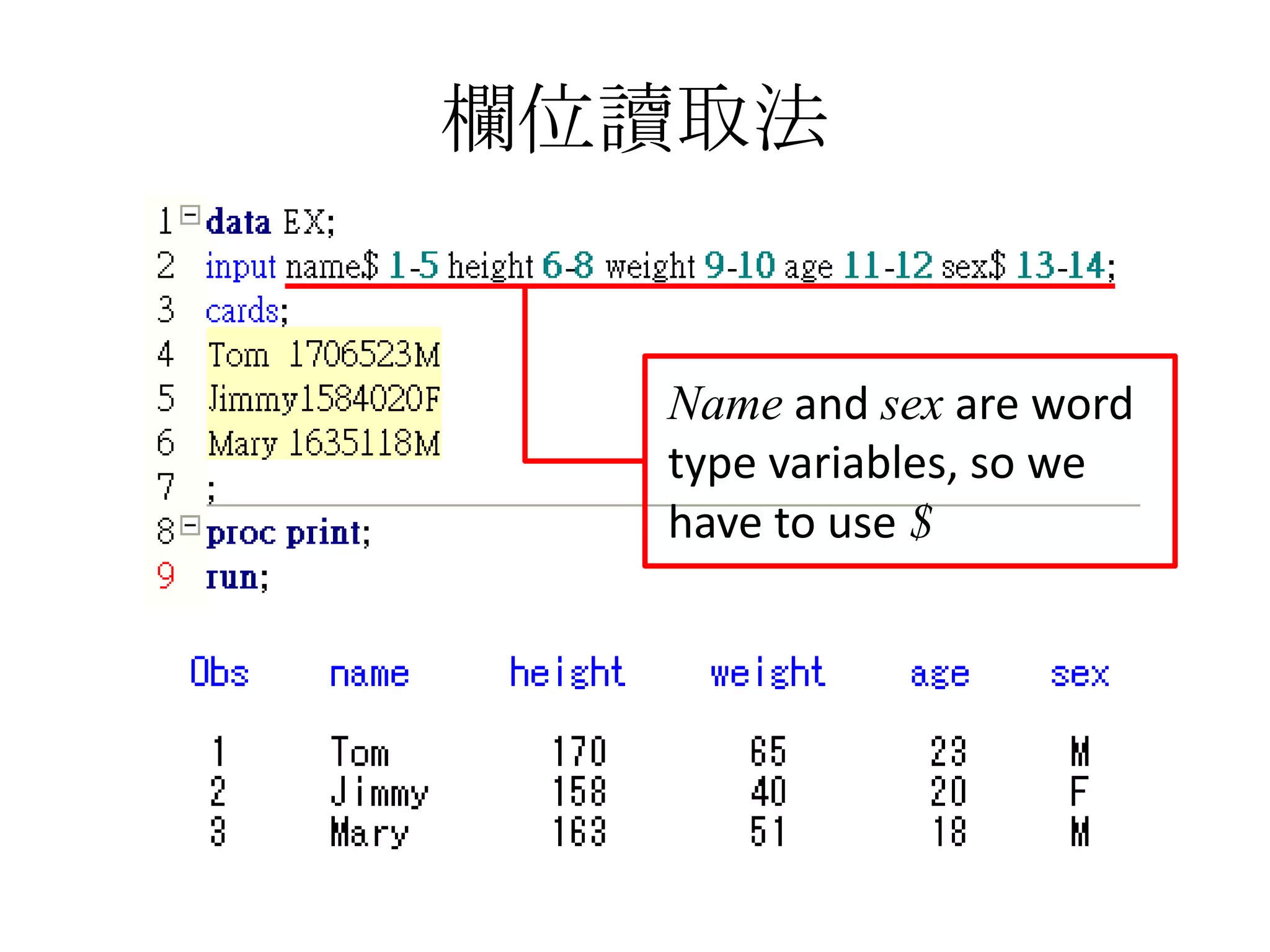
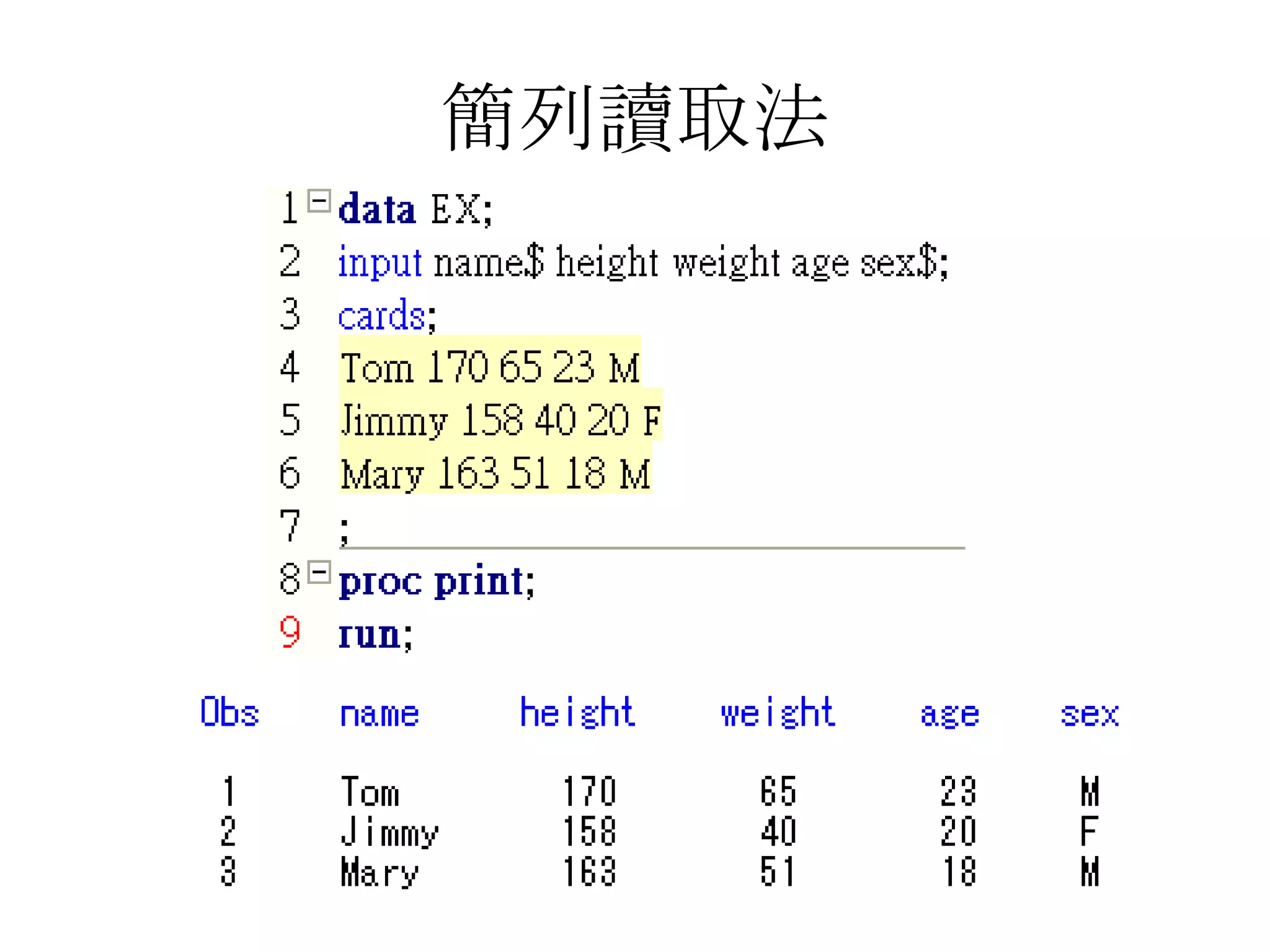
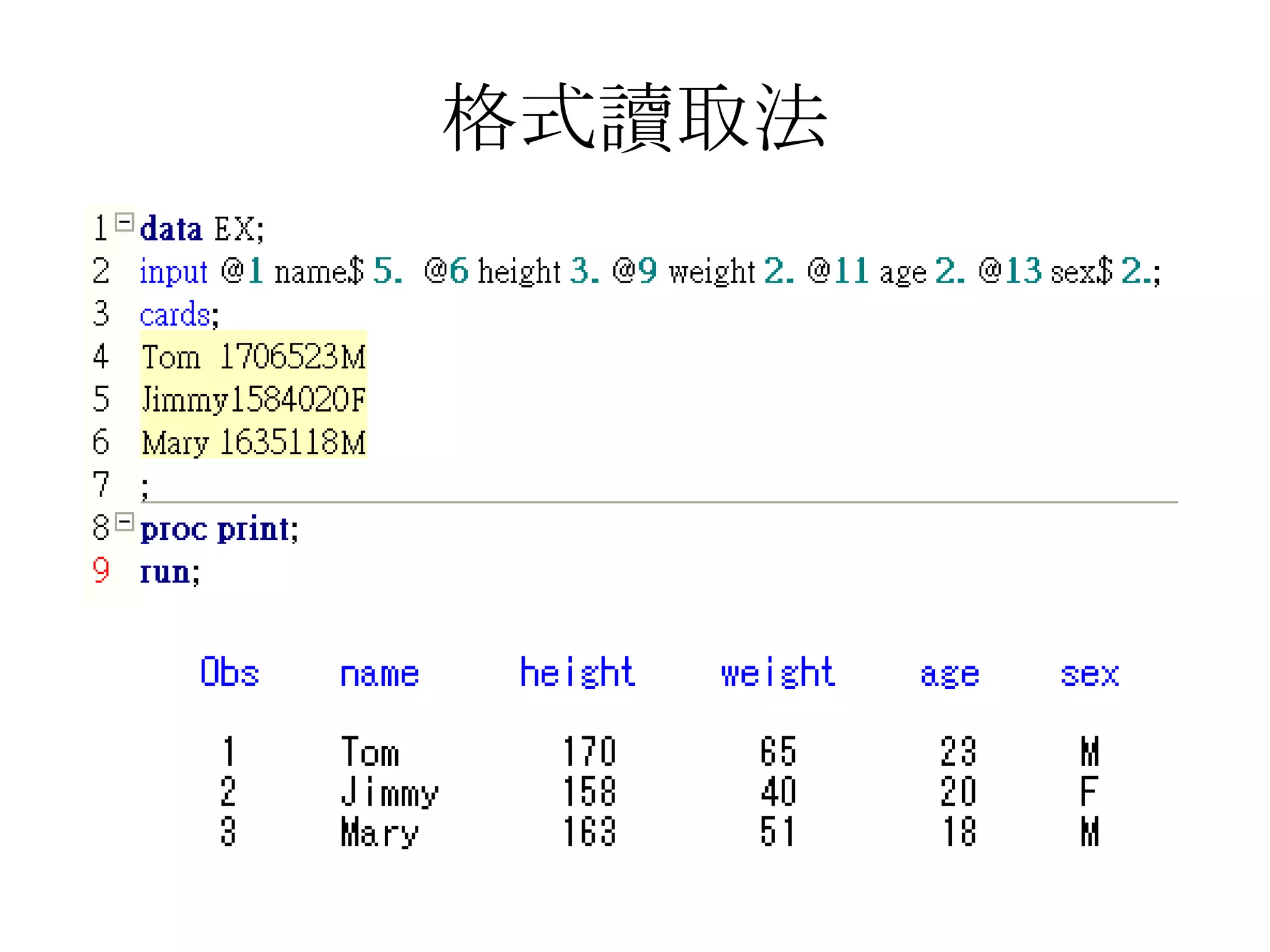
This document summarizes different methods for inputting data in SAS, including column mode, list mode, and formatted mode. Column mode requires calculating data locations, while list mode is easiest, separating data with blanks and only allowing periods for missing values. Formatted mode requires specifying data lengths and allows blanks or periods for missing values. List mode is generally preferred for inputting data when lengths are unequal, as it easily handles variable data with blanks as separators.