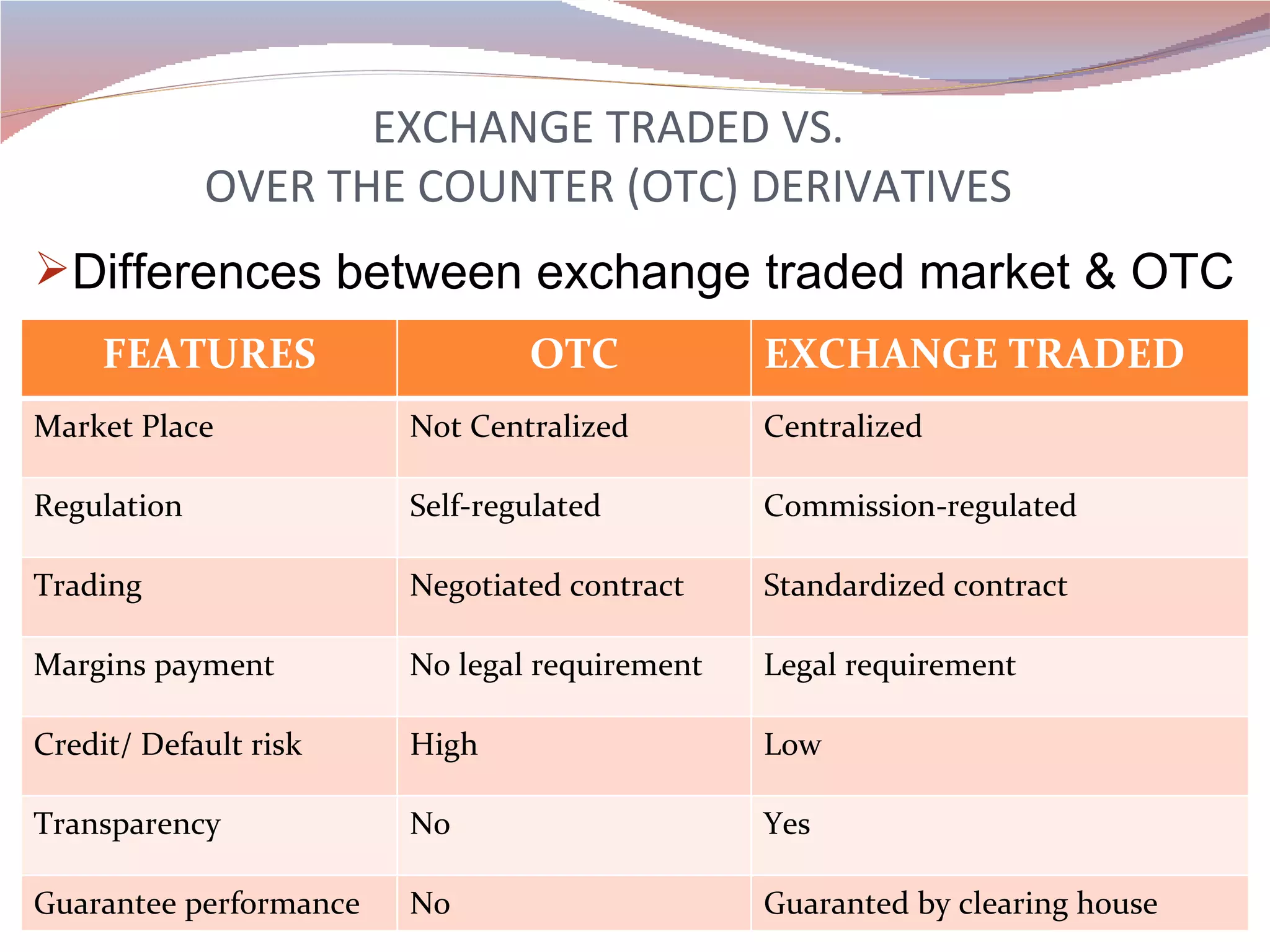
Derivatives are financial instruments whose value is derived from an underlying asset such as a commodity, bond, or equity. There are two main types of derivatives - futures contracts, which are agreements to buy or sell an asset in the future at an agreed upon price, and options contracts, which give the holder the right but not the obligation to buy or sell the underlying asset. Derivatives markets allow participants to manage risks and generate income associated with changes in prices of the underlying assets. Exchanges facilitate trading of standardized derivatives contracts and provide clearing houses to guarantee the performance of all contracts.