Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX






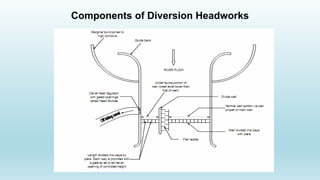


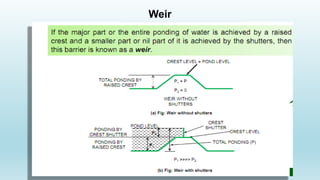

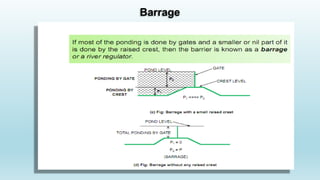

The document discusses diversion headworks, which divert water from a river into a canal. There are two types: storage headworks, which comprise a dam to store excess river water for later release; and diversion headworks, which directly divert water into the canal. Diversion headworks have several components, including a weir or barrage across the river to raise the water level, canal head regulators, and sluices. A weir is a solid obstruction across the river, while a barrage is a low weir with adjustable gates to control the water level.












