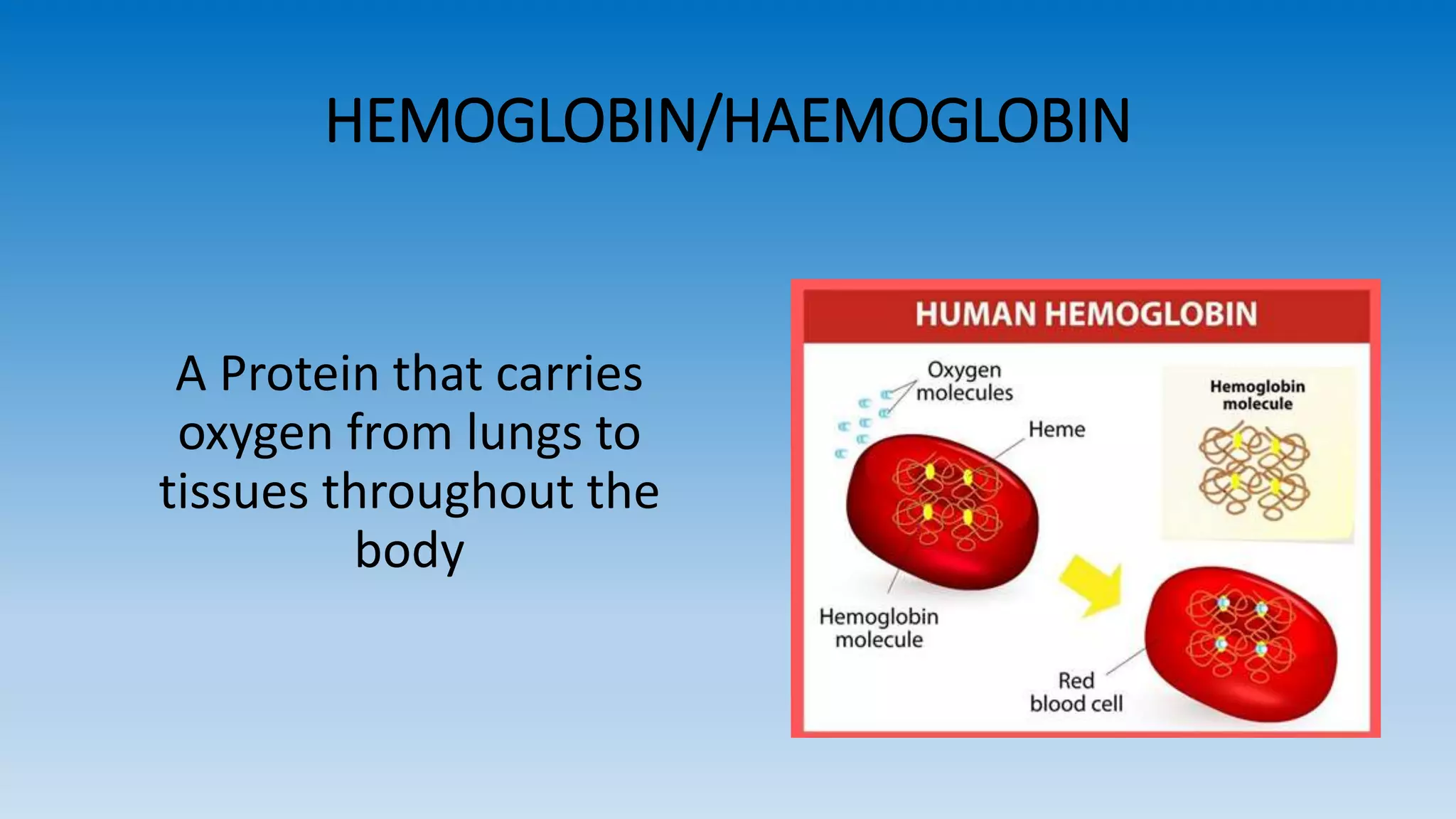
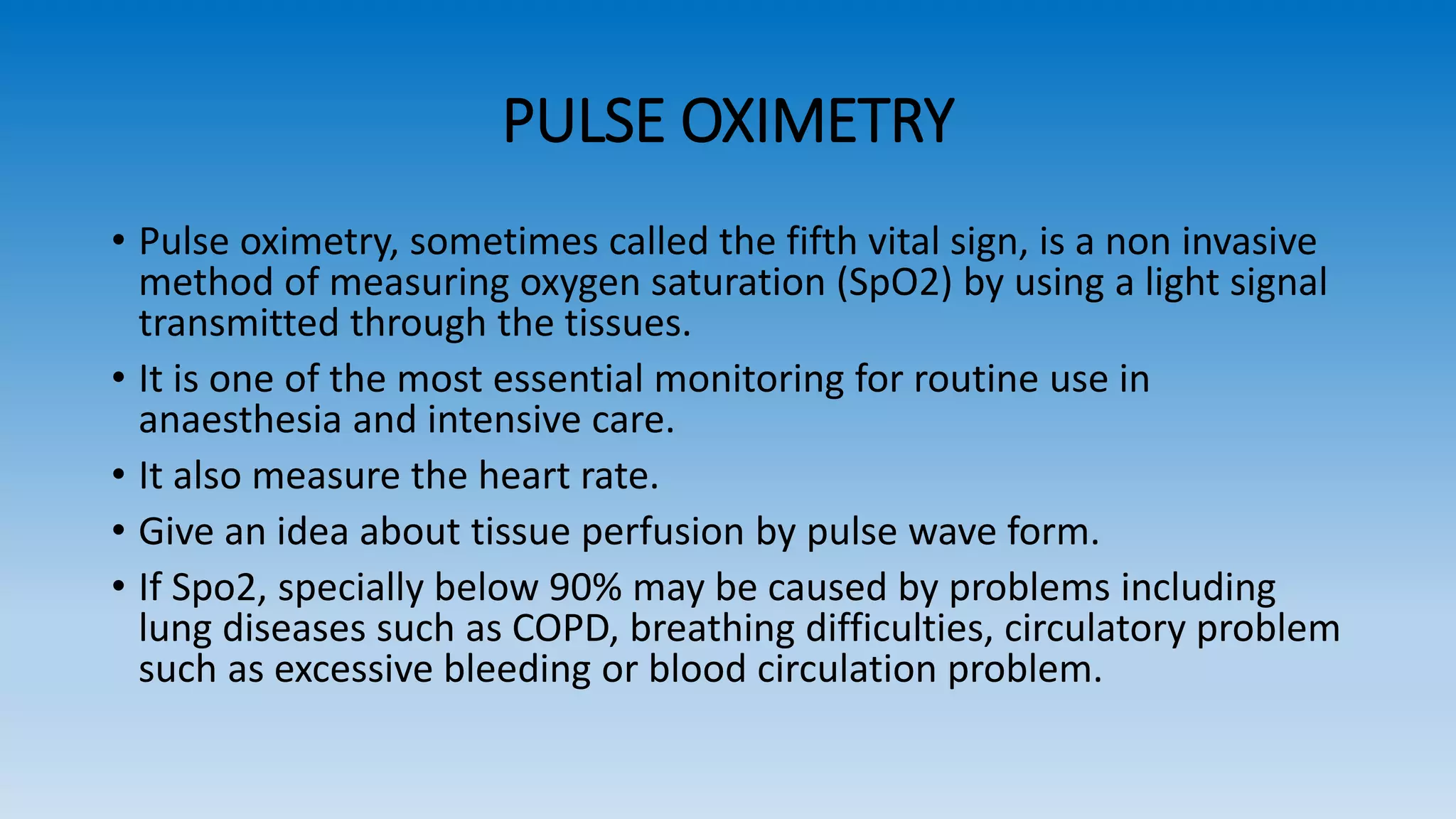
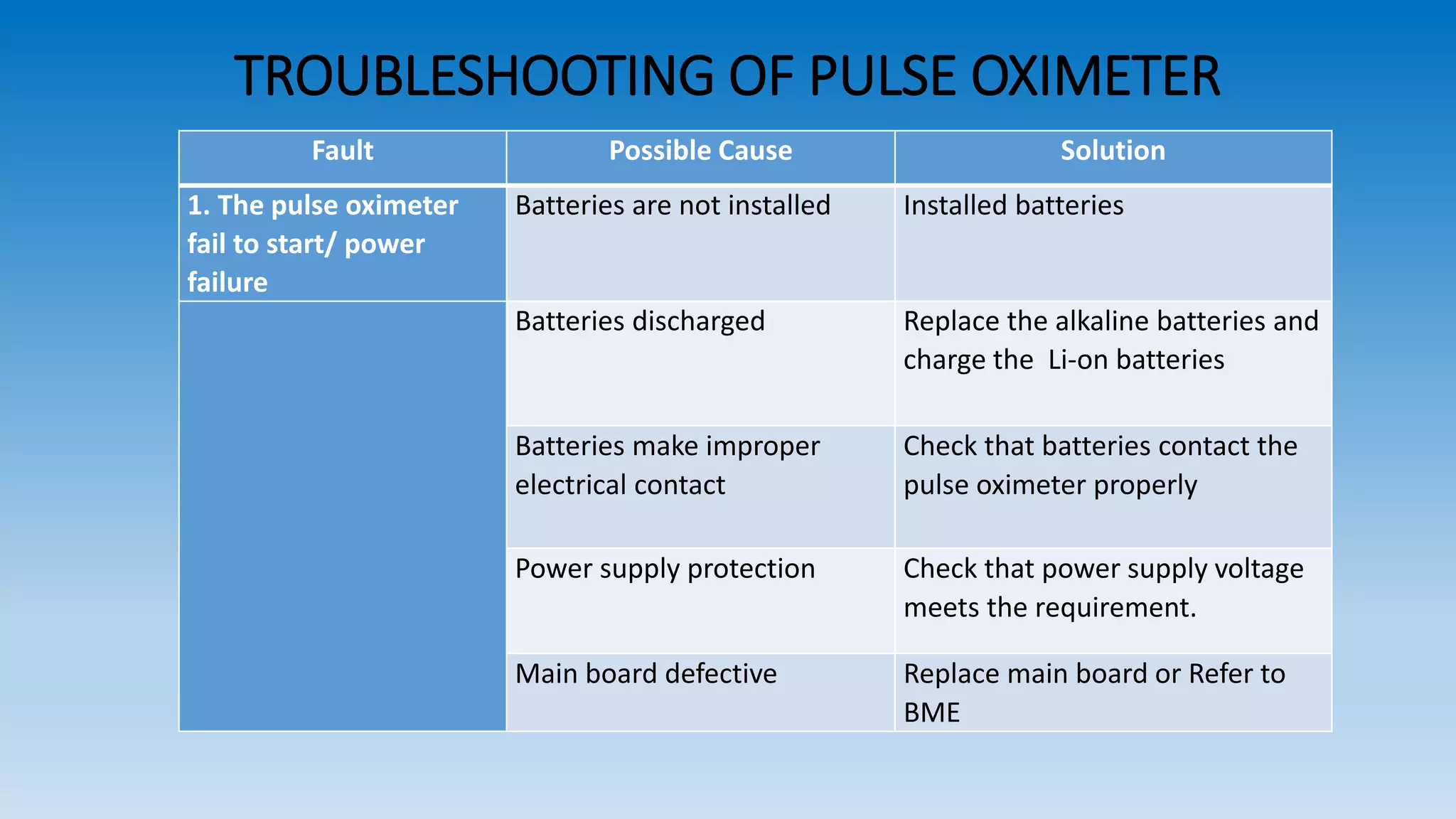
The document explains pulse oximetry, a non-invasive method to measure blood oxygen saturation (SpO2) and heart rate, emphasizing its importance in anesthesia and intensive care. It details the functioning of pulse oximeters, including their components, maintenance, and proper usage protocols, as well as troubleshooting tips for common issues. Additionally, it outlines safety precautions and cleaning recommendations to ensure effective operation.