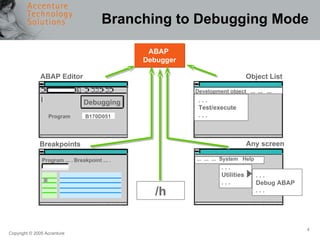
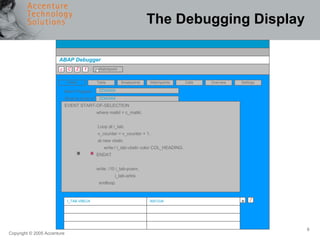
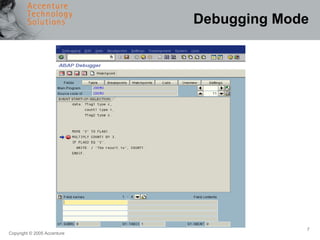
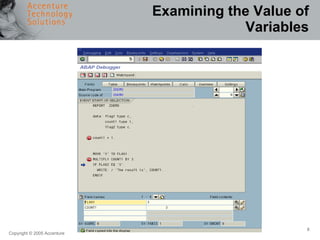
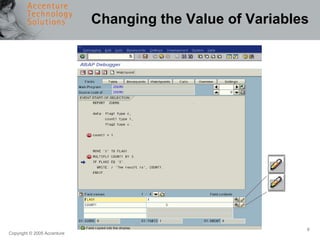
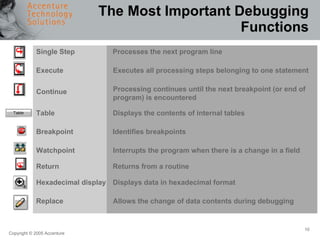
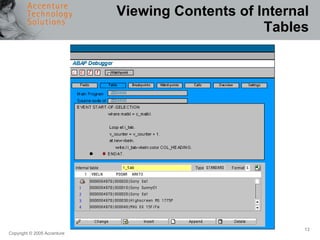
The document provides an overview of debugging in ABAP, including defining debugging, branching to debugging mode, key concepts such as breakpoints and watchpoints, examining and changing variables, and viewing contents of internal tables. It describes debugging modes, the debugging display, and the most important debugging functions such as single step, continue, breakpoint, watchpoint, and hexadecimal display. It also discusses setting breakpoints and watchpoints and using the ABAP debugger.