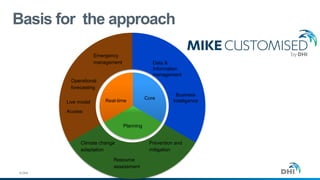
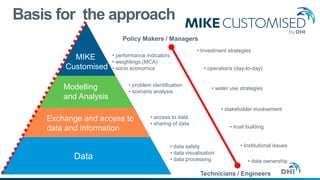
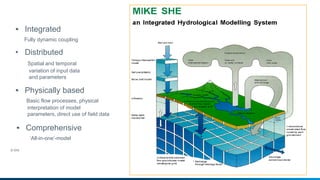
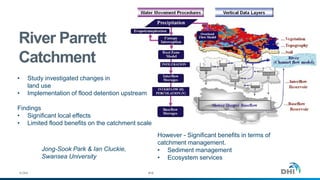
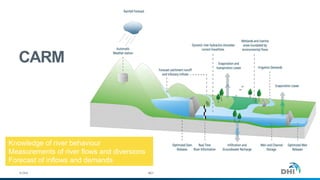
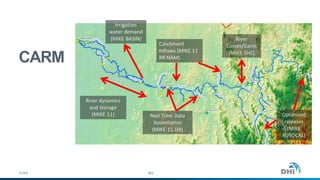
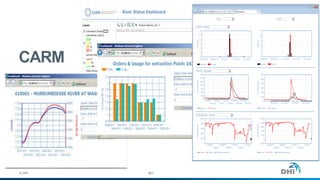
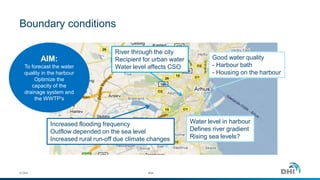
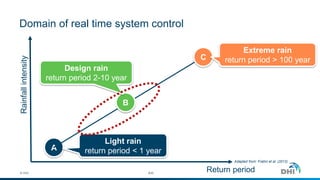
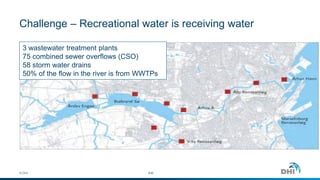
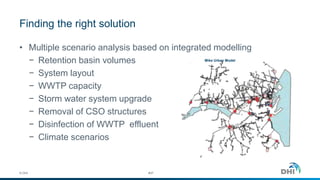
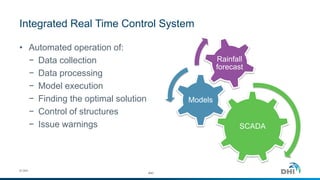
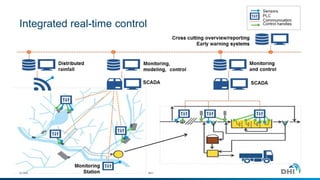
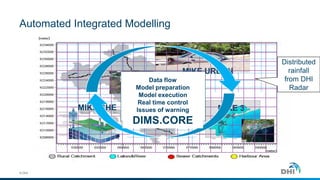
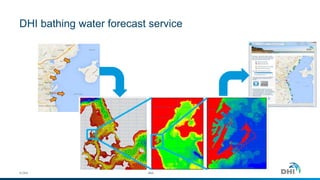
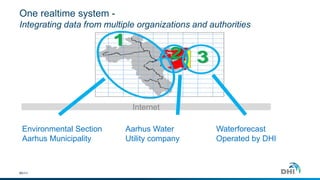
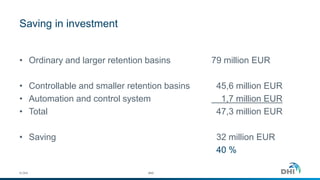
The document presents an integrated modeling approach for managing water environments, focusing on real-time catchment management and climate change adaptation. DHI outlines its expertise and tools for data management, scenario analysis, and stakeholder involvement to address water quality, flood control, and sustainable urban development. Specific case studies, including river management in Aarhus, Denmark, showcase successful implementation of infrastructure and real-time control systems to enhance water quality and reduce flooding risks.