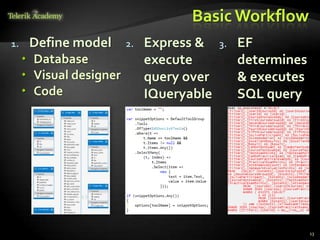
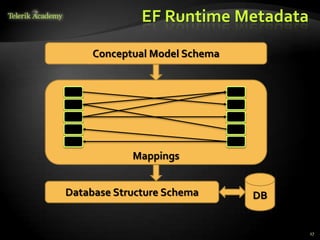
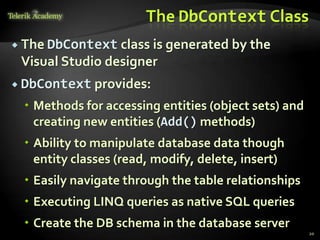
This document provides an overview of Entity Framework (EF), an object-relational mapping (ORM) framework that allows .NET applications to access and manipulate relational data as objects. It discusses EF concepts like the DbContext class, entity classes, associations, and change tracking. It demonstrates basic EF workflows and shows how to perform CRUD operations, execute LINQ queries, extend entity classes, and attach/detach objects. The document also provides homework assignments related to using EF with the Northwind sample database.





























![Executing Native SQL Queries (2)
Native SQL queries can also be parameterized:
37
NorthwindEntities context = new NorthwindEntities();
string nativeSQLQuery =
"SELECT FirstName + ' ' + LastName " +
"FROM dbo.Employees " +
"WHERE Country = {0} AND City = {1}";
object[] parameters = { country, city };
var employees = context.Database.SqlQuery<string>(
nativeSQLQuery, parameters);
foreach (var emp in employees)
{
Console.WriteLine(emp);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/05entity-framework-130724024109-phpapp01/85/05-entity-framework-37-320.jpg)
















