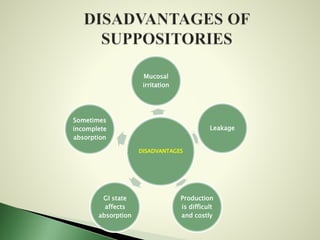
This document summarizes suppositories as solid dosage forms intended for insertion into body cavities where they melt and exert local or systemic effects. It describes the different types of suppositories based on their shape and size for various cavities. Suppository bases are discussed including fatty, water soluble, and emulsifying bases. Cocoa butter and glycerinated gelatin are commonly used bases. The advantages of the suppository route include targeting specific areas, use for patients who cannot swallow, and protecting unstable or irritating drugs. Production methods like hand moulding, hot process, and cold compression are covered. References on industrial pharmacy textbooks are provided at the end.