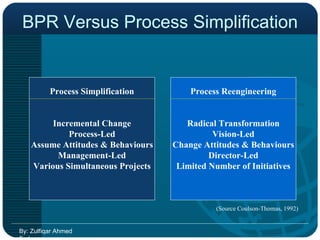
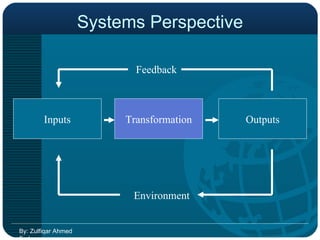
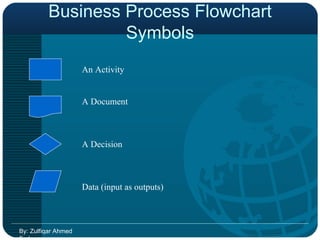
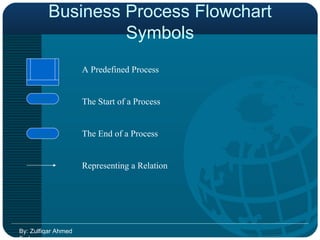
Business Process Re-engineering (BPR) is a fundamental rethinking and radical redesign of business processes aimed at achieving significant improvements in performance metrics like cost, quality, and service. It emphasizes managing change effectively and integrating information processing into work, with principles such as organizing processes around outcomes and enabling worker empowerment. The document further distinguishes BPR from continuous improvement and highlights its phases, challenges, and the role of information technology in facilitating successful BPR implementation.



































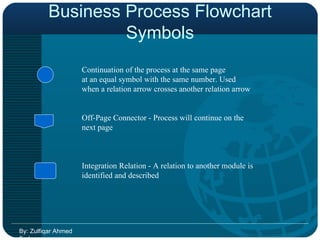
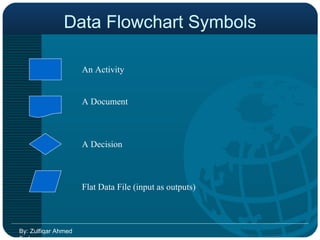
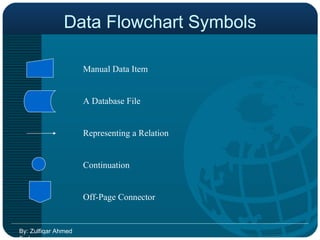
![BPR & ERP Just automating the existing business practices will not help ERP to achieve the anticipated results Business Process Re-engineering [BPR] brings out the deficiencies of the existing setup Business Process Re-engineering [BPR] brings out the deficiencies of the existing setup BPR may be time consuming but the scope can be restricted & controlled by the Management By: Zulfiqar Ahmed Farhan](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bpr-120206042153-phpapp02/85/BPR-OR-Business-Process-Re-Engineer-43-320.jpg)
