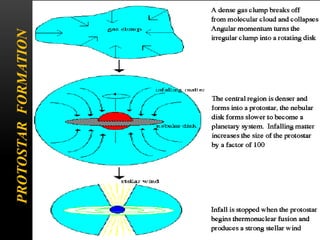
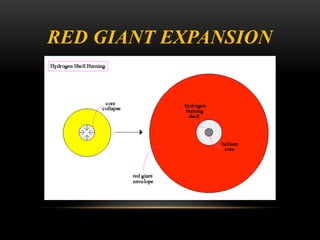
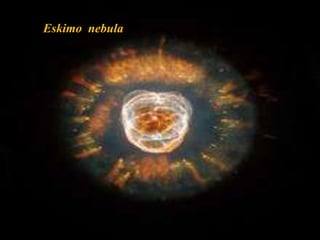
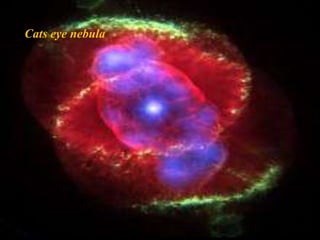
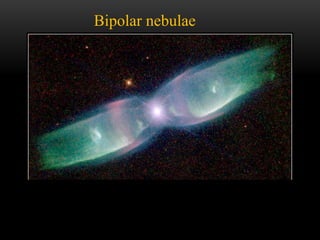
Planetary nebulae form during the late stages of evolution for low-to-medium mass stars. As a star expands into a red giant, it ejects its outer layers through pulsations and stellar winds. The hot core ionizes the ejected gas, causing it to glow brightly. This energized shell of nebulous gas appears as a planetary nebula. Examples are the Helix Nebula and Ring Nebula. More massive stars may explode as supernovae, leaving behind neutron stars or black holes, depending on the star's original mass. The document discusses these stages of stellar evolution and death that give rise to different astronomical phenomena like planetary nebulae and neutron stars.