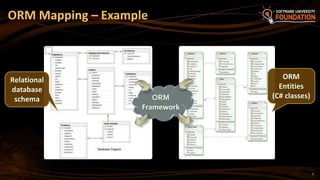
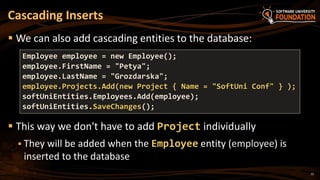
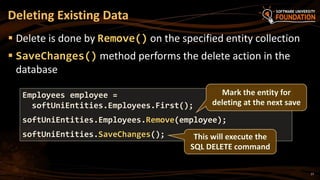
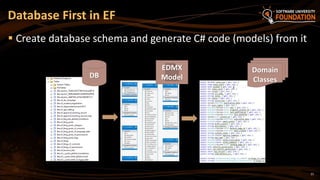
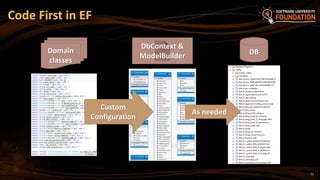
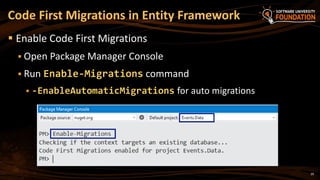
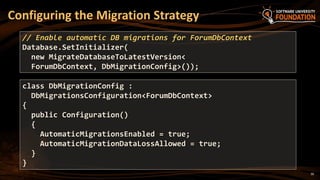
The document provides an overview of Object-Relational Mapping (ORM) technologies and specifically focuses on the Entity Framework (EF) as the standard ORM framework for .NET. It covers fundamental concepts, CRUD operations, and migration strategies using EF, detailing both database-first and code-first approaches for data management and manipulation. Additionally, it includes practical examples and instructions for implementing EF in software development.