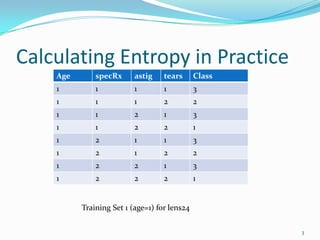
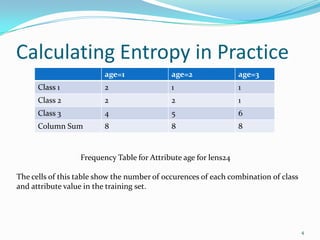
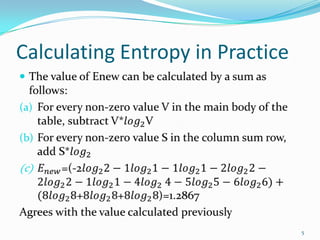
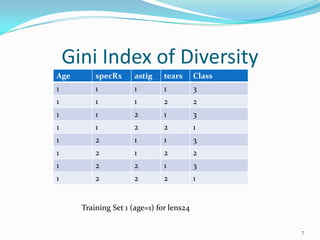
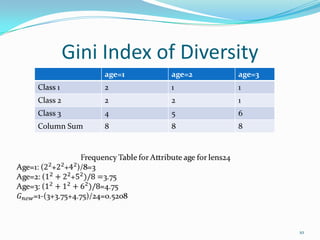
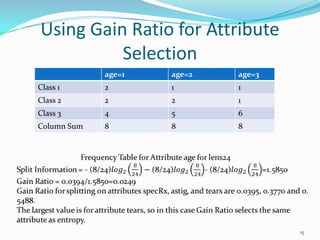
This document discusses different methods for attribute selection in decision tree induction, including calculating entropy, the Gini index of diversity, and using gain ratio. It provides examples calculating these metrics on a sample training dataset to select the best attribute for splitting. The key points made are:
1) Entropy, Gini index, and gain ratio can be used to calculate the information gain of splitting on different attributes to select the optimal one.
2) Gain ratio reduces the bias of information gain by normalizing it by the split information.
3) On the example lens dataset, all three methods (entropy, Gini index, gain ratio) select the "tears" attribute as providing the greatest information gain.