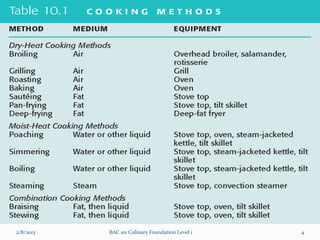
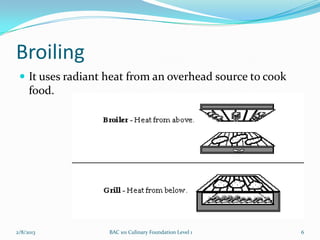
This document outlines different cooking methods taught in a culinary foundations course. It defines dry heat methods like broiling, grilling, roasting, baking, sautéing, stir-frying, pan-frying and deep-frying. Moist heat methods covered are poaching, boiling, steaming and sous vide. Combination methods like braising and stewing are also discussed. For each method, the document explains the cooking process, advantages, disadvantages and safety rules. Students are assigned presentations on Indian or Asian cooking methods using pictures and explanations.