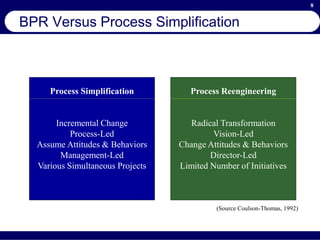
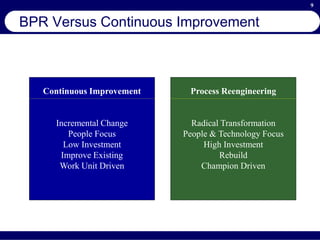
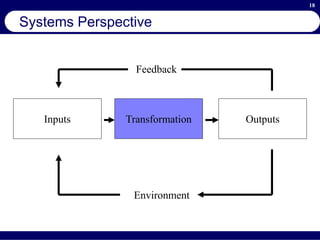
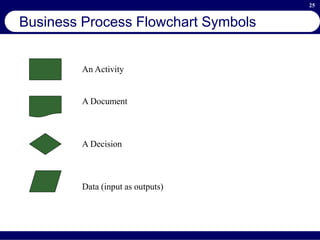
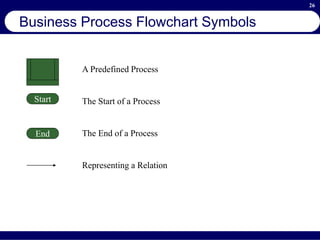
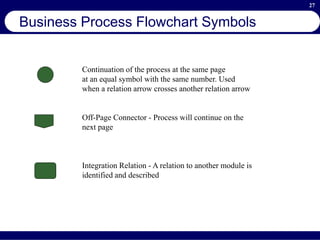
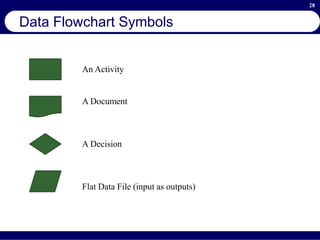
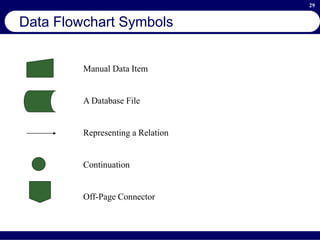
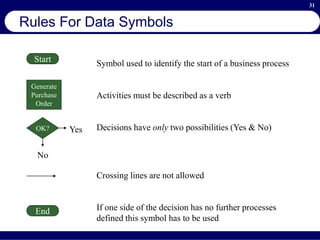
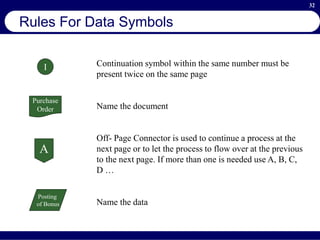
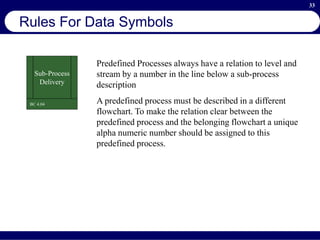
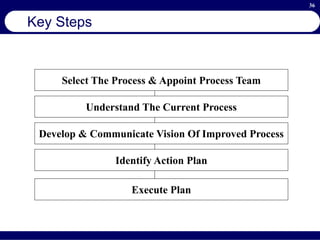
This document provides an overview of business process reengineering (BPR). It defines BPR as the fundamental rethinking and redesign of business processes to achieve dramatic improvements in performance. The document outlines the key characteristics of BPR, including that it takes a systems perspective and focuses on end customers and process-based improvements. It also discusses challenges in implementing a BPR strategy and provides steps to select processes, understand the current process, develop a vision for improvement, and execute a BPR plan.