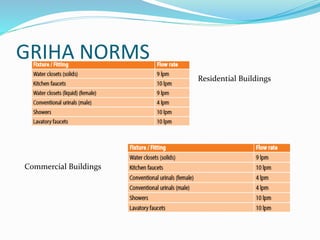
The document outlines the importance of auditing buildings for establishing baselines, defining capital expenditures, and enhancing tenant marketing. It presents methodologies for calculating water consumption, water use reduction, and landscape water requirements, stressing efficient irrigation and fixture usage. Additionally, it details performance metrics for cumulative water usage reduction and conservation effects in buildings.