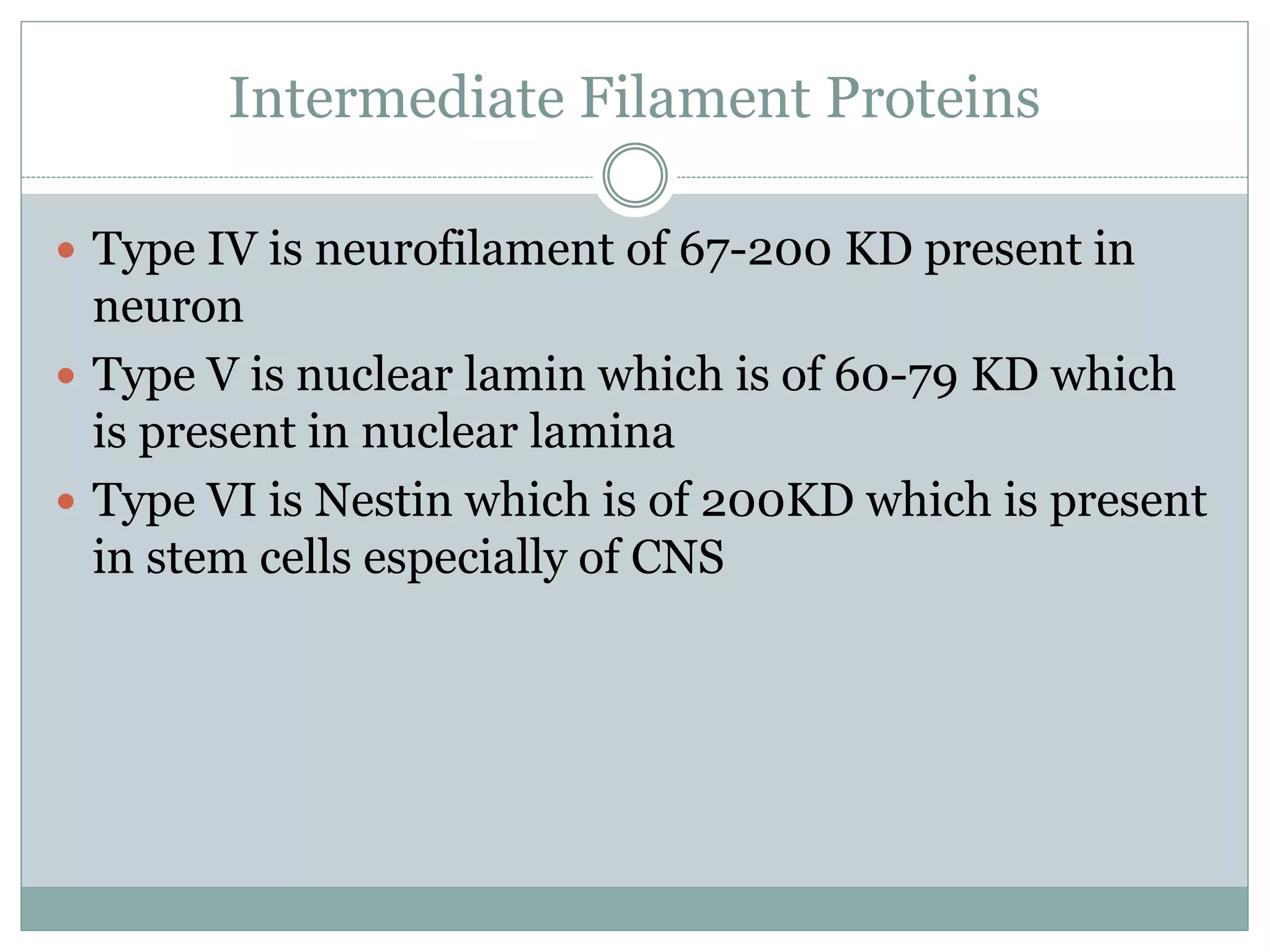
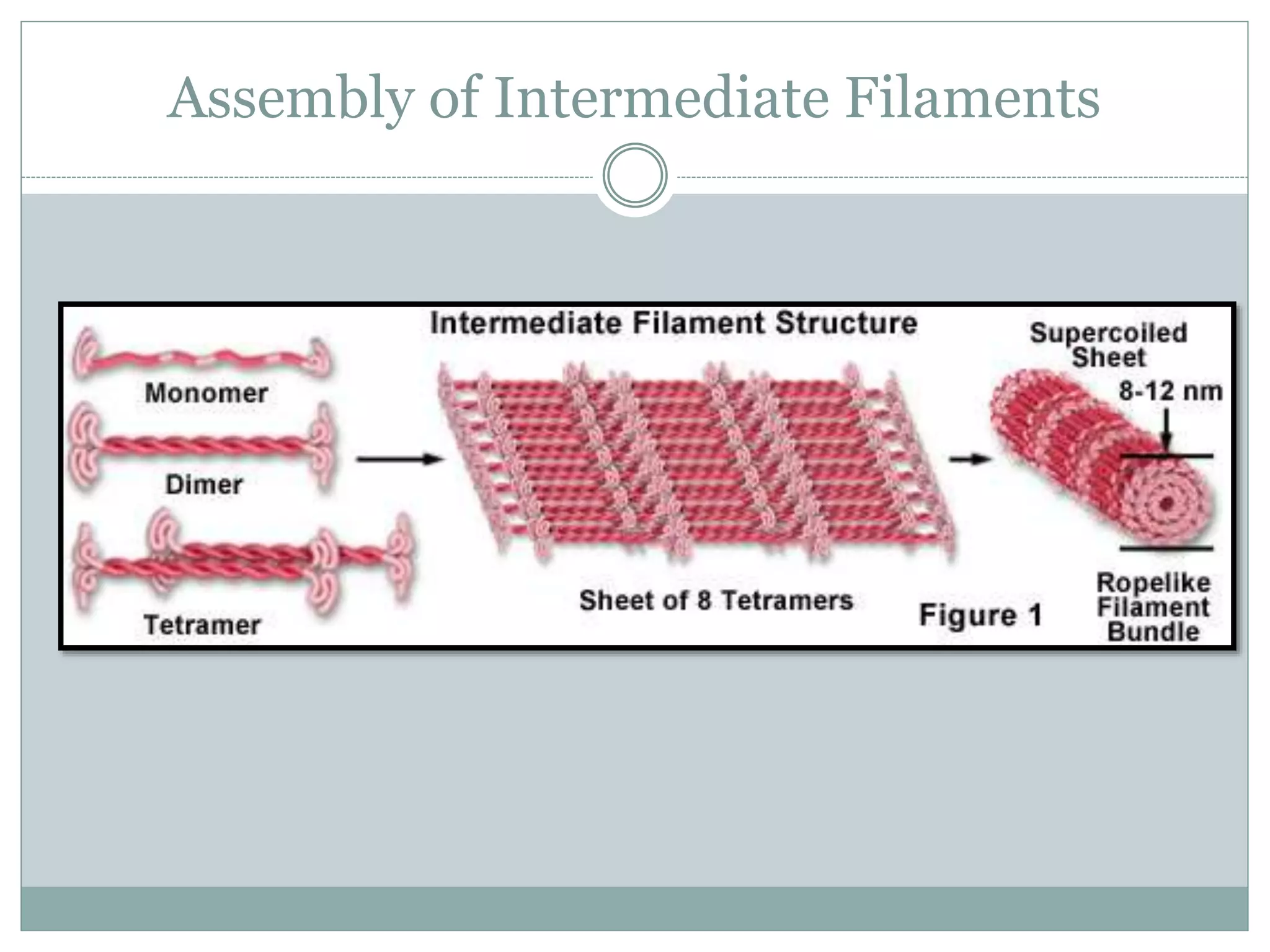
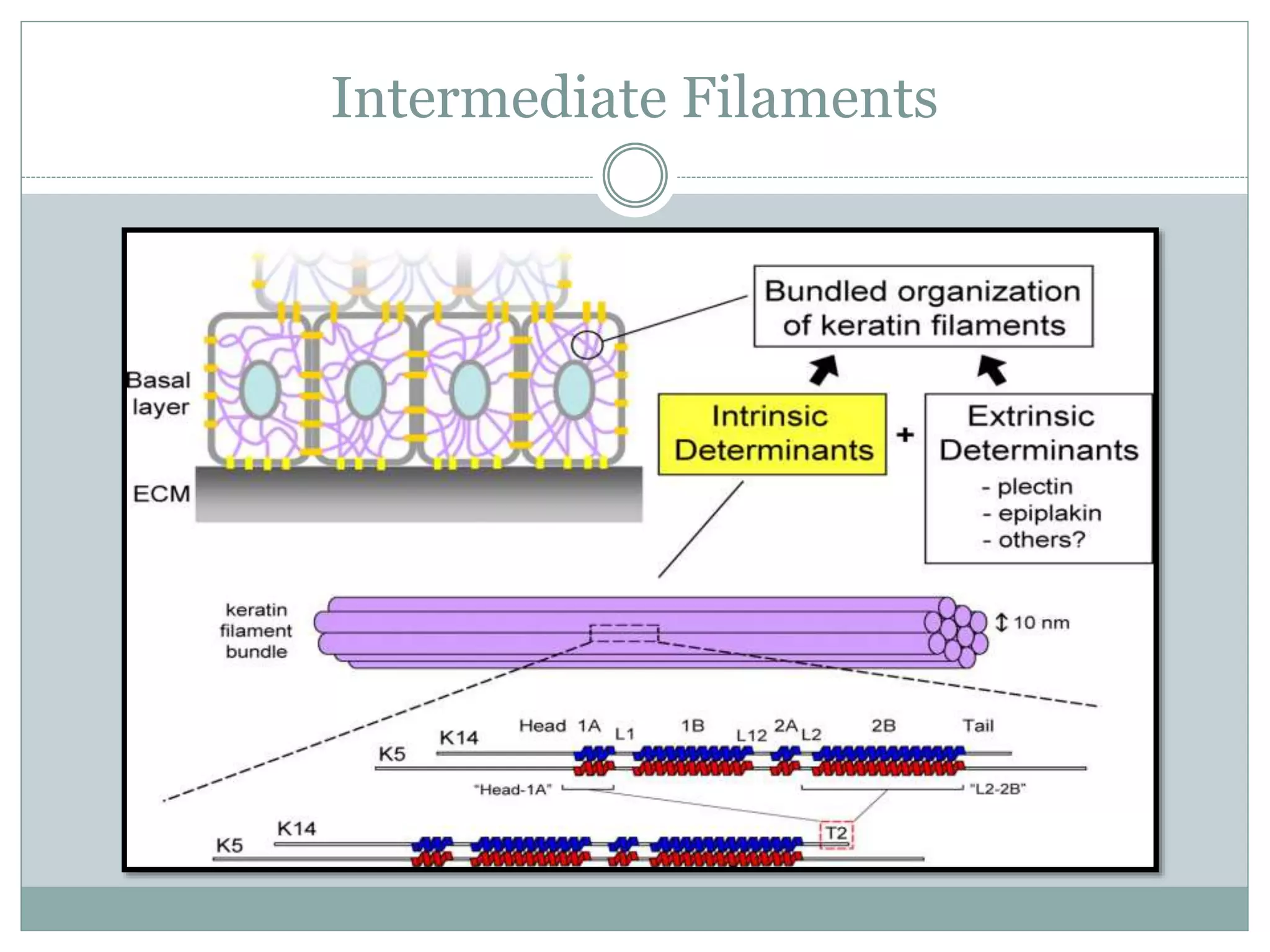
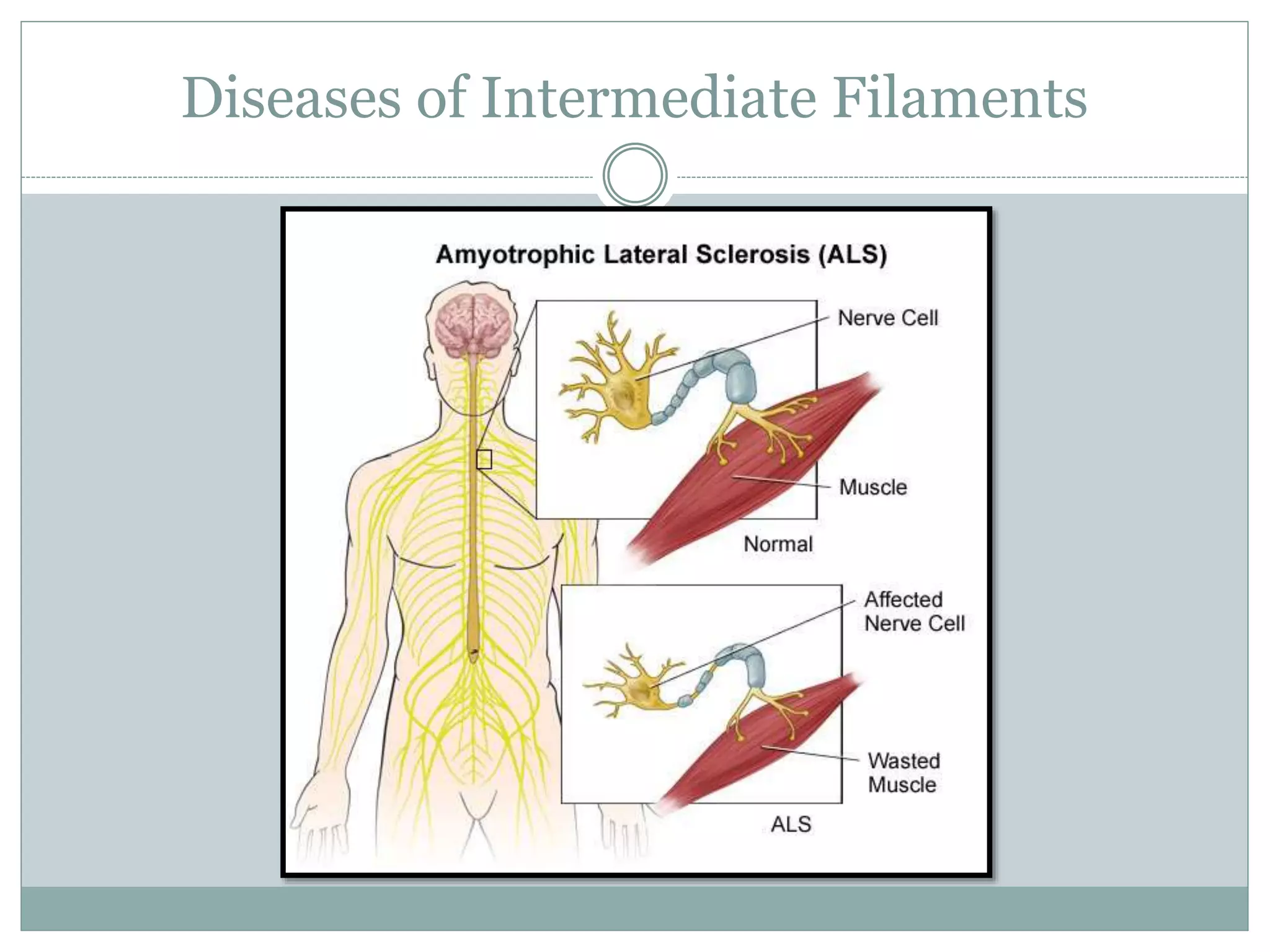
Intermediate filaments are vital cellular components with diameters of 8-11 nm, providing mechanical strength and acting as scaffolds for various cellular processes. Composed of 65 distinct proteins, they include various types such as keratins, vimentin, neurofilaments, and others, which are structured in a stable and antiparallel arrangement. Dysfunction in intermediate filaments can lead to diseases like epidermolysis bullosa simplex and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.