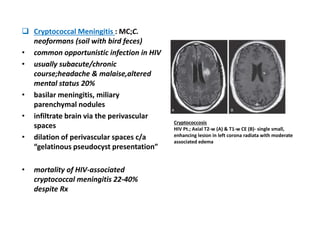
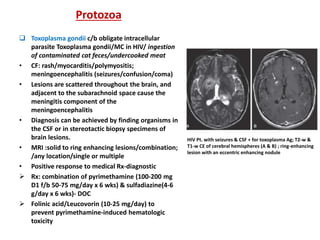
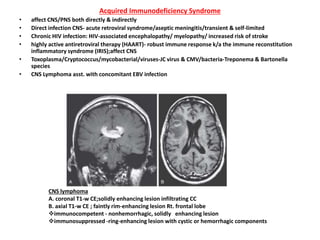
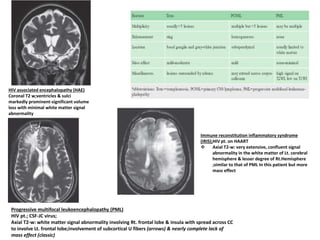
This document discusses infections in neurosurgery, including:
1. The basic science of central nervous system infections, how pathogens enter the CNS, and the roles of microglia and astrocytes in the immune response.
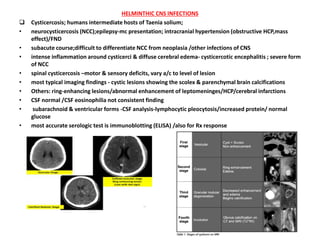
2. Postoperative infections, which are most commonly caused by Staphylococcus aureus and coagulase-negative staphylococci. Risk factors include poor wound healing and device implantation.
3. Empirical treatment regimens typically involve vancomycin, third-generation cephalosporins, and metronidazole to cover gram-positive, gram-negative and anaerobic bacteria. Source control is critical for resolving infections.



![CLASSIFICATION
• Anatomy of the infection (parenchymal, meningeal, parameningeal)
• Presence of space-occupying lesions (e.g. abscess, empyema)
• Diffuse inflammation (e.g. meningitis, encephalitis)
• Also a/c to etiology
• Pathogens enter the CNS directly (e.g., through trauma, neurosurgery),
/Via BBB/CSFB (e.g., bacterial meningitis caused by Escherichia coli), /
via retrograde transport along neural structures (e.g., rabies)
• Iatrogenic routes are more relevant to the neurosurgeon
• Perioperative breeches in structural barriers protecting the CNS (scalp,
cranium, meninges), implantation of foreign bodies (e.g., cerebrospinal
fluid [CSF] shunts, dural implants, electrodes, spinal hardware), and
breeches in mucosal defenses (e.g., intubation, vessel catheterization)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/infectionsinneurosurgery-201007144543/85/Infections-in-neurosurgery-4-320.jpg)




![PRINCIPLES OF TREATMENT
•Postoperative infections tend to be particularly difficult to resolve because of the complex
anatomic changes resulting from craniotomy
•Early and decisive intervention is critical to limit morbidity, and the keystone of successful
treatment is effective source control (i.e., drainage of abscesses and infected fluid
collections and debridement of necrotic tissue)
•Bactericidal rather than bacteriostatic agents are generally preferred
•Most antibiotic agents enter CNS mostly by passive diffusion down a concentration
gradient, with physical barriers BBB and blood-CSF barriers functioning as the primary
determinants of drug distribution
•Inflammation at the site of infection may facilitate entry of drugs across these barriers and
into the brain
•Other inherent physiochemical properties: Mwt., lipophilicity, PPB & ionization state
•Ultimately, adequate dosing - minimal bactericidal concentration [MBC]).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/infectionsinneurosurgery-201007144543/85/Infections-in-neurosurgery-10-320.jpg)

![ CSF Shunt Infections: The Role of Biofilms
• Perioperative contamination/Wound dehiscence over the shunt
/Hematogenous seeding/Distal port contamination
• Biofilm formation occurs with both infection and colonization of
prosthetic medical devices
• Biofilms are in a stationary phase of growth-less susceptible to
antibiotics/less permeable to most antibiotics/prosthetic devices lack a
vascular supply
• Coagulase-negative staphylococci (CoNS)-notorious for their ability to
form biofilm on prosthetic devices
• Soon after placement, bioprosthetic materials are coated with host
proteins, which serve as receptors for bacterial adhesins k/a “microbial
surface components recognizing adhesive matrix molecules,” or
MSCRAMMs- CoNS initiate biofilm formation almost immediately
• Transition state between planktonic and sessile bacteria in biofilms
known as quorum sensing
• Dormant microbes (sessile) within the biofilm are up to a 1000 times
more tolerant of [most] antimicrobial agents than their free-living
(planktonic)
S. epidermidis biofilm formation on a
catheter surface. Note the deposition of
extracellular matrix,manifested as a
complex web of material around and
between microcolonies](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/infectionsinneurosurgery-201007144543/85/Infections-in-neurosurgery-12-320.jpg)



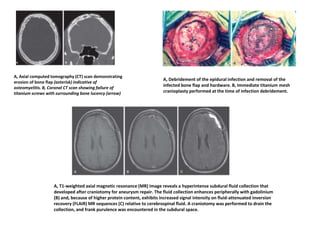



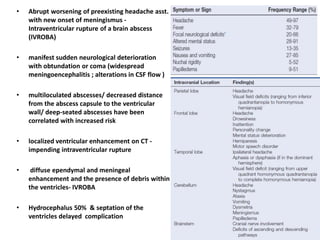
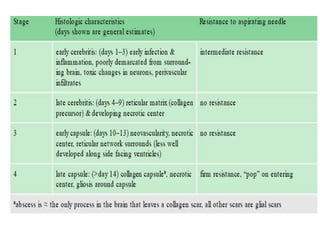

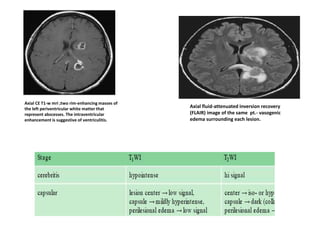
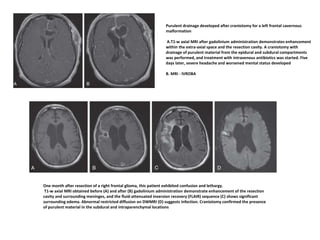



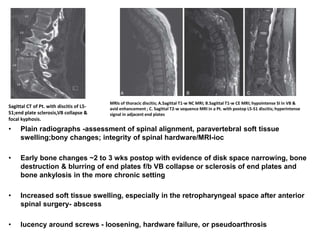










![ Recurrent bacterial meningitis : 2 separate episodes of meningitis separated by a
period of full recovery; 6%
• Risk : 1) anatomic factors (2) immunodeficiencies [(X-linked agammaglobulinemia
(Bruton’s disease),HIV]& (3) chronic parameningeal infections (sinusitis, otitis
media, and mastoiditis. )
• Anatomic factors -congenital (encephaloceles, congenital inner ear
dysplasia,)/acquired (head trauma or skull fracture-csf leak )
• head trauma MCC
• CT scan with thin cuts through the skull base on bone windows
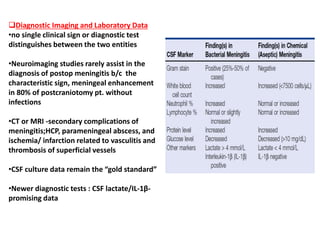
Encephalitis or meningoencephalitis: gram-negative bacillus Legionella
pneumophila/Mycoplasma pneumoniae/L. monocytogenes
• Aseptic meningitis - nonbacterial inflammation of the tissues lining the
brain;viruses/fungi/parasites/protozoa/Rickettsia species
• noninfectious etiologies (e.g., drugs, collagen vascular disorders, sarcoidosis)
• Viruses account for the vast majority of cases of aseptic meningitis
• any age but most common in infants and children.
• Enteroviruses are the most common cause of viral meningitis
• include echovirus, coxsackievirus groups A and B & poliovirus
• transmitted via the fecal-oral route](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/infectionsinneurosurgery-201007144543/85/Infections-in-neurosurgery-42-320.jpg)